Abstract
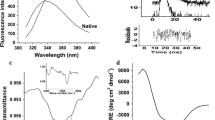
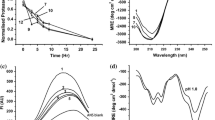
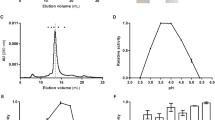
In the present study, the biophysical properties of His6-tagged Bacillus stearothermophilus aminopeptidase II (His6-tagged BsAmpII) are characterized in detail by gel-filtration, analytical ultracentrifugation, and various spectroscopic techniques. Using size-exclusion chromatography and analytical ultracentrifugation, we demonstrate that His6-tagged BsAmpII exists predominantly as a dimer in solution. The enzyme is active and stable at pHs ranging from 6.5 to 8.5. Far-UV circular dichroism analysis reveals that the secondary structures of His6-tagged BsAmpII are significantly altered in the presence of SDS, whereas the presence of 5–10% acetone and ethanol was harmless to the folding of the enzyme. Thermal unfolding of His6-tagged BsAmpII was found to be irreversible and led to the formation of aggregates. The native enzyme started to unfold beyond 0.6 M guanidine hydrochloride and had a midpoint of denaturation at 1.34 M. This protein remained active at concentrations of urea below 2.7 M but experienced an irreversible unfolding by >5 M denaturant. Taken together, this work lays a foundation for potential biotechnological applications of His6-tagged BsAmpII.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gonzales, T., Robert-Baudouy, J.: Bacterial aminopeptidases: properties and functions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 18, 319–344 (1996)
Sträter, N., Sherratt, D.J., Colloms, S.D.: Leucyl aminopeptidase (animal and plant). In: Barrett, A.J., Rawlings, N.D., Woessner, J.F. (eds.) Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes, pp. 1384–1389. Academic Press, New York (1998)
Walling, L.L., Gu, Y.: Plant aminopeptidase: occurrence, function and characterization. In: Taylor, A. (ed.) Aminopeptidases, pp. 173–219. Landes Publishing, Austin, TX (1970)
Terenius, L., Sandin, J., Sakurada, T.: Nociceptin/orphanin FQ metabolism and bioactive metabolites. Peptides 21, 919–922 (2000)
Cappiello, M., Lazzarotti, A., Buono, F., Scaloni, A., D’Ambrosio, C., Amodeo, P., Mendez, B.L., Pelosi, P., Del Corso, A., Mura, U.: New role for leucyl aminopeptidase in glutathione turnover. Biochem. J. 378, 35–44 (2004)
Matsumoto, H., Nagasaka, T., Hattori, A., Rogi, T., Tsuruoka, N., Mizutani, S. Tsujimoto, M.: Expression of placental leucine aminopeptidase/oxytocinase in neuronal cell and its action on neuronal peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 3259–3266 (2001)
Goldberg, A.T., Cascio, P., Saric, T., Rock, K.L.: The importance of the proteasome and subsequent proteolytic steps in the generation of antigenic peptides. Mol. Immunol. 39, 147–164 (2002)
Mitsui, T., Nomura, S., Itakura, A., Mizutani, S.: Aminopeptidase in health and diseases: role of aminopeptidase in the blood pressure regulation. Biol. Pharmaceut. Bull. 27, 768–771 (2004)
Rao, M.B., Tanksale, A.M., Ghatge M.S., Desphande, V.V.: Molecular and biotechnological aspects of microbial proteases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62, 597–635 (1998)
Kamphuis, J., Meijer, E.M., Boesten, W.H.J., Broxterman, Q.B., Kaptein, B., Hermes, H.F.M., Schoemaker, H.E.: Production of natural and synthetic l- and d-amino acids by aminopeptidases and amino amidases. In: Rozzell, J.D., Wagner, F. (eds.) Biocatalytic Production of Amino Acids and Derivatives, pp. 178–206. Wiley, New York (1992)
Fernandez-Espla, M.D., Rul, F.: PepS from Streptococcus thermophilus: a new member of the aminopeptidase T family of thermophilic bacteria. Eur. J. Biochem. 263, 502–510 (1999)
Rawlings, N.D., O’Brien, E., Barrett, A.J.: MEROPS: the protease database. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 343–346 (2002)
Rawlings, N.D., Barrett, A.J., Bateman, A.: MEROPS: the database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D343–D350 (2012)
