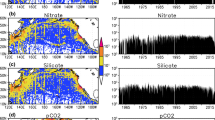
Abstract
The dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) and related chemical species have been measured from 1992 to 2001 at Station KNOT (44°N, 155°E) in the western North Pacific subpolar region. DIC (1.3∼2.3 µ mol/kg/yr) and apparent oxygen utilization (AOU, 0.7∼1.8 µmol/kg/yr) have increased while total alkalinity remained constant in the intermediate water (26.9∼27.3σθ). The increases of DIC in the upper intermediate water (26.9∼27.1σθ) were higher than those in the lower one (27.2∼ 27.3σθ). The temporal change of DIC would be controlled by the increase of anthropogenic CO2, the decomposition of organic matter and the non-anthropogenic CO2 absorbed at the region of intermediate water formation. We estimated the increase of anthropogenic CO2 to be only 0.5∼0.7 µmol/kg/yr under equilibrium with the atmospheric CO2 content. The effect of decomposition was estimated to be 0.8 ± 0.7 µmol/kg/yr from AOU increase. The remainder of non-anthropogenic CO2 had increased by 0.6 ± 1.1 µmol/kg/yr. We suggest that the non-anthropogenic CO2 increase is controlled by the accumulation of CO2 liberated back to atmosphere at the region of intermediate water formation due to the decrease of difference between DIC in the winter mixed layer and DIC under equilibrium with the atmospheric CO2 content, and the reduction of diapycnal vertical water exchange between mixed layer and pycnocline waters. In future, more accurate and longer time series data will be required to confirm our results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Anderson, L. A. and J. L. Sarmiento (1994): Redfield ratios of remineralization determined by nutrient data analysis. Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 8, 65–80.
Bates, N. R. (2001): Interannual variability of oceanic CO2 and biogeochemical properties in the Western North Atlantic subtropical gyre. Deep-Sea Res., Parts II, 48, 1507–1528.
Bates, N. R., A. C. Pequignet, R. J. Johnson and N. Gruber (2002): A short-term sink for atmospheric CO2 in subtropical mode water of the North Atlantic. Nature, 420, 489–493.
Brewer, P. G. (1978): Direct observation of the oceanic CO2 increase. Geophys. Res. Lett., 5, 997–1000.
Chen, C. T. A. and F. J. Millero (1979): Gradual increase of oceanic carbon dioxide. Nature, 227, 205–206.
Culberson, C., R. M. Pytkowitcz and J. E. Hawley (1970): Seawater alkalinity determination by the pH method. J. Mar. Res., 28, 15–21.
Dickson, A. G. and F. J. Millero (1987): A comparison of the equilibrium constants for the dissociation of carbonic acid in seawater media. Deep-Sea Res., 40, 107–118.
Dickson, A. G., G. C. Anderson and J. D. Afghan (2003): Reference materials for oceanic CO2 analysis: 1. Preparation, distribution and use. Mar. Chem. (submitted).
DOE (1994): Handbook of Methods for the Analysis of the Various Parameters of the Carbon Dioxide in Sea Water; Ver. 2, ed. by A. G. Dickson and C. Goyet.
Favorite, F., A. J. Dodimead and K. Nasu (1976): Oceanography of the subarctic Pacific region, 1960–1971. INPFC, 33, 1–187, Vancouver.
Gloor, M., N. Gruber, J. Sarmiento, C. L. Sabine, R. A. Feely and C. Rodenbeck (2003): A first estimate of present and preindustrial air-sea CO2 flux patterns based on oceanic interior carbon measurements and models. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, 1010, doi:10.1029/2002GL015594.
Honda, M. C., K. Imai, Y. Nojiri, F. Hoshi, T. Sugawara and M. Kusakabe (2002): The biological pump in the northwestern North Pacific based on fluxes and major components of particulate matter obtained by sediment-trap experiments (1997–2000). Deep-Sea Res. II, 49, 5595–5625.
Imai, K., Y. Nojiri, N. Tsurushima and T. Saino (2002): Time series of seasonal variation of primary productivity at station KNOT (44°N, 155°E) in the sub-arctic western North Pacific. Deep-Sea Res. II, 49, 5395–5408.
Isoda, Y., S. Shimizu, T. Izawa and T. Azumaya (2002): Interannual variations of North Pacific Intermediate Water across 155E and 180E sections in the subarctic North Pacific. Umi to Sora, 77, 143–151.
Johnson, K., A. E. King and J. M. Sieburth (1985): Coulometric TCO2 analyses for marine studies: An introduction. Mar. Chem., 16, 61–81.
Keeling, C. D. and T. P. Whorf (2002): Atmospheric CO2 records from sites in the SIO air sampling network. In Trends, A Compendium of Data on Global Change, Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy, Oak Ridge, Tenn., U.S.A.
Knap, A., A. Michaels, A. Close, H. Ducklow and A. Dickson (eds.) (1996): Protocols for the Joint Global Ocean Flux Study (JGOFS) core measurements. JGOFS Report No. 19, vi + 170 pp. Reprint of the IOC manuals and guides No. 29, UNESCO.
Kono, T. (1997): Modification of the Oyashio Water in the Hokkaido and Tohoku areas. Deep-Sea Res. I, 44, 669–688.
McNeil, B. I., R. J. Matear, R. M. Key, J. L. Bullister and J. L. Sarmiento (2003): Anthropogenic CO2 uptake by the ocean based on the global chlorofluorocarbon data set. Science, 299, 235–239.
