Abstract
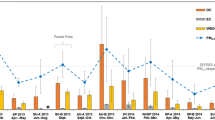
An established three stage sequential leach scheme was applied to a series of selected high volume aerosol samples (n = 35) collected from the Turkish Eastern Mediterranean coastline (Erdemli). Samples were selected according to their air mass back trajectory history to reflect the contrasting mixtures of aerosol material present in the Eastern Mediterranean marine aerosol. Two populations were adopted, those samples which were classed as “anthropogenic” and those which were “Saharan” dominated aerosol populations. Applying the three stage leach it was possible to define the proportion for each of the considered metals (Al, Fe, Cu, Pb, Cd, Zn and Mn) present in the (a) “exchangeable” (b) “carbonate / oxide” and (c) “refractory” phases, representing novel solid state aerosol speciation data for this marine system. Clear trends were established, conforming with data from previous studies with mainly crustal derived metals (Al and Fe) being present in the refractory phases (Al > 88%; Fe > 84%) and those influenced by anthropogenic sources being dominating in the exchangeable phase, although for these metals the variability was comparatively high (12–64%; 19–85%; 40–100% for Zn, Pb and Cd, respectively). For the majority, greater exchangeable fractions were present the lower the crustal source contribution to the aerosol population, whereas the “refractory” fraction exhibited contrasting behaviour. This was illustrated by the novel application of the mixing diagram, presenting each of the three speciation stages against the corresponding percent anthropogenic contribution to each collected sample. Zn, Pb and Cd all illustrated progressive decrease in the percent exchangeable with increasing crustal contribution to the aerosol population. The percent exchangeable was discussed in terms of its use to represent the upper limit of the bioavailable fraction of metal associated with the aerosol, post deposition. The mixing diagram approach enabled the prediction of the residual fractions for Cd, Pb and Zn (41 ± 4%; 62 ± 4% and 82 ± 5%, respectively,) in Saharan end-member material.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Masri, M.S., Al-Kharfan, K., Al-Shamali, K.: Speciation of Pb, Cu and Zn determined by sequential extraction for identification of air pollution sources in Syria. Atmos. Environ. 40, 753–761 (2006)
Andreae, T.W., Andreae, M.O., Ichoku, C., Maenhaut, W., Cafmayer, J., Karnieli, A., Orlovsky, L.: Light scattering by dust and anthropogenic aerosol at a remote site in the Negev Desert, Israel. J. Geophys. Res. 107(D2) (2002), doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2001JD900252
Baker, A.R., French, M., Linge, K.L.: Trends in aerosol nutrient solubility along a west-east transect of the Saharan dust plume. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, LO7805 (2006a) doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2005GL024764
Baker, A.R., Jickells T.D., Witt M., Linge K.L.: Trends in the solubility of iron, aluminium, manganese and phosphorous in aerosol collected over the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Chem. 98, 43–58 (2006b)
Bonnet, S., Guieu, C.: Dissolution of atmospheric iron in seawater. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31 (2004) doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2003GL018423
Chen, Y., Siefert, R.A.L.: Determination of various types of labile atmospheric iron over remote oceans. J. Geophys. Res. 108(D24) (2003) doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2003JD003515
Chen, Y., Street, J., Paytan, A.: Comparison between pure water and seawater soluble nutrient concentrations of aerosols from the Gulf of Aquaba. Mar. Chem. 101, 141--152 (2006)
Chester, R., Lin, F.J., Murphy, K.J.T.: A three stage sequential leaching scheme for the characterisation of the sources and environmental mobility of trace metals in the marine aerosol. Environ. Technol. Lett. 10, 887–900 (1989)
