Abstract
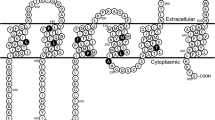
ABCC6 is a human ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter of the plasma membrane associated with Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), an autosomal recessive disease characterized by ectopic calcification of elastic fibers in dermal, ocular and vascular tissues. Similar to other ABC transporters, ABCC6 encloses the core structure of four domains: two transmembrane domains (TMDs) and two nucleotide binding domains (NBDs) but also an additional N-terminal extension, including a transmembrane domain (TMD0) and a cytosolic loop (L0), which is only found in some members of ABCC subfamily, and for which the function remains to be established. To investigate the functional roles of this N-terminal region, we generated several domain deletion constructs of ABCC6, expressed in HEK293 and polarized LLC-PK1 cells. ABCC6 lacking TMD0 displayed full transport activity as the wild type protein. Unlike the wild type protein, ABCC6 without L0 was not targeted to the basolateral membrane. Moreover, homology modeling of L0 suggests that it forms an ATPase regulatory domain. Furthermore, we show that the expression of ABCC6 is linked to a cellular influx of Ca2+. The results suggest that TMD0 is not required for transport function and that L0 maintains ABCC6 in a targeting-competent state for the basolateral membrane and might be involved in regulating the NBDs. These findings shed new light on a possible physiological function of ABCC6 and may explain some of the hallmarks of the clinical features associated with PXE that could contribute to the identification of novel pharmacological targets.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABC:
-
ATP binding cassette
- ER:
-
endoplasmic reticulum
- NBD:
-
nucleotide binding domain
- PPi:
-
pyrophosphate
- PXE:
-
pseudoxanthoma elasticum
- SUR:
-
sulfonylurea-binding receptor
- TMD:
-
transmembrane domain
References
Armentano MF, Ostuni A, Infantino V, et al. (2008) Identification of a new splice variant of the human ABCC6 transporter. Biochem Res Int 2008:912478. doi:10.1155/2008/912478
Babenko AP, Bryan J (2002) SUR-dependent modulation of KATP channels by an N-terminal KIR6.2 peptide. defining intersubunit gating interactions. J Biol Chem 277:43997–44004. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208085200
Bakos E, Evers R, Calenda G, et al. (2000) Characterization of the amino-terminal regions in the human multidrug resistance protein (MRP1). J Cell Sci 113(Pt 24):4451–4461
Bakos E, Evers R, Szakács G, et al. (1998) Functional multidrug resistance protein (MRP1) lacking the N-terminal transmembrane domain. J Biol Chem 273:32167–32175
Belinsky MG, Chen Z-S, Shchaveleva I, et al. (2002) Characterization of the drug resistance and transport properties of multidrug resistance protein 6 (MRP6, ABCC6). Cancer Res 62:6172–6177
Biasini M, Bienert S, Waterhouse A, et al. (2014) SWISS-MODEL: modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res 42:W252–W258. doi:10.1093/nar/gku340
Birnbaumer L (2009) The TRPC class of ion channels: a critical review of their roles in slow, sustained increases in intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49:395–426. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094928
Boraldi F, Quaglino D, Croce MA, et al. (2003) Multidrug resistance protein-6 (MRP6) in human dermal fibroblasts. comparison between cells from normal subjects and from pseudoxanthoma elasticum patients. Matrix Biol 22:491–500
Chan KW, Zhang H, Logothetis DE (2003) N-terminal transmembrane domain of the SUR controls trafficking and gating of Kir6 channel subunits. EMBO J 22:3833–3843. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg376
Chassaing N, Martin L, Calvas P, et al. (2005) Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: a clinical, pathophysiological and genetic update including 11 novel ABCC6 mutations. J Med Genet 42:881–892. doi:10.1136/jmg.2004.030171
Cuviello F, Tellgren-Roth Å, Lara P, et al. (2015) Membrane insertion and topology of the amino-terminal domain TMD0 of multidrug-resistance associated protein 6 (MRP6). FEBS Lett. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2015.10.030
De Boussac H, Ratajewski M, Sachrajda I, et al. (2010) The ERK1/2-hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha axis regulates human ABCC6 gene expression in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 285:22800–22808. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.105593
Fang K, Csanády L, Chan KW (2006) The N-terminal transmembrane domain (TMD0) and a cytosolic linker (L0) of sulphonylurea receptor define the unique intrinsic gating of KATP channels. J Physiol 576:379–389. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.112748
Finger RP, Charbel Issa P, Ladewig MS, et al. (2009) Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: genetics, clinical manifestations and therapeutic approaches. Surv Ophthalmol 54:272–285. doi:10.1016/j.survophthal.2008.12.006
