Abstract
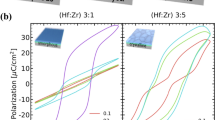
Lead hafnate titanate (PHT) thin film was deposited by pulse laser deposition, characterized for the usage as a ferroelectric capacitor in view of Ferroelectric Random Access Memory (FeRAM) devices, and compared with a lead zirconate titanate (PZT) reference, which was fabricated in the same conditions. Results indicate that the 126 nm-thickness PHT thin film with a low temperature self-buffer layer has a single (111)-orientation. The following electric measurements were performed to investigate the possibility of this thin film to use in the FeRAM applications by contrast to a PZT reference. This PHT sample demonstrates a good ferroelectric property with the remanent polarization of 51 μC/cm2. The remanent polarization with no obvious degradation has been observed after 2 × 109 fatigue reversals, which indicate that the PHT thin film a promising candidate in view of FeRAM applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Kohlstedt, Y. Mustafa, A. Gerber et al., Microelectron. Eng. 80, 296 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.mee.2005.04.084
T. Morimoto, O. Hidaka, K. Yamakawa et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 39, 2110 (2000). doi:10.1143/jjap.39.2110
S.R. Shannigrahi, H.M. Jang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 1051 (2001). doi:10.1063/1.1392970
Z.-K. Shen, Z.-H. Chen, Z.-J. Qiu et al., Microelectron. Eng. 87, 869 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.mee.2009.12.049
N. Kotova, Y. Podgorny, D. Seregin, A. Sigov, A. Vishnevskiy, K. Vorotilov, Ferroelectrics 465, 54 (2014). doi:10.1080/00150193.2014.893806
M. Dekkers, M.D. Nguyen, R. Steenwelle, P.M. te Riele, D.H.A. Blank, G. Rijnders, Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 012902 (2009). doi:10.1063/1.3163057
B.H. Park, B.S. Kang, S.D. Bu, T.W. Noh, J. Lee, W. Jo, Nature 401, 682 (1999). doi:10.1038/44352
F.Q. Zhang, Y.X. Li, J. Inorg. Mater. 29, 449 (2014). doi:10.3724/sp.j.1077.2014.13669
Y.-J. Seo, W.-S. Lee, Microelectron. Eng. 75, 149 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.mee.2004.03.086
J. Lindner, M. Schumacher, M. Dauelsberg et al., Adv. Mater. Opt. Electron. 10, 163 (2000). doi:10.1002/1099-0712(200005/10)10:3/5<163:aid-amo405>3.0.co;2-a
Y.-J. Seo, S.-W. Park, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 45, 3 (2004)
V.V. Sidsky, A.V. Semchenko, A.G. Rybakov et al., J. Rare Earths 32, 277 (2014). doi:10.1016/s1002-0721(14)60065-x
P.J. Schorn, T. Schneller, U. Bottger, R. Waser, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 88, 1312 (2005). doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2004.00177.x
A.Q. Jiang, J.F. Scott, M. Dawber, C. Wang, J. Appl. Phys. 92, 6756 (2002). doi:10.1063/1.1516841
M. Dawber, J.F. Scott, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1060 (2000). doi:10.1063/1.125938
G. Fantozzi, H. Idrissi, C. Favotto, M. Roubin, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 20, 1671 (2000). doi:10.1016/s0955-2219(00)00051-0
R. Pan, Y. He, M. Li, P. Li, P. Liu, Z. Xia, Mater. Sci. Eng. B (2014). doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2014.06.012
C.G. Wu, Y.R. Li, J. Zhu, X.Z. Liu, W.L. Zhang, J. Appl. Phys. 105, 044107 (2009). doi:10.1063/1.3081971
Y.L. Lin, J. Zhu, Z.P. Wu et al., J. Alloys Compd. 627, 182 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.12.122
J. Frantti, Y. Fujioka, S. Eriksson, S. Hull, M. Kakihana, Inorg. Chem. 44, 9267 (2005). doi:10.1021/ic051169m
J.P. Chang, Y.S. Lin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 3666 (2001). doi:10.1063/1.1418265
J. Müller, U. Schröder, T.S. Böscke et al., J. Appl. Phys. 110, 114113 (2011). doi:10.1063/1.3667205
A.K. Tagantsev, I. Stolichnov, E.L. Colla, N. Setter, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 1387 (2001). doi:10.1063/1.1381542
X.P. Wang, J. Zhu, W.B. Luo, Y. Zhang, Y.R. Li, J. Appl. Phys. 104, 074112 (2008). doi:10.1063/1.2996080
W. Li, J. Gu, C. Song, D. Su, J. Zhu, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 114104 (2005). doi:10.1063/1.2134877
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Supporting Project from the Education Ministry of China (No. 625010112) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51372030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Zhu, J. & Liu, X. Improved fatigue property of hafnium substitute lead zirconate titanate deposited by pulse laser deposition. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 1819–1823 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5731-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5731-7