Odintsov, S.G., Sabata I., Bourenkov, G., Rybin, V., Bochtler, M.: Staphylococcus aureus aminopeptidase S is a founding member of a new peptidase clan. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 27792–27799 (2005)
Odintsov, S.G., Sabata I., Bourenkov, G., Rybin, V., Bochtler, M.: Substrate access to the active sites in aminopeptidase T, a representative of a new metallopeptidase clan. J. Mol. Biol. 354, 403–412 (2005)
Minagawa, E., Kaminogawa, S., Matsuzawa, H., Ohta, T., Yamauchi, K.: Isolation and characterization of a thermostable aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase T) from Thermus aquaticus YT-1, an extremely thermophilic bacterium. Agric. Biol. Chem. 52, 755–763 (1988)
Stoll, E., Weder, H.G., Zuber, H.: Aminopeptidase II from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 438, 212–220 (1976)
Kuo, L.Y., Hwang, G.Y., Lai, Y.J., Yang, S.L., Lin, L.L.: Overexpression, purification, and characterization of the recombinant leucine aminopeptidase II of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Curr. Microbiol. 47, 40–45 (2003)
Kuo, L.Y., Hwang, G.Y., Yang, S.L., Hua, Y.W., Chen, W., Lin, L.L.: Inactivation of Bacillus stearothermophilus leucine aminopeptidase II by hydrogen peroxide and site-directed mutagenesis of methionine residues on the enzyme. Protein J. 23, 295–302 (2004)
Hwang, G.Y., Kuo, L.Y., Tsai, M.R., Yang, S.L., Lin, L.L.: Histidines 345 and 378 of Bacillus stearothermophilus leucine aminopeptidase II are essential for the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 87, 355–359 (2005)
Yang, S.L., Chen, R.S., Chen, W., Lin, L.L.: Identification of glutamate residues important for catalytic activity of Bacillus stearothermophilus leucine aminopeptidase II. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 90, 195–199 (2006)
Lin, L.L., Chen, Y.P., Yang, J.C., Hua, Y.W., Wang, W.C., Kuo, L.Y.: Significance of the conserved Tyr352 and Asp380 residues in the catalytic activity of Bacillus stearothermophilus aminopeptidase II as evaluated by site-directed mutagenesis. Protein J. 27, 215–222 (2008)
Brown, P.H., Schuck P.: Macromolecular size-and-shape distributions by sedimentation velocity analytical ultracentrifugation. Biophys. J. 90, 4651–4661 (2006)
Schuck, P.: Size-distribution analysis of macromolecules by sedimentation velocity ultracentrifugation and Lamm equation modeling. Biophys. J. 78, 1606–1619 (2000)
Benjwal, S., Verma, S., Röhm K.H., Gursky, O.: Monitoring protein aggregation during thermal unfolding in circular dichroism experiments. Protein Sci. 15, 635–639 (2006)
Royer, C.A., Mann, C.J., Matthews, C.R.: Resolution of the fluorescence equilibrium unfolding profile of trp aporepressor using single tryptophan mutants. Protein Sci. 2, 1844–1852 (1993)
Pace, C.N.: Measuring and increasing protein stability. Trends Biotechnol. 8, 93–98 (1990)
Hensley, P.: Defining the structure and stability of macromolecular assemblies in solution: the re-emergence of analytical ultracentrifugation as a practical tool. Structure 4, 367–373 (1996)
Laue, T.M., Statford, W.F.: Modern applications of analytical ultracentrifugation. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 28, 75–100 (1999)
Wang, Z.F., Huang, M.Q., Zou, X.M., Zhou, H.M.: Unfolding, conformational change of active sites and inactivation of creatine kinase in SDS solutions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1251, 109–114 (1995)
He, B., Zhang, Y., Zhang, T., Wang, H.R., Zhou, H.M.: Inactivation and unfolding of aminoacylase during denaturation in sodium dodecysulphate solution. J. Protein Chem. 14, 349–357 (1995)
Zhong, L., Johnson, W.C., Jr.: Environment affects amino acid preference for secondary structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 4462–4465 (1992)
Papavoine, C.H., Konings, R.N., Hilbers, C.W., van de Ven, F.J.: Location of M13 coat protein in sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles as determined by NMR. Biochemistry 33, 12990–12997 (1994)
