Abstract
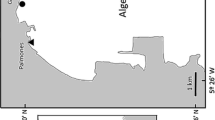
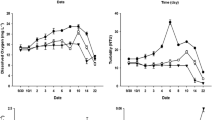
Many neurotransmitters, such as γ-amino butyric acid (GABA), can act as chemical cues influencing settlement and metamorphosis in benthic marine invertebrates. This effect has been described especially in mollusks, such as mussels, clams, or haliotids. This study describes the first record of the effect of GABA on patellogastropod populations. Special attention was paid to the effect of the compound on recruitment processes. The experiment was carried out using 10 × 10 cm artificial limestone plates that were drilled into intertidal rocks at different inclinations, and periodically treated with a 1 mM GABA solution. A total of five limpet species was considered (four patellid limpet species and the pulmonate Siphonaria pectinata). Each individual recorded on the plates as well as within a 20 × 20 cm quadrant was measured, identified to species level, and its straight-line distance to the application point was registered. Treated surfaces were the first to possess both adults and recruits. Individuals also were found in a higher number around GABA-treated plates than around controls. The results indicated that the compound may not only enhance recruitment, but also might accelerate it. Recruits were located at higher distances from GABA treated plates than from control surfaces. This supports the hypothesis that this is the life history stage most sensitive to the compound. The behavior shown by the individuals belonging to the two endangered patellid species present in the study area (Patella ferruginea and Cymbula nigra) also were analyzed. For the former, the results indicated that the use of GABA may have similar effects on recruitment similar to the presence of adult conspecifics. This is the first report of the effect of GABA on patellid limpet recruitment and population dynamics. Conservational implications of the results are discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aversano, F. R. 1986. Esperimento di insediamento artificiale di Patella ferruginea Gmelin, 1791 nelle acque del Golfo di Arzachena (Sardegna settentrionale). Boll. Malacol. 22:169–170.
Bryan, P. J., and Qian, P. Y. 1998. Induction of larval attachment and metamorphosis in the abalone Haliotis diversicolor (Reeve). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 223:39–41.
Bulleri, F. 2005. Experimental evaluation of early patterns of colonisation of space on rocky shores and seawalls. Mar. Environ. Res. 60:335–374.
Burke, R. D. 1983. The induction of metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae: stimulus and response. Can. J. Zool. 61:1701–1719.
Burke, R .D. 1984. Pheromonal control of metamorphosis in the Pacific Sand Dollar, Dendraster excentricus. Science 27:442–443.
Butler, A. J. 1986. Recruitment of sessile invertebrates at five sites in Gulf St. Vincent, South Australia. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 97:13–36.
Butman, C. A. 1987. Larval settlement of soft-sediment invertebrates: the spatial scales of pattern explained by active habitat selection and the emerging role of hydrodynamical processes. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 25:113–165.
Coon, S. L., Bonar, D. B., and Weiner, R. M. 1985. Induction of settlement and metamorphosis of the pacific oyster, crassostrea gigas (Thunberg), by L-DOPA and catecholamines. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 94:211–221.
Davies, M. S., and Blackwell, J. 2007. Energy saving through trail following in a marine snail. Proc. R. Soc. B. 274:1233–1236.
Davies, M. S., Hawkins, S. J., and Jones, H. D. 1992. Pedal mucus and its influence on the microbial food supply of two intertidal gastropods, Patella vulgata L. and Littorina littorea (L.). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 161:57–77.
Eckman, J. E. 1983. Hydrodynamic processes affecting benthic recruitment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 28:241–257.
Espinosa, F. 2006. Caracterización biológica del molusco protegido Patella ferruginea Gmelin, 1791 (Gastropoda: Patellidae): bases para su gestión y conservación. Ph.D. dissertation. Universidad de Sevilla.
Espinosa, F., Guerra-García, J. M., Fa, D., and García-Gómez, J. C. 2006. Effects on competition on an endangered limpet Patella ferruginea (Gastropoda: Patellidae): Implications for conservation. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 330:482–492.
Espinosa, F., Rivera-Ingraham, G. A., and García-Gómez, J. C. 2008. Seasonal activity and foraging behaviour of the endangered limpet Patella ferruginea. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 20:173–181.
Espinosa, F., Rivera-Ingraham, G. A., Fa, D., and García-Gómez, J. C. 2009. Effect of human pressure on population size structure of the endangered ferruginean limpet: towards future management measures. J. Coast. Res. 25:857–863.
Frenkiel, L. 1975. Contribution à l’étude des cycles de reproduction des Patellidae en Algérie. Pubbl. Stn. Zool. Napoli 39:153–189.
Gapasin, R. S. J., and Polohan, B. B. 2004. Induction of larval settlement and metamorphosis in the donkey-ear abalone, Haliotis asinina Linnaeus, by chemical cues. Hydrobiologia 519:9–17.