Fiser A, Sali A (2003) Modeller: generation and refinement of homology-based protein structure models. Methods Enzymol 374:461–491. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(03)74020-8
Hegedus T, Orfi L, Seprodi A, et al. (2002) Interaction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors with the human multidrug transporter proteins, MDR1 and MRP1. Biochim Biophys Acta 1587:318–325
Higgins CF (1992) ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol 8:67–113. doi:10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435
Jansen RS, Küçükosmanoglu A, de Haas M, et al. (2013) ABCC6 prevents ectopic mineralization seen in pseudoxanthoma elasticum by inducing cellular nucleotide release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:20206–20211. doi:10.1073/pnas.1319582110
Kamada K, Miyata M, Hirano T (2013) Molecular basis of SMC ATPase activation: role of internal structural changes of the regulatory subcomplex ScpAB. Structure 21:581–594. doi:10.1016/j.str.2013.02.016
Lee H, Lara P, Ostuni A, et al. (2014) Live-cell topology assessment of URG7, MRP6102 and SP-C using glycosylatable green fluorescent protein in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 450:1587–1592. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.07.046
Mason DL, Michaelis S (2002) Requirement of the N-terminal extension for vacuolar trafficking and transport activity of yeast Ycf1p, an ATP-binding cassette transporter. Mol Biol Cell 13:4443–4455. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-07-0405
Matsuzaki Y, Nakano A, Jiang Q-J, et al. (2005) Tissue-specific expression of the ABCC6 gene. J Invest Dermatol 125:900–905. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23897.x
Miglionico R, Armentano MF, Carmosino M, Salvia AM, Cuviello F, Bisaccia FOA (2014) Dysregulation of gene expression in ABCC6 knockdown HepG2 cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett 19:517–526
Mikhailov MV, Campbell JD, de Wet H, et al. (2005) 3-D structural and functional characterization of the purified KATP channel complex Kir6.2-SUR1. EMBO J 24:4166–4175. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600877
Mikhailov MV, Mikhailova EA, Ashcroft SJ (2001) Molecular structure of the glibenclamide binding site of the beta-cell K(ATP) channel. FEBS Lett 499:154–160
Ostuni A, Lara P, Armentano MF, et al. (2013) The hepatitis B x antigen anti-apoptotic effector URG7 is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. FEBS Lett 587:3058–3062. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.07.042
Ostuni A, Miglionico R, Monné M, et al. (2011) The nucleotide-binding domain 2 of the human transporter protein MRP6. J Bioenerg Biomembr 43:465–471
Paumi CM, Chuk M, Chevelev I, et al. (2008) Negative regulation of the yeast ABC transporter Ycf1p by phosphorylation within its N-terminal extension. J Biol Chem 283:27079–27088. doi:10.1074/jbc.M802569200
Sinkó E, Iliás A, Ujhelly O, et al. (2003) Subcellular localization and N-glycosylation of human ABCC6, expressed in MDCKII cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 308:263–269
Slot AJ, Molinski SV, Cole SPC (2011) Mammalian multidrug-resistance proteins (MRPs). Essays Biochem 50:179–207. doi:10.1042/bse0500179
Ter Beek J, Guskov A, Slotboom DJ (2014) Structural diversity of ABC transporters. J Gen Physiol 143:419–435. doi:10.1085/jgp.201411164
Uitto J, Pulkkinen L, Ringpfeil F (2001) Molecular genetics of pseudoxanthoma elasticum: a metabolic disorder at the environment-genome interface? Trends Mol Med 7:13–17
Volkov A, Mascarenhas J, Andrei-Selmer C, et al. (2003) A prokaryotic condensin/cohesin-like complex can actively compact chromosomes from a single position on the nucleoid and binds to DNA as a ring-like structure. Mol Cell Biol 23:5638–5650
Westlake CJ, Cole SPC, Deeley RG (2005) Role of the NH2-terminal membrane spanning domain of multidrug resistance protein 1/ABCC1 in protein processing and trafficking. Mol Biol Cell 16:2483–2492. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-12-1113
Winkler M, Kühner P, Russ U, et al. (2012) Role of the amino-terminal transmembrane domain of sulfonylurea receptor SUR2B for coupling to K(IR)6.2, ligand binding, and oligomerization. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 385:287–298. doi:10.1007/s00210-011-0708-9
Xue P, Crum CM, Thibodeau PH (2014) Regulation of ABCC6 trafficking and stability by a conserved C-terminal PDZ-like sequence. PLoS one 9:e97360. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097360
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the undergraduate student Michela Pupillo for her work on the homology model of L0 in ABCC6. This project was supported by the University of Basilicata.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 2.55 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miglionico, R., Gerbino, A., Ostuni, A. et al. New insights into the roles of the N-terminal region of the ABCC6 transporter. J Bioenerg Biomembr 48, 259–267 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-016-9654-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-016-9654-z