Abstract
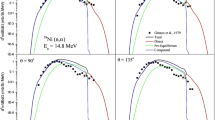
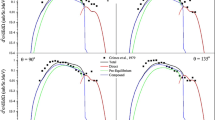
Nuclear reaction codes give us simplicity to investigate phenomena of nuclear physics. There have many computer programs such as TALYS, EMPIRE, ALICE/ASH, PCROSS, FLUKA and GEANT4. The stopping power of alpha, deuteron, proton and triton in 54Fe materials is acquired as it has helpful applications of shielding and choosing the proper thickness of the target. Level density is very important to understanding nuclear reaction mechanism. The knowledge of level density for reaction cross-section calculations are required for various application such as astrophysics, accelerator driven sub-critical systems, nuclear medicine, fission and fusion reactor design and neutron capture. In this study, we calculated the cross-sections of 54Fe using TALYS 1.6 and EMPIRE 3.1 codes for different reactions through the four level density models. Stopping powers and penetrating distances were calculated for the alpha, deuteron, proton and triton particles, taking into consideration all possible reactions in 54Fe for incident energies of 1–45 MeV using GEANT4 calculation code. The obtained reaction cross-section results have been compared with the each other and against the experimental nuclear reaction data existing in EXFOR database.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.P. Liu et al., J. Alloys Compd. 579, 599 (2013)
P.M. Raole et al., Trans. IIM 62, 2 (2009)
M. Victoria et al., Nucl. Fusion 41, 1047 (2001)
K. Ehrlich, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 357, 595 (1999)
A. Kaplan et al., J. Fusion Energ. 29, 353 (2010)
A. Kaplan et al., J. Fusion Energ. 33, 510 (2014)
H. Aytekin et al., J. Fusion Energ. 30, 21 (2011)
T. Nishio et al., J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2, 955 (2002)
A. Kaplan et al., J. Fusion Energ. 32, 344 (2013)
E. Tel et al., J. Fusion Energ. 32, 304 (2013)
A. Kaplan, J. Fusion Energ. 32, 382 (2013)
A. Kaplan et al., J. Fusion Energ. 32, 431 (2013)
H. Aytekin et al., J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 298, 95 (2013)
A. Aydın et al., J. Fusion Energ. 27, 308 (2008)
E. Tel et al., J. Fusion Energ. 31, 184 (2012)
A. Kaplan, V. Çapalı, J. Fusion Energ. 33, 299 (2014)
A.J. Koning et al., Nucl. Phys. A. 810, 13 (2008)
V. Yadav et al., Proc. DAE Symp. Nucl. Phys. 57, 734 (2012)
A. Koning, S. Hilaire, S. Goriely, TALYS–1.6 A Nuclear Reaction Program, User Manual (NRG, The Netherlands), First Edition, December 23 (2013)
M. Herman et al., Nucl. Data Sheets 108, 2655 (2007)
M. Herman et al., EMPIRE–3.1 Rivoli Modular System for Nuclear Reaction Calculations and Nuclear Data Evaluation, User’s Manual (2012)
S. Agostinelli et al., Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A. 506, 250 (2003)
Brookhaven National Laboratory, National Nuclear Data Center, EXFOR/CSISRS (Experimental Nuclear Reaction Data File). Database Version of November 20, 2013 (2013), http://www.nndc.bnl.gov/exfor/
R. Crasta et al., J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 290, 367 (2011)
A.J. Koning, M.C. Duijvestijn, Nucl. Phys. A 744, 15 (2004)
C. Kalbach, Phys. Rev. C 33, 818 (1986)
J.J. Griffin, Phys. Rev. Lett. 17, 478 (1966)
C. Cline, M. Blann, Nucl. Phys. A 172, 225 (1971)
C.K. Cline, Nucl. Phys. A 193, 417 (1972)
I. Ribansky et al., Nucl. Phys. A 205, 545 (1973)
W. Dilg et al., Nucl. Phys. A 217, 269 (1973)
A. Gilbert, A.G.W. Cameron, Can. J. Phys. 43, 1446 (1965)
A.V. Ignatyuk et al., Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 29, 450 (1979)
A.V. Ignatyuk et al., Phys. Rev. C47, 1504 (1993)
H. Bethe, Ann. Phys. 5, 325 (1930)
M. Inokuti, Rev. Mod. Phys. 43, 297 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özdoğan, H., Çapalı, V. & Kaplan, A. Reaction Cross-Section, Stopping Power and Penetrating Distance Calculations for the Structural Fusion Material 54Fe in Different Reactions. J Fusion Energ 34, 379–385 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-014-9809-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-014-9809-z