Abstract
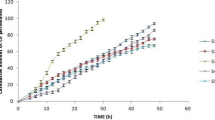
To improve the poor compatibility among different components of Drug-in-adhesive type patch, two novel plasters (Drug-in-fiber and Drug-in-adhesive/fiber) were developed based on ibuprofen (IBU)-loaded fiber mats. These fibrous mats were fabricated via electrospinning of cellulose acetate/poly(vinylpyrrolidone) composites in a binary solvent of N,N-dimethyl acetamide/acetone. Physical status studies suggested that Drug-in-fiber could inhibit IBU re-crystallization, but the active ingredients were released at a relatively slow rate due to the dual-resistance of fiber mat and adhesive matrix. To overcome this shortcoming, Drug-in-adhesive/fiber was designed by coupling medicated hydrophilic pressure sensitive adhesive and IBU-loaded fiber mat. This method endowed Drug-in-adhesive/fiber a fast IBU release rate and high permeated drug amount though simulative skins. This design separated enhancer from adhesive matrix, which guaranteed Drug-in-adhesive/fiber excellent adhesion forces. Hence, the plasters based on medicated fiber mats improved the compatibility among patch components.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wokovich AM, Prodduturi S, Doub WH, Hussain AS, Buhse LF. Transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) adhesion as a critical safety, efficacy and quality attribute. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2006;64:1–8.
Prausnitz MR, Langer R. Transdermal drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26:1261–8.
Langer R. Transdermal drug delivery: past progress, current status, and future prospects. Adv Drug Dev Rev. 2004;56:557–8.
Sartorelli P, Andersen HR, Angerer J, Corish J, Drexler H, Goen T, Griffin P, Hotchkiss SAM, Larese F, Montomoli L. Percutaneous penetration studies for risk asessment. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2000;8:133–52.
Chang HC, Wu SS, Wang YF, Wang HM. Quantification of porcine skin permeability in transdermal diffusion with a numerical model. J Taiwan Inst Chem E. 2010;41:136–42.
Kim JI, Choi HK. Effect of additives on the crystallization and the permeation of ketoprofen from adhesive matrix. Int J Pharm. 2002;236:81–5.
Sugibayashi K, Morimoto Y. Polymers for transdermal drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 1994;29:177–85.
Latsch S, Selzer T, Fink L, Kreuter J. Crystallisation of estradiol containing TDDS determined by isothermal micro-calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, and optical microscopy. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2003;56:43–52.
Zhang J, Deng L, Zhao H, Liu M, Jin H, Li J, Dong A. Pressure sensitive adhesive properties of poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone)/D, l-lactic acid oligomer/glycerol/water blends for TDDS. J Biomat Sci-Polym E. 2010;21:1–15.
Jain P, Banga AK. Inhibition of crystallization in Drug-in-adhesive-type transdermal patches. Inter J Pharm. 2010;394:68–74.
Yu JJ, Chien T, Chien Y. Transdermal dual-controlled delivery of testosterone and estradiol: (I) impact of system design. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1991;17:1883–904.
Schulz M, Fussnegger B, Bodmeiera R. Drug release and adhesive properties of crospovidone-containing matrix patches based on polyisobutene and acrylic adhesives. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2010;41:675–84.
Yu DG, Shen XX, Branford-White C, White K, Zhu LM. Annie Bligh SW. Oral fast-dissolving drug delivery membranes prepared from electrospun polyvinylpyrrolidone ultrafine fibers. Nanotechnology. 2009;20:055104–12.
Yu DG, Zhu LM, Branford-White CJ, Yang JH, Wang X, Li Y, Qian W. Solid dispersions in the form of electrospun core-sheath nanofibers. Int J Nanomed. 2010;6:3271–80.
Shi Y, Zhang J, Xu S, Dong A. Electrospinning of artemisinin-loaded core-shell fibers for inhibiting drug re-crystallization. J Biomat Sci-Polym E. 2012;. doi:10.1080/09205063.
Godin B, Touitou E. Transdermal skin delivery: predictions for humans from in vivo, ex vivo and animal models. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:1152–61.
Kreilgaard M. Dermal Pharmacokinetics of micro-emulsion formulations determination by in vivo micro-dialysis. Pharm Res. 2001;18:367–73.
Zhang J, Liu Z, Du H, Zeng Y, Deng L, Xing J, Dong A. A novel hydrophilic adhesive matrix with self-enhancement for drug percutaneous permeation through rat skin. Pharm Res. 2009;26:1398–406.