Pervushin, K.V., Orekhov, V.Y., Popov, A.I., Musina, L.Y., Arseniev, A.S.: Three-dimensional structure of (1-71) bacterioopsin solubilized in methanol/chloroform and SDS micelles determined by 15N-1H heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. Eur. J. Biochem. 219, 571–583 (1994)
Micelli, S., Meleleo, D., Picciarelli, V., Stoico, M.G., Gallucci, E.: Effect of nanomolar concentrations of sodium dodecyl sulfate, a catalytic inductor of α-helices, on human calcitonin incorporation and channel formation in planar membranes. Biophys. J. 87, 1065–1075 (2004)
Montserret, R., McLeich, M., Bockmann, A., Geourjon, C., Penin, F.: Involvement of electrostatic interaction in the mechanism of peptide folding induced by sodium dodecyl sulfate binding. Biochemistry 39, 8362–8373 (2000)
Gupta, M.N., Roy, I.: Enzymes in organic media: forms, functions and applications. Eur. J. Biochem. 271, 2575–2583 (2004)
Freire, E., van Osdol, W.W., Mayorga, O.L., Sanchez-Ruiz, J.M.: Calorimetrically determined dynamics of complex unfolding transitions in proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 19, 159–188 (1990)
Sanchez-Ruiz, J.M.: Theoretical analysis of Lumry–Eyring models in differential scanning calorimetry. Biophys. J. 61, 921–935 (1992)
Galisteo, M.L., Mateo, P.L., Sanchez-Ruiz, J.M.: Kinetic study on the irreversible thermal denaturation of yeast phosphoglycerate kinase. Biochemistry 3, 2061–2066 (1991)
Lepock, J.R., Ritchie, K.P., Kolios, M.C., Rodahl, A.M., Heinz, K.A., Kruuv, J.: Influence of transition rates and scan rate on kinetic simulations of differential scanning calorimetry profiles of reversible and irreversible protein denaturation. Biochemistry 31, 12706–12712 (1992)
Plaza del Pino, I.M., Ibarra-Molero, B., Sachez-Ruiz, J.M.: Lower kinetic limit to protein thermal stability: a proposal regarding protein stability in vivo and its relation with misfolding diseases. Proteins 40, 58–70 (2000)
Vogl, T., Jatzke, C., Hinz, H.J., Benz, J., Huber, R.: Thermodynamic stability of Annexin V E17G: equilibrium parameters from an irreversible unfolding reaction. Biochemistry 36, 1657–1668 (1997)
Fitter, J.: The perspectives of studying multi-domain protein folding. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 1672–1681 (2009)
Zheng, J.Y., Janis, L.J.: Influence of pH, buffer species, and storage temperature on physiochemical stability of a humanized monoclonal antibody LA298. Int. J. Pharm. 308, 46–51 (2006)
Katayama, D.S., Nayar, R., Chou, D.K., Valente, J.J., Cooper, J., Henry, C., Vander Velde, D.G., Villarete, L., Liu, C.P., Manning, M.C.: Effect of buffer species on the thermally induced aggregation of interferon-tau. J. Pharm. Sci. 95, 1212–1226 (2006)
Monera, O.D., Kay, C.M., Hodges, R.S.: Protein denaturation with guanidine hydrochloride or urea provides a different estimate of stability depending on the contributions of electrostatic interactions. Protein Sci. 3, 1984–1991 (1994)
Lakowicz, J.R.: Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York (1999)
Del Vecchio, P., Granziano, G., Granata, V., Barone, G., Mandrich, L., Rossi, M., Manco, G.: Denaturing action of urea and guanidine hydrochloride towards two thermophilic esterases. Biochem. J. 367, 857–863 (2002)
Karan, R., Capes, M.D., DasSarma, S.: Function and biotechnology of extremophilic enzymes in low water activity. Aquat. Biosys. 8, 4 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the manuscript. Financial support (NSC 100-2313-B-415-003-MY3) from the National Science Council of Taiwan is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, TF., Lin, MG., Lo, HF. et al. Biophysical characterization of a recombinant aminopeptidase II from the thermophilic bacterium Bacillus stearothermophilus . J Biol Phys 40, 25–40 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-013-9332-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-013-9332-x