Abstract
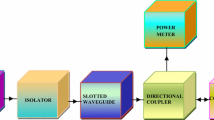
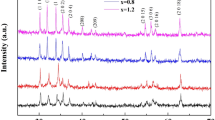
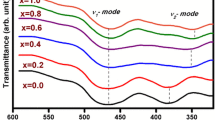
The Co2+ and W4+ ions substituted M-type hexagonal ferrites, with chemical compositional formula Ba0.5Sr0.5CoxWxFe12−2xO19 (x = 0.0, 0.2, 0.8 and 1.0), were synthesized by a standard ceramic method. The phase evolution of the compositions was characterized by using an X-ray diffraction. The microwave absorption of compositions has been investigated as a function of frequency, substitution and thickness from 8.2 to 12.4 GHz by an absorber testing device method. The microwave absorption has been evaluated using the standard model of quarter wavelength mechanism and an impedance matching mechanism. The microwave absorption is enhanced in x = 0.0 and 0.2, with former owes 97.0 % absorbed power at 11.22 GHz and 2.4 mm respectively. Compositions x = 0.0, 0.2 and 0.8 exhibit −10 dB absorption bandwidth of 500 MHz while x = 1.0 owes 330 and 340 MHz.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.C. Aphesteguy, A. Pamiani, D. Digiovanni, S.E. Jacobo, Microwave-absorbing characteristics of epoxy resin composites containing nanoparticles of NiZn and NiCuZn ferrites. Phys. B 404, 2713 (2009)
X. Huang, J. Zhang, M. Lai, T. Sang, Preparation and microwave absorption mechanisms of the NiZn ferrite nanofibers. J. Alloys Compd. 627, 367 (2015)
U.R. Lima, M.C. Nasar, M.C. Rezende, J.H. Araugo, Ni–Zn nanoferrite for radar-absorbing material. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 1666 (2008)
P. Meng, K. Xiong, L. Wang, S. Li, Y. Cheng, G. Xu, Tunable complex permeability and enhanced microwave absorption properties of BaNixCo1−xTiFe10O19. J. Alloys Compd. 628, 75 (2015)
J. Liu, J. Zhang, P. Zhang, S. Wang, C. Lu, Y. Li, M. Zhang, Tunable microwave absorbing properties of barium hexa-ferrite nano powders by surface carbonized layers. Mater. Lett. 158(53), 53–57 (2015)
H. Wu, G. Wu, Q. Wu, L. Wang, Facile synthesis and microwave absorbability of C@Ni–NiO core–shell hybrid solid sphere and multi-shelled NiO hollow sphere. Mater. Charact. 97, 18 (2014)
H. Wu, G. Wu, L. Wang, Peculiar porous α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 nanospheres: facile synthesis and electromagnetic properties. Powder Technol. 269, 443 (2015)
Y. Ren, L. Yang, L. Wang, T. Xu, G. Wu, H. Wu, Facile synthesis, photoluminescence properties and microwave absorption enhancement of porous and hollow ZnO. Powder Technol. 281, 20 (2015)
H. Wu, Q. Wu, L. Wang, Design and wide range microwave absorption of porous Co–Co3O4 hybrid hollow sphere with magnetic multi-resonance mechanisms. Mater. Charact. 103, 1 (2015)
W. Hu, L. Wang, Q. Wu, H. Wu, Facile synthesis, magnetic and optical properties of double-shelled Co3O4 hollow microspheres. Adv. Powder Technol. 25, 1780 (2014)
H. Wu, G. Wu, Y. Ren, L. Yang, L. Wang, X. Lid, Co2+/Co3+ ratio dependence of electromagnetic wave absorption in hierarchical NiCo2O4–CoNiO2 hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 7677 (2015)
H. Wu, L. Wang, Y. Wang, S. Guo, Z. Shen, Enhanced microwave performance of highly ordered mesoporous carbon coated by Ni2O3 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 525, 82 (2012)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, Y. Ren, Y. Wang, Z. Wang, H. Wu, Synthesis and characterization of γ-Fe2O3@C nanorod-carbon sphere composite and its application as microwave absorbing material. J. Alloys Compd. 652, 346 (2015)
Q. Wu, G. Wu, L. Wang, W. Hu, H. Wu, Facile synthesis and optical properties of Prussian Blue microcubes and hollow Fe2O3 microboxes. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 30, 476 (2015)
H. Wu, L. Wang, H. Wu, Q. Lian, Synthesis and significantly enhanced microwave absorption properties of hematite dendrites/polyaniline nanocomposite. Appl. Phys. A 115, 1299 (2014)
G. Wu, Y. Cheng, Q. Xie, Z. Jia, F. Xiang, H. Wu, Facile synthesis of urchin-like ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Mater. Lett. 144, 157 (2015)
K.-K. Ji, Y. Li, M.-S. Cao, Mn, Ti substituted barium ferrite to tune electromagnetic properties and enhanced microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 5128 (2016)