Mehrbach, C., C. H. Culberson, J. E. Hawley and R. M. Pytkowicz (1973): Measurement of the apparent dissociation constants of carbonic acid in the seawater at atmospheric pressure. Limnol. Oceanogr., 18, 897–907.
Midorikawa, T., S. Sonoki, K. Saito, H. Takano, H. Kamiya, M. Ishii and H. I. Inoue (2003): Seasonal changes in oceanic pCO2 in the Oyashio region from winter to spring. J. Oceanogr., 59, 871–882.
Millero, F. J. (1996): Chemical Oceanography. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 272 pp.
Minobe, S. (1999): Resonance in bidecadal and pentadecadal climate oscillations over the North Pacific: role in climate regime shifts. Geophys. Res. Lett., 26, 855–858.
Ono, T., S. Watanabe, K. Okuda and M. Fukasawa (1998): Distribution of total carbonate and related properties in the North Pacific along 30°N. J. Geophys. Res., 103, 30873–30883.
Ono, T., Y. W. Watanabe and S. Watanabe (2000): Recent increase of DIC in the western North Pacific. Mar. Chem., 72, 317–328.
Ono, T., T. Midorikawa, Y. W. Watanabe, K. Tadokoro and T. Saito (2001): Temporal increases of phosphate and apparent oxygen utilization in the subsurface waters of western subarctic Pacific from 1968 to 1998. Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, 3285–3288.
Ono, T., K. Tadokoro, T. Midorikawa, J. Nishioka and T. Saino (2002): Multi-decadal decrease of net community production in western subarctic North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29, 10.1029/2001GL014332.
Redfield, A. C., B. H. Ketchum and F. A. Richards (1963): The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. p. 26–77. In The Sea, ed. by M. H. Hill, Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Reid, J. L. (1965): Intermediate waters of the Pacific Ocean. The John Hopkins Oceanographic Study, 2, Baltimore, p. 85.
Slansky, C. M., R. A. Feely and R. H. Wanninkhof (1997): The stepwise linear regression method for calculating anthropogenic CO2 invasion into the North Pacific Ocean. Proceeding of International Marine Science Symposium on Biogeochemical Processes in the North Pacific, 70–79, Japan.
Takahashi, Y., E. Matsumoto and Y. Watanabe (1999): Improved method for calculating anthropogenic CO2 in the upper layer of the North Pacific subtropical gyre along 175°E. J. Oceanogr., 55, 717–730.
Talley, L. D. (1991): An Okhotsk Sea anomaly: implications for ventilation in the North Pacific. Deep-Sea Res. A, 38,Suppl., S171–S190.
Tsunogai, S. (2000): North Pacific water’s larger potential sink capacity for absorbing anthropogenic CO2 and the processes recovering it. p. 533–560. In Dynamics and Characterization of Marine Organic Matter, ed. by N. Handa, E. Tanoue and T. Hama, TERRAPUB, Tokyo.
Tsunogai, S., T. Ono and S. Watanabe (1993): Increase in the total carbonate in the western North Pacific water and a hypothesis on the missing sink of anthropogenic carbon. J. Oceanogr., 49, 305–315.
Tsurushima, N., Y. Nogiri, K. Imai and S. Wanatabe (2002): Seasonal variations of carbon dioxide system and nutrients in the surface mixed layer at Station KNOT (44°N, 155°E) in the subarctic North Pacific. Deep-Sea Res. II, 49, 5377–5394.
Ueno, H. and I. Yasuda (2000): Distribution and formation of the mesothermal structure (temperature inversions) in the North Pacific subarctic region. J. Geophys. Res., 105, 16885–16898.
Watanabe, Y. W., Y. Takahashi, T. Kitao and K. Harada (1996): Total amount of oceanic excess CO2 taken from the North Pacific Subpolar Region. J. Oceanogr., 52, 301–312.
Watanabe, Y. W., T. Ono and A. Shimamoto (2000): Increase in the uptake rate of oceanic anthropogenic carbon in the North Pacific determined by CFC ages. Mar. Chem., 72, 297–315.
Wanatabe, Y. W., T. Ono, A. Shimamoto, T. Sugimoto, M. Wakita and S. Watanabe (2001): Probability of a reduction in the formation rate of the subsurface water in the North Pacific during the 1980s and 1990s. Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, 3289–3292.
Wanatabe, Y. W., T. Ono, M. Wakita, N. Maeda and T. Gamo (2003): Synchronous bidecadal periodic changes of oxygen, phosphate and temperature between the Japan Sea deep water and the North Pacific intermediate water. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, 10.1029/2003GL018338.
Weiss, R. F. (1970): The solubility of nitrogen, oxygen and argon in water and seawater. Deep-Sea Res., 17, 721–735.
Winn, C. D., Y. H. Lee, F. T. Mackenzie and D. M. Karl (1998): Rising surface ocean dissolved inorganic carbon at the Hawaii Ocean Time-series site. Mar. Chem., 60, 33–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakita, M., Watanabe, S., Watanabe, Y.W. et al. Temporal Change of Dissolved Inorganic Carbon in the Subsurface Water at Station KNOT (44°N, 155°E) in the Western North Pacific Subpolar Region. J Oceanogr 61, 129–139 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-005-0026-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-005-0026-2