Chester, R., Murphy, K.J.T., Lin, F.J., Berry, A.S., Bradshaw, G.A., Corcoran, P.A.: Factors controlling the solubilities of trace metals from non-remote aerosol deposited to the sea surface by the dry deposition mode. Mar. Chem. 42, 107–126 (1993)
Chester, R., Bradshaw, G.F., Corcoran, P.A.: Trace metal chemistry of the North Sea particulate aerosol; concentrations, sources and seawater fates. Atmos. Environ. 28(17), 2873–2883 (1994)
Chester, R., Keyse, S., Nimmo, M.: In: Martin J-M, Barth H. (eds.) Factors controlling the solubility of Pb in rainwater; the solid state speciation of Pb in scavenged aerosols. Water Poll. Res. Report 32, 287–298 (1995)
Chester, R., Nimmo, M., Keyses, S.: The influence of Saharan and middle eastern desert-derived dust on the trace metal composition of Mediterranean aerosols and rainwaters: an overview. In: Guerzoni, S., Chester, R. (eds.) The impact of desert dust across the Mediterranean, pp. 253–273. Kluwer, The Netherlands (1996)
Chester, R., Nimmo, M., Fones, G.R., Keyse, S., Zhang, J.: The solubility of Pb in coastal marine rainwaters: pH-dependent relationships. Atmos. Environ. 34, 3875–3887 (2000)
Chiapello I., Bergametti G., Chatenet B., Bousquet P., Dulac B., Santos Soares E.: Origins of African dust transported over the northeastern tropical Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. 102(D12), 13,701–13,709 (1997)
Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E., Aranda-Rodriguez, R., Buykx, S.E.J.: Development and validation of capillary electrophoresis for the determination of selected metal ions in airborne particulate matter after sequential extraction. Anal. and Bioanal. Chem. 372, 467–472 (2002)
Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E., Kelly, M., Chen, H., Chakrabarti, C.L.: Evaluation of capillary electrophoresis combined with a BCR sequential extraction for determining distribution of Fe, Zn, Cu, Mn, and Cd in airborne particulate matter. Anal. Chim. Acta 498, 175–187 (2003)
Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E., Kelly, M., Chen, H., Chakrabarti, C.L.: Application of capillary electrophoresis combined with a modified BCR sequential extraction for estimating the distribution of selected trace metals in PM2.5 fractions of urban airborne particulate matter. Chemosphere 58, 1365–1376 (2005)
Desboeufs, K.V., Sofikitis, A., Losno, R., Colin, J.L., Ausset, P.: Dissolution and solubility of trace metals from natural and anthropogenic aerosol particulate matter. Chemosphere 50, 195–203 (2005)
Falkovich, A.H., Schkolnik, G., Ganor, E., Rudich, Y.: Adsorption of organic compounds pertinent to urban environments onto mineral dust particles. J. Geophys. Res. 109, D02208 (2004) doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2003JD003919
Fernandez, A.J., Ternero, M., Barragan, F.J., Jimenez, J.C.: An approach to characterization of sources of urban airborne particles through heavy metal speciation. Chemosphere 2, 123–136 (2000)
Fernandez Espinosa A.J., Ternero M., Barragan F.J., Jimenez J.C.: A chemical speciation of trace metals for fine urban particles. Atmos. Environ. 36, 773–780 (2002)
Fuchtjohann, L., Jakubowski, N., Galdthe, D., Barnowski, C., Klockow, D., Broekaert, J.A.C.: Determination of soluble and insoluble nickel compounds in airborne particulate matter by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma spectrometry. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 366, 142–145 (2000)
Guerzoni, S., Molinaroli, E., Rossini, P., Rampazzo, G., Quarantotto, G., De Falco, G., Cristini, S.: Role of desert aerosol in metal fluxes in the Mediterranean area. Chemosphere 39, 229–246 (1999)
Guieu, C., Chester, R., Nimmo, M., Martin, J.M., Guerzoni, S., Nicolas, E., Mateu, J., Keyse, S.: Atmospheric input of dissolved and particulate metals to the North Western Mediterranean. Deep-Sea Res. II 44, 665–674 (1997)
Guieu, C., Loye-Pilot, M-D., Ridame, C., Thomas C.: Chemical characterization of the Saharan dust end-member: some biogeochemical implications for the western Mediterranean Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 107 (D15) (2002) doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2001JD000582.