A. Baniasadi, A. Ghasemi, M.A. Ghadikolaei, A. Nemati, E. Paimozd, Microwave absorption properties of Ti–Zn substituted strontium hexaferrite. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 1901 (2016)
Y. Cheng, X. Ren, Permeability and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of sintered barium hexaferrites with substitution of Co2+–Zr4+. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 772 (2016)
S.S. Li, K. Xiong, P. Meng, X. Ren, G. Xu, Sol–gel synthesis of copper(II) and titanium(IV) ions co-doped barium ferrite submicrometer crystals and their microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 5710 (2015)
Ali-Sharbati, J.-M.V. Khani, Influence of Ho substitution on structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of PbM-type hexaferrites nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25, 244 (2014)
R.S. Alam, M. Moradi, H. Nikmanesh, J. Ventura, M. Rostami, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of BaMgx/2Mnx/2CoxTi2xFe12−4xO19hexaferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 402, 20 (2016)
S.E. Jacobo, P.G. Bercoff, Structural and electromagnetic properties of yttrium-substituted Ni–Zn ferrites range. Ceram. Int. 42, 7664 (2016)
I. Sadiq, S. Naseem, M.N. Ashiq, M.A. Iqbal, I. Ali, M.A. Khan, S. Niaz, M.U. Rana, Spin canting effect and microwave absorption properties of Sm–Mn substituted nanosized material. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 406, 184 (2016)
P.T. Tho, C.T.A. Xuan, D.M. Quang, T.N. Bach, T.D. Thanh, N.T.H. Le, D.H. Manh, N.X. Phuc, D.N.H. Nam, Microwave absorption properties of dielectric La1.5Sr0.5NiO4 ultrafine particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B186, 101 (2014)
L. Wang, H. Yu, X. Ren, G. Xu, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of BaMnxCo1−xTiFe10O19. J. Alloys Compd. 588, 212 (2014)
C. Singh, S.B. Narang, I.S. Hudiara, Y. Bai, K. Marina, Hysteresis analysis of Co–Ti substituted M-type Ba–Sr hexagonal ferrite. Mater. Lett. 63, 1991 (2009)
M.R. Meshram, N.K. Agrawal, B. Sinha, P.S. Misra, Characterization of M-type barium hexagonal ferrite-based wide band microwave absorber. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 271, 2007 (2004)
P. Singh, V.K. Babbar, A. Razdan, R.K. Puri, T.C. Goel, Complex permittivity, permeability, and X-band microwave absorption of CaCoTi ferrite composites. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 4362 (2000)
E. Neckenburger, H. Severin, J.K. Vogel, G. Winkler, Ferrite hexagonaler Kristallstrustur mit hoher Grenzfrequenz. Z. Angew. Phys. 18, 65 (1964)
R.C. Pullar, Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater Sci. 57, 1191 (2012)
C. Singh, S.B. Narang, I.S. Hudiara, Y. Bai, F. Tabatabaei, Static magnetic properties of Co and Ru substituted Ba–Sr ferrite. Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 176 (2008)
C.B. Carter, M.G. Norton, Ceramic materials: science and engineering (Springer, Berlin, 2013), p. 58
B. Wang, J. Wei, Y. Yang, T. Wang, F. Li, Investigation on peak frequency of the microwave absorption for carbonyl iron/epoxy resin composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 1101 (2011)
N.-N. Song, Y.J. Ke, H.-T. Yang, H. Zhang, X.-Q. Zhang, B.-G. Shen, Z.-H. Cheng, Integrating giant microwave absorption with magnetic refrigeration in one multifunctional intermetallic compound of LaFe11.6Si1.4C0.2H1.7. Sci. Rep. 2291, 1 (2013)
A.M. Nicolson, G.F. Ross, Measurement of the intrinsic properties of materials by time-domain techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 19, 377 (1970)
T. Inui, K. Konishi, K. Oda, Fabrications of broad-band RF-absorber composed of planar hexagonal ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 35, 3148 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, R., Singh, C., Kaur, D. et al. Microwave absorption characteristics of Co2+ and W4+ substituted M-type Ba0.5Sr0.5CoxWxFe12−2xO19 hexagonal ferrites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 228–235 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5515-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5515-0