Abstract
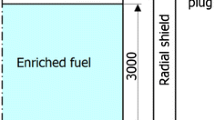
In this study, a neutronic performance of the Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion Fission Energy (LIFE) molten salt blanket is investigated. Neutronic calculations are performed by using XSDRNPM/SCALE5 codes in S8–P3 approximation. The thorium molten salt composition considered in this calculation is 75 % LiF—25 % ThF4, 75 % LiF—24 % ThF4—1 % 233UF4, 75 % LiF—23 % ThF4—2 % 233UF4. Also, effects of the 6Li enrichment in molten salt are performed for all heavy metal salt. The radiation damage behaviors of SS-304 structural material with respect to higher fissionable fuel content and 6Li enrichment are computed. By higher fissionable fuel content in molten salt and with 6Li enrichment (20 and 50 %) in the coolant in form of 75 % LiF—23 % ThF4—2 % 233UF4, an initial TBR >1.05 can be realized. On the other hand, the 75 % LiF—25 % ThF4 or 75 % LiF—24 % ThF4—1 % 233UF4 molten salt fuel as regards maintained tritium self-sufficiency is not suitable as regards improving neutronic performance of LIFE engine. A high quality fissile fuel with a rate of ~2,850 kg/year of 233U can be produced with 75 % LiF—23 % ThF4—2 % 233UF4. The energy multiplication factor is increased with high rate fission reactions of 233U occurring in the molten salt zone. Major damage mechanisms in SS-304 first wall stell have been computed as DPA = 48 and He = 132 appm per year with 75 % LiF—23 % ThF4—2 % 233UF4. This implies a replacement of the SS-304 first wall stell of every between 3 and 4 years.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.J. Duderstadt, G.A. Moses, Inertial Confinement Fusion (Wiley, USA, 1982)
S. Şahin, M.J. Khan, R. Ahmed, Fuel breeding and actinide transmutation in the life engine. Fusion Eng. Des. 86, 227 (2011)
R.W. Moir et al., Molten salt fuel version of Laser Inertial Fusion Fission Energy (LIFE). Fusion Sci. Technol. 56, 632–640 (2009)
K.J. Kramer et al., Parameter study of the LIFE engine nuclear design. Energy Convers. Manage. 51(9), 1744–1750 (2010)
E.I. Moses, T. Diaz de la Rubia, J.F. Latkowski, J.C. Farmer, R.P. Abbott, K.J. Kramer, P.F. Peterson, H.F. Shaw, R.F. Lehman II, A sustainable nuclear fuel cycle based on Laser Inertial Fusion Energy (LIFE). Fusion Sci. Technol. 56(2), 566–572 (2009)
R.P. Abbott, M.A. Gerhard, K.J. Kramer, J.F. Latkowski, K.L. Morris, P.F. Peterson, J.E. Seifried, Thermal and mechanical design aspects of the LIFE engine. Fusion Sci. Technol. 56(2), 618–624 (2009)
K.J. Kramer, J.F. Latkowski, R.P. Abbott, J.K. Boyd, J.J. Powers, J.E. Seifried, Neutron transport and nuclear burnup analysis for the Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion–Fission Energy (LIFE) engine. Fusion Sci. Technol. 56(2), 625–631 (2009)
W.R. Meier et al., System modeling for the Laser Fusion–Fission Energy (LIFE) power plant. Fusion Sci. Technol. 56(2), 647–651 (2009)
S. Şahin, H.M. Şahin, A. Acır, LIFE hybrid reactor as reactor grade plutonium burner. Energy Convers. Manage. 63, 44–50 (2012)
J.C. Farmer, T. Diaz de la Rubia, E. Moses, (Report Draft) The complete burning of weapons grade plutonium and highly enriched uranium with (Laser Inertial Fusion–Fission Energy) LIFE engine, LLNL-TR-410152 (2009)
S. Şahin, M. Al-Eshaikh, Fission power flattening in hybrid blankets using mixed fuel. Fusion Technol. 12, 395–408 (1987)
S. Şahin, Power flattening in a catalyzed (D, D) fusion driven hybrid blanket using nuclear waste actinides. Nucl. Technol. 92, 93–105 (1990)
L.M. Petrie, SCALE5-Scale System Driver, NUREG/CR-0200, Revision 7, Volume III, Section M1, ORNL/NUREG/CSD-2/V3/R7 (Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, 2004)
N.M. Greene, L.M. Petrie, XSDRNPM, a one-dimensional discrete-ordinates code for transport analysis, NUREG/CR-0200, Revision 7, 2 , Section F3, ORNL/NUREG/CSD-2/V2/R7 (Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, 2004)
N.M. Greene, BONAMI, Resonance Self-shielding by the BONDARENKO Method, NUREG/CR-0200, Revision 6, Volume 2, Section F1, ORNL/NUREG/CSD-2/V2/R7 (Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, 2004)
N.M. Greene, L.M. Petrie, R.M. Westfall, NITAWL-III, Scale System Module for Performing Resonance Shielding and Working Library Production, NUREG/CR-0200, Revision 6, Volume 2, Section F2, ORNL/NUREG/CSD-2/V2/R7 (Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, 2004)
A. Acır, Effect of nuclear data libraries on tritium breeding in a (D–T) fusion driven reactor. J. Fusion Energ. 27, 301–307 (2008)
M. Übeyli, A. Acır, Utilization of thorium in a high power density hybrid reactor with innovative coolants. Energy Convers. Manage. 48(2), 576–582 (2007)
M. Übeyli, A. Acır, Neutronic investigation on the ARIES-ST fusion reactor with fissionable molten salts. Energy Convers. Manage. 51(12), 2531–2534 (2010)
M. Übeyli, Neutronic performance of HYLIFE-II fusion reactor using various thorium molten salts. Ann. Nucl. Energy 33, 1417–1423 (2006)
M. Übeyli, H. Yapıcı, Utilization of heavy metal molten salts in the ARIES-RS fusion reactor. J. Fusion Energ. 27(3), 200–205 (2008)
H. Yapıcı, Study of fissile fuel breeding concept for the force-free helical reactor. Fusion Eng. Des. 65(4), 599–609 (2003)
D.L. Smith et al., Blanket comparison and selection study-final report. Argonne National Laboratory Report, ANL/FPP-84-1 (1984)
R.W. Moir et al., HYLIFE-II, a molten-salt inertial fusion energy power plant design-final report. Fusion Technol. 25(1), 5 (1994)
A. Blink et al., in High-Yield Lithium-Injection Fusion–Energy (HYLIFE) Reactor, ed. by K.L. Essary, K.E. Lewis. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Report, UCRL-53559 (1985)
M. Perlado, M.W. Guinan, K. Abe, Radiation Damage in Structural Materials, in Energy from Inertial Fusion, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna (1995), p. 272
S.J. Zinkle, Materials in extreme nuclear environments (Invited Presentation, National Ignition Facility, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, March 17, 2008)
S.J. Zinkle, Microstructures and mechanical properties of irradiated metals and alloys, Materials Issues for Generation IV Systems: Status, Open Questions and Challenges, Book Series: NATO Science for Peace and Security Series B—Physics and Biophysics, pp. 227–244, (2008) doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-8422-5-11
S.J. Zinkle, Fusion materials science: overview of challenges and recent progress. Phys. Plasmas 12, 058101 (2005)
Acknowledgments
The author also appreciates the constructive comments of the referees that have helped improve the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acır, A. Neutronic Analysis of the Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion–Fission Energy (LIFE) Engine Using Various Thorium Molten Salts. J Fusion Energ 32, 634–641 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-013-9628-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-013-9628-7