Hand, J.H., Mahowald, N.M., Chen, Y., Siefert, R.L., Luo, C., Subrmaniam, A., Fung, I.: Estimates of atmospheric processed soluble iron form observation and a global mineral aerosol model: biogeochemical implications. J. Geophys. Res. 109, D17205 (2004) doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2004JD004574
Heal, M.R., Hibbs, L.R., Agius, R.M., Beverrlan, I.J.: Total and water-soluble trace metal content of urban background PM10, PM2.5, and black smoke in Edinburgh, UK. Atmos. Environ. 39, 1417–1430 (2005)
Herut, B.: Levels of aerosol trace metals along the Mediterranean coast of Israel (1997). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 10, 89–93 (2001)
Herut, B., Nimmo, M., Medway, A., Chester, R., Krom, M.: Dry deposition at the Mediterranean coast of Israel (SE Mediterranean): sources and fluxes. Atmos. Environ. 35, 803–813 (2001)
Jickells, T.D.: Atmospheric inputs of metals and nutrients to the oceans: their magnitude and effects. Mar. Chem. 48, 199–214 (1995)
Koçak, M., Nimmo, M., Kubilay, N., Herut, B.: Spatio-temporal aerosol trace metal concentrations and sources in the Levantine Basin of the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 38, 2133–2144 (2004)
Koçak, M., Kubilay, N., Herut, B., Nimmo, M.: Total and leachable atmospheric particulate fluxes of heavy metals (Al, Fe, Mn, Pb, Cd, Zn, Cu) over the Levantine Basin; a refined assessment. Atmos. Environ. 39, 7330–7341 (2005)
Kubilay, N., Saydam, C.: Trace elements in atmospheric particulates over the Eastern Mediterranean: concentration, sources and temporal variability. Atmos. Environ. 29, 2289–2300 (1995)
Lim, B., Jickells, T.D., Colin, J.L., Losno, R.: The solubilities of Al, Pb, Cu and Zn in rain sampled in the marine environment over the North Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 8, 349–362 (1994)
Mahowald, N.M., Baker, A., Bergametti, G., Brooks, N., Duce, R.A., Jickells, T.D., Kubilay, N., Propsero, J.M., Tegen: Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inouts to the Ocean. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 19, GB4025 (2005) doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2004GB002402
Pinzani, M.C.C., Somogyi, A., Siminovici, A.S., Ansell, S., Steenari, B.M., Lindovist, O.: Direct determination of Cadmium speciation in municipal solid waste fly ash by synchrotron radiation induced μ-X-ray fluorescence and μ-X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 3165–3169 (2002)
Profumo, A., Spini, G., Cucca, L., Pesavento M.: Determination of inorganic nickel compounds in the particulate matter of emissions and workplace air by selective sequential extraction. Talanta 61, 465–472 (2003)
Rudnick, R.L., Gao, S.: Composition of the continental crust. Treatise in Geochem. 3, 1–46 (2003)
Sedwick, P.N., Church, T.M., Bowie, A.R., Marsay, C.M., Ussher, S.J., Achilles, K.M., Lethaby, P.J., Johnson, R.J., Sarin, M.M., McGillicuddy, D.J.: Iron in the Sargasso Sea (Bermuda Atlantic Time-series Study region) during summer: Eolian imprint, spatiotemporal variability, and ecological implications. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 19(4) (2005)
Slejkovec, Z., Salma, I., van Eletren, J.T., Zemplen-Papp, E.: Speciation of arsenic in coarse and fine urban aerosols using sequential extraction combined with liquid chromatography and atomic fluorescence detection. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 366, 830–834 (2000)
Sobonska, S., Riqo, N., Laboudigue, A., Bremard, C., Laureyns, J., Merlin, J.C., Wignacourt, P.: Microchemical investigation of dust emitted by a lead smelter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 33, 1334–1339 (1999)
Spokes, L.J., Jickells T.D., Lim B.: Solubilisation of aerosol trace metals by cloud processing: a Laboratory study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 58, 3281–3287 (1994)
Taylor, S.R., McLennan, S.M.: The continental crust; Its composition and evolution. Blackwell, Oxford, UK (1985)
Voutsa, D., Samara, C.: Labile and bioaccessible fractions of heavy metals in the airborne particulate matter from urban and industrial areas. Atmos. Environ. 36, 3583–3590 (2002)
Wedepohl, H.: The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59, 1217–1239 (1995)
Zatka, V.J., Warner J.S., Maskery D.: Chemical speciation of nickel in airborne dusts: analytical methods and results of an interlaboratory test program. Environ. Sci. Technol. 26, 138–144 (1992)
Zhu, X.R., Prospero, J.M., Millero, F.J., Savoie, D.L., Brass, G.W.: The solubility of ferric ion(do you mean iron?) in marine aerosol solutions at ambient relative humidities. Mar. Chem. 38, 91–107 (1992)
Acknowledgements
This study was funded in part by the Middle East Technical University (AFP-2001-07-01-01) and NATO (through a linkage grant of EST.CLG.977811). We would like to thank Emin Özsoy for making available the ECMWF trajectory analysis through collaboration with the Turkish State Meteorological Office and in addition acknowledgement is made for the use of ECMWF’s computing and archive facilities. The assistance of MEDPOL III and project 18.635 is also acknowledged. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koçak, M., Kubilay, N., Herut, B. et al. Trace Metal Solid State Speciation in Aerosols of the Northern Levantine Basin, East Mediterranean. J Atmos Chem 56, 239–257 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-006-9053-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-006-9053-7