Abstract
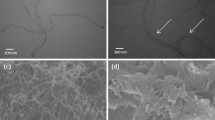
The in vitro cytotoxicity of both the multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) in suspension with culture medium and the tetracalcium phosphate/monetite cement with addition of 0.8 wt% of MWCNTs on fibroblasts and osteoblasts were studied. The cytotoxicity was evaluated by MTS test (formazan) and live/dead staining. No cytotoxicity of MWCNT extract was measured contrary to about 60% reduction in proliferation of fibroblasts in MWCNT suspension as compared with negative control. The several contact cytotoxicity of MWCNT composite cement surfaces on seeded cells was demonstrated by MTS test and live/dead staining of damaged fibroblasts and dead osteoblasts after 72 h of culture. The detailed microstructure analysis showed a significant refinement of the surface texture due to the formation of thin needle-like hydroxyapatite particles on MWCNTs and this effect could be responsible for cytotoxicity of composites.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen M, Qin X, Zeng G. Review biodegradation of carbon nanotubes, graphene, and their derivatives. Trends Biotechnol. 2017;35:No. 9 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.12.001836-846.
Toyokuni S. Genotoxicity and carcinogenicity risk of carbon nanotubes. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65:2098–110.
Thurnherr T, Brandenberger C, Fischer K, Diener L, Manser P, Maeder-Althaus X, et al. A comparison of acute and long-term effects of industrial multiwalled carbon nanotubes on human lung and immune cells in vitro. Toxicol Lett. 2011;200:176–86.
Fukushima S, Kasai T, Umeda Y, Ohnishi M, Sasaki T, Matsumoto M. Review Carcinogenicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes: challenging issue on hazard assessment. J Occup Health. 2018;60:10–30.
Cheung W, Pontoriero F, Taratula O, Chen AM, He H. DNA and carbon nanotubes as medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62:633–49.
Wang J, Sun P, Bao Y, Liu J, An L. Cytotoxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes on PC12 cells. Toxicol in Vitro. 2011;25:242–50.
Reddy AR, Reddy YN, Krishna DR, Himabindu V. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes induce oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells. Toxicology. 2010;272:11–6.
Song M, Zeng L, Yuan S, Yin J, Wang H, Jiang G. Study of cytotoxic effects of single-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with different chemical groups on human MCF7 cells. Chemosphere. 2013;92:576–82.
Siddiqui MA, Wahab R, Ahmad J, Farshori NN, Musarrat J, Al-Khedhairy AA. Evaluation of cytotoxic responses of raw and functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes in human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells. Vacuum. 2017;146:578–85.
Roda E, Castoldi AF, Coccini T, Mustarelli P, Quartarone E, Profum A, et al. In vitro toxicity assessment of single- and multi-walled carbon nanotubes in human astrocytoma and lung carcinoma cells. Toxicol Lett. 2007;172S:S1–240.
Usui Y, Aoki K, Narita N, Murakami N, Nakamura I, Nakamura K, et al. Carbon nanotubes with high bone-tissue compatibility and bone-formation acceleration effects. Small. 2008;4:240–6.
Boroujeni NM, Zhou H, Luchini TJ, Bhaduri SB. Development of multi-walled carbon nanotubes reinforced monetite bionanocomposite cements for orthopedic applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2013;33:4323–30.
Wang S, Zhang S, Wang Y, Sun X, Sun K. Reduced graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes reinforced calcium phosphate cement. Ceram Int. 2017;43:13083–8.
Chew KK, Low KL, Sharif Zein SH, McPhail DS, Gerhardt LC, Roether JA, et al. Reinforcement of calcium phosphate cement with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and bovine serum albumin for injectable bone substitute applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4:331–3.
Lin B, Zhou H, Leaman DW, Goel VK, Agarwal AK, Bhaduri SB. Sustained release of small molecules from carbon nanotube-reinforced. monetite calcium phosphate cement. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;43:92–6.
Oyefusi A, Olanipekun O, Neelgund GM, Peterson D, Stone JM, Williams E, et al. Hydroxyapatite grafted carbon nanotubes and graphene nanosheets: Promising bone implant materials. Spectrochim Acta A: Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014;132:410–6.