Guo R, Du X, Zhang R, Deng L, Dong A, Zhang J. Bio-adhesive film formed from a novel organic-inorganic hybrid gel for transdermal drug delivery system. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011;79:574–83.
Tungprapa S, Jangchud I, Supaphol P. Release characteristics of four model drugs from drug-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate fiber mats. Polymer. 2007;48:5030–41.
Hoogstraate AJ, Verhoef J, Brussee J, IJzerman AP, Spies F, Boddé HE. Kinetics, ultrastructural aspects and molecular modelling of transdermal peptide flux enhancement by N-alkylazacycloheptanones. Int J Pharm. 1991;76:37–47.
Zhang J, Liu M, Jin H, Deng L, Xing J, Dong A. In vitro enhancement of lactate esters on the percutaneous penetration of drugs with different lipophilicity. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010;11:894–903.
Kommuru R, Khan MA, Reddy IK. Racemate and enantiomers of Ketoprofen: phase diagram, thermodynamic studies, skin permeability, and use of chiral permeation enhancers. J Pharm Sci. 1998;87:833–40.
Ren C, Fang L, Ling L, Wang Q, Liu S, Zhao L, He Z. Design and in vitro evaluation of an indapamide transdermal patch. Int J Pharm. 2009;370:129–35.
Schulz M, Fussnegger B, Bodmeier R. Adsorption of carbamazepine onto crospovidone to prevent drug recrystallization. Int J Pharm. 2011;391:169–76.
Taghizadeh SM, Bajgholi S. A new Liposomal-Drug-in-adhesive patch for transdermal delivery of sodium diclofenac. J Biomat Nanobiotechnol. 2011;2:576–81.
Al-Saidan SM. Transdermal self-permeation enhancement of ibuprofen. J Control Release. 2004;100:199–209.
Charnay C, Bégu S, Tourné-Péteilh C, Nicole L, Lerner DA, Devoisselle JM. Inclusion of ibuprofen in mesoporous templated silica: drug loading and release property. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2004;57:533–40.
Yu DG, Zhang XF, Shen XX, Brandford-White C, Zhu LM. Ultrafine ibuprofen-loaded polyvinylpyrrolidone fiber mats using electrospinning. Polym Int. 2009;58:1010–3.
Yu DG, Yang JM, Branford-White C, Lu P, Zhang L, Zhu LM. Third generation solid dispersions of ferulic acid in electrospun composite nanofibers. Int J Pharm. 2010;400:158–64.
Kolhe P, Misra E, Kannana RM, Kannan S, Lieh-Lai M. Drug complexation, in vitro release and cellular entry of dendrimers and hyperbranched polymers. Int J Pharm. 2003;259:143–60.
Cilurzo F, Alberti E, Minghetti P, Gennari CGM, Casiraghi A, Montanari L. Effect of drug chirality on the skin permeability of ibuprofen. Int J Pharm. 2010;386:71–6.
Imani M, Lahooti-Fard F, Taghizadeh SM, Takrousta M. Effect of adhesive layer thickness and drug loading on estradiol crystallization in a transdermal drug delivery system. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010;11:1268–75.
Taghizadeh SM, Soroushnia A, Mohamadnia F. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of a new fentanyl patch based on functional and non-functional pressure sensitive adhesives. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2011;11:278–84.
Cilurzo F, Gennari CG, Minghetti P. Adhesive properties: a critical issue in transdermal patch development. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012;9:33–45.
Lin SY, Lee CJ, Lin YY. Drug-polymer interaction affecting the mechanical properties, adhesion strength and release kinetics of piroxicam-loaded eudragit E films plasticized with different plasticizers. J Control release. 1995;33:375–81.
Maillard-Salin DG, Bécourt P, Couarraze G. A study of the adhesive–skin interface: correlation between adhesion and passage of a drug. Int J Pharm. 2000;200:121–6.
Ho KY, Dodou K. Rheological studies on pressure-sensitive silicone adhesives and Drug-in-adhesive layers as a means to characterise adhesive performance. Int J Pharm. 2007;333:24–33.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81041085; 51103097).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Xu, S., Dong, A. et al. Design and in vitro evaluation of transdermal patches based on ibuprofen-loaded electrospun fiber mats. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 24, 333–341 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-012-4805-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-012-4805-1