García-Lavandeira, M., Silva, A., Abad, M., Pazos, A. J., Sánchez, J. L., and Parallé, L. 2005. Effects of GABA an epinephrine on the settlement and metamorphosis of the larvae of four species of bivalve molluscs. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 316:149–156.
Gibson, G. D., and Chia, F. S. 1994. A metamorphic inducer in the opistobranch Haminaea callidegenita: Partial purification and biological activity. Biol. Bull. 187:133–142.
Gray, D. R., and Hodgson, A. N. 1998. Foraging and homing behaviour in the high-shore, crevice-dwelling limpet Helcion pectunculus (Prosobranchia: Patellidae). Mar. Biol. 132:283–294.
Grosberg, R. K. 1982. Intertidal zonation of barnacles: the influence of planktonic zonation of larvae on vertical distribution of adults. Ecology 63:894–899.
Guerra-García, J. M., Corzo, J., Espinosa, F., and García-Gómez, J. C. 2004. Assessing habitat use of the endangered marine mollusc Patella ferruginea (Gastropoda: Patellidae) in northern Africa: preliminary results and implications for conservation. Biol. Conserv. 116:319–326.
Hadfield, M. G. 1984. Settlement requirements of molluscan larvae: new data on chemical and genetic roles. Aquaculture 39:283–298.
Hadfield, M. G., and Pennington, J. T. 1990. Nature of metamorphic signal and its internal transduction in larvae of the nudibranch Phestilla sibogae. Bull. Mar. Sci. 46:455–464
Hadfield, M. G., and Scheuer, D. 1985. Evidence for a soluble metamorphic inducer in Phestilla: ecological, chemical and biological data. Bull. Mar. Sci. 37:556–566.
Jensen, R. A., and Morse, D. E. 1990. Chemically induced metamorphosis of polychaete larvae in both the laboratory and the ocean environment. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:911–930.
Keough, M. J., and Downes, B. J. 1982. Recruitment of marine invertebrates: the role of active larval choices and early mortality. Oecologia 54:348–352.
Krug, P. J., and Manzi, A. E. 1999. Waterborne and surface-associated carbohydrates as settlement cues of larvae of the specialist marine hervibore Alderia modesta. Biol. Bull. 197:94–103.
Laborel-Deguen, F., and Laborel, J. 1990. Nouvelles donnees sur la patelle geante Patella ferruginea Gmelin en Mediterraneé. I. Statut, Répartition et Etude des populations. Haliotis 10:41–54.
Laborel-Deguen, F., and Laborel, J. 1991. Statut de Patella ferruginea Gmelin en Méditerranée, pp. 91–103, in C. F. Boudouresque, M. Avon and V. Gravez (eds.). Les Espèces Marines à Protéger en Méditerranée. GIS Posidonie Publishers, Marseille.
Laimek, P., Clark, S., Stewart, M., Pfeffer, F., Wanichanon, C., Hanna, P., and Sobhon, P. 2008. The presence of GABA in gastropod mucus and its role in inducing larval settlement. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 354:182–191.
Li, H., Lin, W., Zhang, G., Cai, Z., Cai, G., Chang, Y., and Xing, K. 2006. Enhancement of larval settlement and metamorphosis through biological and chemical cues in the abalone Haliotis diversicolor supertexta. Aquaculture 258:416–423.
Mesías-Gansbiller, C., El Amine Bendimerad, M., Román, G., Pazos, A. J., Sánchez, J. L., and Pérez-Parallé, M. L. 2008. Settlement behavior of black scallop larvae (Chlamys varia L.) in response to GABA, epinephrine and IBMX. J. Shellfish Res. 27:261–264.
MMAMRM (2008) Estrategia de conservación de la lapa ferrugínea (Patella ferruginea) en España. Conferencia Sectorial de Medio Ambiente, Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Medio Rural y Marino. P. 56. Madrid, Spain.
Moreno, D. 2004. Prosobranquios y Heterobranquios. Fauna Andaluza, pp. 79–114. in J. A. Tinaut and F. Pascual (eds.). Proyecto Andalucía. Naturaleza XIV, Zoología II, los Animales Esquizocelomados: Moluscos, Anélidos, Sipuncúlidos y Equiúridos. Publicaciones Comunitarias, Grupo Hércules, Sevilla.
Morse, D. E., and Morse, A. N. C. 1991. Enzymatic characterization of the morphogen recognized by Agaricia humilis (Scleractinian coral) larvae. Biol. Bull. 181:104–122.
Morse, D. E., Hooker, N., Duncan, H., and Jensen, L. 1979a. γ-aminobutyric acid, a neurotransmitter, induces planktonic abalone larvae to settle and begin metamorphosis. Science 204:407–410.
Morse, D. E., Hooker, N., Jensen, L., and Duncan, H. 1979b. Induction of larval settling and metamorphosis by γ-aminobutyric acid and its congeners from crustose red algae. II. Applications to cultivation, seed-production and bioassays; principal causes of mortality and interference. Proc. World Marinculture Soc. 10:81–91.