Gholami F, Zein SHS, Gerhardt LCH, Low KL, Tan SH, McPhail DS, et al. Cytocompatibility, bioactivity and mechanical strength of calcium phosphate cement reinforced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and bovine serum albumin. Ceram Int. 2013;39:4975–98.
Zancanela DC, de Faria AN, Simão AM, Gonçalves RR, Ramos AP, Ciancaglini P. Multi and single walled carbon nanotubes: effects on cell responses and biomineralization of osteoblasts cultures. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2016;27:62 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-016-5673-x.
Zhang M, Yang M, Morimoto T, Tajima N, Ichiraku K, Fujita K, et al. Size-dependent cell uptake of carbon nanotubes by macrophages: a comparative and quantitative study. Carbon. 2018;127:93–101.
Zhou L, Forman HJ, Ge Y, Lunec J. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes: a cytotoxicity study in relation to functionalization, dose and dispersion. Toxicol in Vitro. 2017;42:292–8.
Figarol A, Pourchez J, Boudard D, Forest V, Tulliani JM, Lecompte JP, et al. Biological response to purification and acid functionalization of carbon nanotubes. J Nanopart Res. 2014;16:2507.
Figarol A, Pourchez J, Boudard D, Forest V, Akono C, Tulliani JM, et al. In vitro toxicity of carbon nanotubes, nano-graphite and carbon black, similar impacts of acid functionalization. Toxicol in Vitro. 2015;30:476–85.
Song ZM, Wang L, Chen N, Cao A, Liu Y, Wang H. Biological effects of agglomerated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;142:65–7.
Allegri M, Perivoliotis DK, Bianchi MG, Chiu M, Pagliaro A, Koklioti MA, et al. Toxicity determinants of multi-walled carbon nanotubes: The relationship between functionalization and agglomeration. Toxicol Rep. 2016;3:230–43.
Wick P, Manser P, Limbach LK, Dettlaff-Weglikowska U, Krumeich F, Roth S. et al. The degree and kind of agglomeration affect carbon nanotube cytotoxicity. Toxicol Lett. 2007;168:121–31.
Pulskamp K, Diabate S, Krug HF. Carbon nanotubes show no sign of acute toxicity but induce intracellular reactive oxygen species in dependence on contaminants. Toxicol Lett. 2007;168:58–74.
Barabás R, Katona G, Bogya ES, Diudea MV, Szentes A, Zsirka B, et al. Preparation and characterization of carboxyl functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes–hydroxyapatite composites. Ceram Int. 2015;41:12717–27.
Akasaka T, Watari F, Sato Y, Tohji K. Apatite formation on carbon nanotubes. Mater Sci Eng C. 2006;26:675–8.
Ahn GS, Seol DW, Pyo SG, Lee D. Calcium phosphate cement-multi-walled carbon nanotube hybrid material (CPC-MWCNT Hybrid) enhances osteogenic differentiation. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;8:390–7.
Li X, Fan Y, Watari F. Current investigations into carbon nanotubes for biomedical application. Biomed Mater. 2010;5:022001 https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-6041/5/2/022001.
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Ning F, Guo D, Xu Z. Synthesis and cellular biocompatibility of two kinds of HAP with different nanocrystal morphology. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2007;83:121–6.
Haders DJ, Kazanecki CC, Denhardt DT, Riman RE. Crystallographically engineered, hydrothermally crystallized hydroxyapatite films: an in vitro study of bioactivity. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2010;2010:1531–42.
Okada S, Ito H, Nagai A, Komotori J, Imai H. Adhesion of osteoblast-like cells on nanostructured hydroxyapatite. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:591–7.
Eliaz N, Shmueli S, Shur I, Benayahu D, Aronov D, Rosenman G. The effect of surface treatment on the surface texture and contact angle of electrochemically deposited hydroxyapatite coating and on its interaction with bone-forming cells. Acta Biomater. 2009;2009:3178–91.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Slovak Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education of the Slovak Republic and the Slovak Academy of Sciences, Project No. 2/0047/17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medvecky, L., Giretova, M., Kralikova, R. et al. In vitro cytotoxicity of calcium phosphate cement reinforced with multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 30, 54 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-019-6256-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-019-6256-4