Abstract
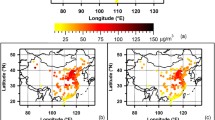
Long-term measurements of ambient particulate matter less than 2.5 μm in diameter (PM2.5) and its chemical compositions were performed at a rural site in Korea from December 2005 to August 2009. The average PM2.5 concentration was 31 μg m−3 for the whole sampling period, and showed a slightly downward annual trend. The major components of PM2.5 were organic carbon, SO 2−4 , NO −3 , and NH +4 , which accounted for 55 % of total PM2.5 mass on average. For the top 10 % of PM2.5 samples, anionic constituents and trace elements clearly increased while carbonaceous constituents and NH +4 remained relatively constant. Both Asian dust and fog events clearly increased PM2.5 concentrations, but affected its chemical composition differently. While trace elements significantly increased during Asian dust events, NO −3 , NH +4 and Cl were dramatically enhanced during fog events due to the formation of saturated or supersaturated salt solution. The back-trajectory based model, PSCF (Potential Source Contribution Function) identified the major industrial areas in Eastern China as the possible source areas for the high PM2.5 concentrations at the sampling site. Using factor analysis, soil, combustion processes, non-metal manufacture, and secondary PM2.5 sources accounted for 77 % of the total explained variance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashbaugh, L.L., Malm, W.C., Sadeh, W.M.: A residence time probability analysis of sulfur concentrations at Grand Canyon National Park. Atmos. Environ. 19, 1263–1270 (1985)
Birch, M.E., Cary, R.A.: Elemental carbon-based method for monitoring occupational exposure to particulate diesel exhaust. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 25(3), 221–241 (1996)
Chen, Y.S., Sheen, P.C., Chen, E.R., Liu, Y.K., Wu, T.N., Yang, C.Y.: Effects of Asian dust storm events on daily mortality in Taipei, Taiwan. Environ. Res. 95, 151–155 (2004)
Choi, E.K., Kim, Y.P.: Major factors affecting PM2.5 water content in Seoul and Gosan. J. Kor. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 20, 803–810 (2004)
Chow, J.C., Fujita, E.M., Watson, J.G., Lu, Z., Lawson, D.R., Ashbaugh, L.: Evaluation of filter-based aerosol measurements during the 1987 southern California air quality study. Environ. Monit. Assess. 30, 49–80 (1994)
Cohen, M.D., Flagan, R.C., Seinfeld, J.H.: Studies of concentrated electrolyte solutions using the electrodynamic balance. 2. Water activities for mixed-electrolyte solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 91, 4575–4582 (1987)
Federal Highway Administration, U.S. Department of Transportation, User Guidelines for Waste and Byproduct Materials in Pavement Construction, Publication Number: FHWA-RD-97-148 (1998)
Finlayson-Pitts, B., Pitts, J.J.R.: Chemistry of the upper and lower atmosphere. Academic, New York (2000)
Forsberg, B., Hansson, H.C., Johansson, C., Areskoug, H., Persson, K., Järvholm, B.: Comparative health impact assessment of local and regional particulate air pollutants in Scandinavia. Ambio 34, 11–9 (2005)
Glavas, S.D., Nikolakis, P., Ambatzoglou, D., Mihalopoulos, N.: Factors affecting the seasonal variation of mass and ionic composition of PM2.5 at a central Mediterranean coastal site. Atmos. Environ. 42, 5365–5373 (2008)
Han, Y.J., Holsen, T.M., Hopke, P.K., Yi, S.M.: Comparison between back-trajectory based modeling and Lagrangian backward dispersion modeling for locating sources of reactive gaseous mercury. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 1715–1723 (2005)
Han, Y.J., Holsen, T.M., Hopke, P.K.: Estimation of source locations of total gaseous mercury measured in New York State using trajectory-based models. Atmos. Environ. 41, 6033–6047 (2007)
Han, Y.J., Kim, T.S., Kim, H.: Ionic constituents and source analysis of PM2.5 in three Korean cities. Atmos. Environ. 42, 4735–4746 (2008)