Moschella, P. S., Abbiati, M., Aberg, P., Airoldi, L., Anderson, J. M., Bacchiocchi, F., Bulleri, F., Dinesen, G. E., Frost, M., Gacia, E., Granhag, L., Jonsson, P. R., Satta, M. P., Sundelöf, A., Thompson, R. C. and Hawkins, S. J. 2005. Low-crested coastal defence structures as artificial habitats for marine life: using ecological criteria in design. Coast Eng. 52:1053–1071.
Ocaña, T. M. J., and Emson, R. H. 1999. Maturation, spawning and development in Siphonaria pectinata Linnaeus (Gastropoda: Pulmonata) at Gibraltar. J. Molluscan Stud. 65:185–193.
Pawlik, J. R. 1990. Natural and artificial induction of metamorphosis of Phragmatopoma lapidosa californica (Polychaeta: Sabellaridae) with a critical look at the effects of bioactive compounds on marine invertebrate larvae. Bul. Mar. Sci. 46:512–536.
Pawlik, J. R. 1992. Chemical ecology of the settlement of benthic marine invertebrates. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 30:273–335.
Pawlik, J. R., Butman, C. A., and Starczak, V. R. 1991. Hydrodynamic facilitation of gregarious settlement of a reef-building tube worm. Science 251:421–424.
Pearce, C. M., and Scheibling, R. E. 1990. Induction of metamorphosis of larvae of the green sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis, by coralline red algae. Biol. Bull. 179:304–311.
Rivera-Ingraham, G.A. 2010. Biología de la conservación de especies de patélidos en el umbral Atlántico-Mediterráneo. PhD dissertation. University of Seville, Spain.
Rivera-Ingraham, G. A., Espinosa, F., and García-Gómez, J. C. in press. doi:10.1017/S0025315410000159. Ecological considerations and Niche differentiation between juvenile and adult black limpets (Cymbula nigra). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK.
Rodríguez, S. R., Ojeda, F. P., and Inestrosa, N. C. 1993. Settlement of benthic marine invertebrates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 97:193–207.
Searcy-Bernal, R., and Anguiano-Beltrán, C. 2007. Optimizing the concentration of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) for inducing larval metamorphosis in Red Abalone Haliotis rufescens (Mollusca: Gastropoda). J. World Aquacult. Soc. 29: 463–470.
Sutherland, J. P. 1990. Recruitment regulates demographic variation in a tropical intertidal barnacle. Ecology 71:955–972.
Swanson, R. L., Williamson, J. E., De Nys, R., Kumar, N., Bucknall, M. P., and Steinberg, P. D. 2004. Induction of settlement of larvae of the sea urchin Holopneustes purpurascens by histamine from a host alga. Biol. Bull. 206:161–172.
Swanson, R. L., De Nys, R., Hugget, M. J., Green, J. K., and Steinberg, P. D. 2006. In situ quantification of a natural settlement cue and recruitment of the Australian sea urchin Holopneustes purpurascens. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 314:1–14.
Takahashi, Y., Itoh, K., Ishii, M., Suzuki, M., and Itabashi, Y. 2002. Induction of larval settlement and metamorphosis of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius by glycoglycerolipids from the green alga Ulvella lens. Mar. Biol. 140:763–771.
Templado, J. 2001. Patella ferruginea (Gmelin, 1791), pp. 41–49, in M. A. Ramos, D. Bragado and J. Fernández (eds.). Los Invertebrados no Insectos de la Directiva Hábitats en España. Organismo Autónomo Parques Nacionales. Dirección General de Conservación de la Naturaleza, Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Madrid.
Thorson, G. 1950. Reproductive and larval ecology of marine bottom invertebrates. Biol. Rev. 25:21–62.
Wieczorek, S. K., and Todd, C. D. 1998. Biofilm cues and larval settlement. Biofouling 12:81–118.
Wright, W. G. 1983. Species-energy theory: an extension of the species-area theory. Oikos 41:496–506.
Yang, Y., and Wu, B. 1995. Induction of larval settlement and metamorphosis of Haliotis discus hannai Ino (Gastropoda: Mollusca). Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 13:71–77.
Acknowledgements
This study was financed with a predoctoral grant from the Spanish Ministry of Science awarded to G. A. Rivera-Ingraham (AP2006-04220) and by “Autoridad Portuaria de Ceuta”. The authors express their gratitude to “Consejería de Medio Ambiente-Obimasa” in Ceuta for its support and legal assessment and to three anonymous referees for their comments and corrections on the original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivera-Ingraham, G.A., Espinosa, F. & García-Gómez, J.C. Effect of γ-amino Butyric Acid on Limpet Populations: Towards the Future Management and Conservation of Endangered Patellid Species. J Chem Ecol 37, 1–9 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-010-9884-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-010-9884-1