Hoh, E., Hites, R.A.: Sources of toxaphene and other organochlorine pesticides in North America as determined by air measurements and potential source contribution function analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38(15), 4187–4194 (2004)
Hong, Y.C., Pan, X.C., Kim, S.Y., Park, K., Park, E.J., Kin, X., Yi, S.M., Kim, Y.H., Park, C.H., Song, S., Kim, H.: Asian dust storm and pulmonary function of school children in Seoul. Sci. Total Environ. 408, 754–759 (2010)
Huh, J.B., Yi, S.M.: Source identification of PM2.5 in Gwanyang by positive matrix factorization. Proceeding of the 38th meeting of KOSAE, Korean Soc. for Atmos. Environ. (2004)
IPCC: 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories (2006)
Jeong, J.I., Park, R.J., Woo, J.H., Han, Y.J., Yi, S.M.: Source contributions to carbonaceous aerosol concentrations in Korea. Atmos. Environ. 45, 1116–1125 (2011)
Jung, J.H., Han, Y.J.: Study on characteristics of PM2.5 and its ionic constituents in Chuncheon, Korea. J. Kor. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 24, 682–692 (2008)
Junge, C.: Die Konstitution des atmospharischen aerosols. Ann. Meteorol. 5, 1–55 (1952)
Kang, C.M., Lee, H.S., Kang, B.W., Lee, S.K., Sunwoo, Y.: Chemical characteristics of acidic gas pollutants and PM2.5 species during hazy episodes in Seoul, South Korea. Atmos. Environ. 38, 4747–4760 (2004a)
Kang, C.M., Lee, H.S., Sunwoo, Y.: Ion component characteristics of fine particles in Seoul’s atmosphere during the winter and summer of 1997. J. Kor. Soc. Environ. Eng. 24, 1209–1218 (2004b)
Kang, G.U., Kim, N.S., Shin, E.S.: Seasonal characteristics of atmospheric PM10 and PM2.5 in Iksan, Korea. J. Environ. Health Sci. 37(1), 29–43 (2011)
Kim, H.S., Huh, J.B., Hopke, P.K., Holsen, T.M., Yi, S.M.: Characteristics of the major chemical consitituents of PM2.5 and smog events in Seoul, Korea in 2003 and 2004. Atmos. Environ. 41(32), 6762–6770 (2007)
Kim, N.K., Kim, Y.P., Kang, C.-H.: Long-term trend of aerosol composition and direct radiative forcing due to aerosols over Gosan: TSP, PM10, and PM2.5 data between 1992 and 2008. Atmos. Environ. 45, 6107–6115 (2011)
Lee, H.S., Kang, B.W.: Chemical characteristics of principal PM2.5 species in Chongju, South Korea. Atmos. Environ. 35, 739–746 (2001)
Lee, J.H., Kim, Y.P., Moon, K.C., Kim, H.K., Lee, C.B.: Fine particle measurements at two background sites in Korea between 1996 and 1997. Atmos. Environ. 35, 635–643 (2001)
Lee, B.K., Jun, N.Y., Lee, H.K.: Comparison of particulate matter characteristics before, during, and after Asian dust events in Incheon and Ulsan, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 38(11), 1535–1545 (2004)
Lee, H., Park, S.S., Kim, K.W., Kim, Y.J.: Source identification of PM2.5 particles measured in Gwangju, Korea. Atmos. Res. 88, 199–211 (2008)
Lee, H.W., Lee, T.J., Kim, D.S.: Identifying ambient PM2.5 sources and estimating their contributions by using PMF: Separation of gasoline and diesel automobile sources by analyzing ECs and OCs. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 25(1), 75–89 (2009a)
Lee, T.J., Huh, J.B., Yi, S.M., Kim, S.D., Kim, D.S.: Estimation of PM10 source contributions on three cities in the metropolitan area by using PMF Model. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 25(4), 275–288 (2009b)
Malm, W.C., Kohnson, C.E., Bresch, J.F.: In: Pace, T.G. (ed.) Application of principal component analysis for purposes of identifying source-receptor relationships in receptor methods for source apportionment, pp. 127–148. Air Pollution Control Association, Pittsburgh (1986)
Ministry of Environment, http://stat.me.go.kr/nesis
Moon, K.J., Han, J.S., Kong, B.J., Lee, M.D., Jung, I.R.: Characteristics of chemical species in gaseous and aerosol phase measured at Gosan, Korea during ABC-EAREX 2005. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 21(6), 675–687 (2005)
Moon, K.J., Han, J.S., Kong, B.R., Jung, I.R., Cliff, S.S., Cahill, T.A., Perry, K.D.: Size-resolved source apportionment of ambient particles by positive matrix factorization at Gosan, Jeju island during ACE-Asia. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 22(5), 590–603 (2006)
Moon, K.J., Park, S.M., Park, J.S., Song, I.H., Jang, S.K., Kim, J.C., Lee, S.J.: Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Seoul Metropolitan area in 2010. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 27(6), 711–722 (2011)
National Emissions Inventory (NEI) of Korea, Ministry of Environment, Korea (2008)
Nguyen, T.H., Lee, B.K.: Characteristic of particulate matter and metals in the ambient air from a residential area in the largest industrial city in Korea. Atmos. Res. 98, 526–537 (2010)
Pandis, S.N., Harely, R.H., Cass, G.R., Seinfeld, J.H.: Secondary organic aerosol formation and transport. Atmos. Environ. 26A, 2269–2282 (1992)
Park, S.S., Kim, Y.J.: Source contributions to fine particulate matter in an urban atmosphere. Chemosphere 59(22), 217–226 (2005)
Park, S.S., Lee, K.H., Kim, Y.J., Kim, T.Y., Cho, S.Y., Kim, S.J.: High time-resolution measurements of carbonaceous species in PM2.5 at an urban site of Korea. Atmos. Res. 89, 48–61 (2008)
Polissar, A.V., Hopke, P.K., Harris, J.M.: Source regions for atmospheric aerosol measured at Barrow, Alaska. Environ. Sci. Tech. 35, 4214–4226 (2001)
Richardson, C.B., Spann, J.F.: Measurement of the water cycle in a levitated ammonium sulfate particle. J. Aerosol Sci. 15, 563–571 (1984)
Seinfeld, J.H., Pandis, S.N.: Atmospheric chemistry and physics: From air pollution to climate change. Wiley (2006)
Sunder Raman, R.: Investigation of the nature and behavior of carbonaceous species and source apportionment of ambient particulate matter. Ph.D. Dissertation, Clarkson University, Potsdam, NY (2006)
Sunder Raman, R, Hopke, P.K., Holsen, T.M.: Characterization of fine aerosol and its inorganic components at two rural locations in New York State. Environ. Monit. Assess. 144, 351–366 (2008)
Turpin, B.J., Huntizicker, J.J.: Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantitation of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS. Atmos. Environ. 29, 3527–3544 (1995)
U.S. EPA: Compendium Method IO-4.2: Determination of reactive acidic and basic gases and strong acidity of atmospheric fine particles (<2.5 μm), EPA/625/R-96/010a (1999)
Wang, Y., Zhuang, G., Zhang, X., Huang, K., Xu, C., Tang, A., Chen, J., An, Z.: The ion chemistry, seasonal cycle, and sources of PM2.5 and TSP aerosol in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 40, 2935–2952 (2006)
Wang, S., Xing, J., Chatani, S., Hao, J., Klimont, Z., Cofala, J., Amann, M.: Verification of anthropogenic emissions of China by satellite and ground observations. Atmos. Environ. 45, 6347–6358 (2011)
Wittig, A.E., Anderson, N., Khlystove, A.Y., Pandis, S.N., Davidson, C., Robinson, A.L.: Pittsburgh air quality study overview. Atmos. Environ. 38, 3107–3125 (2004)
Yang, L., Zhou, X., Wang, Z., Zhou, Y., Cheng, S., Xu, P., Gao, X., Nie, W., Wang, X., Wang, W.: Airborne fine particulate pollution in Jinan, China: concentrations, chemical compositions and influence on visibility impairment. Atmos. Environ. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.02.029
Zheng, M., Salmon, L.G., Schauer, J.J., Zeng, L., Kiang, C.S., Zhang, Y., Cass, G.R.: Seasonal trends in PM2.5 source contributions in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 39, 3967–3976 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD, Basic Research Promotion Fund) (KRF-2008-331-D00278), and by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2009-0072989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, YJ., Kim, SR. & Jung, JH. Long-term measurements of atmospheric PM2.5 and its chemical composition in rural Korea. J Atmos Chem 68, 281–298 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-012-9225-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-012-9225-6