Abstract
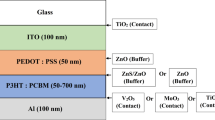
This study investigates the zinc oxide (ZnO) buffer layer thickness in the photovoltaic performance of inverted organic solar cells (OSCs) based on an active layer blend of poly(3-hexylthiophene), (P3HT) and [6, 6]-phenyl-C61 butyric acid methyl ester, (PCBM). The ZnO buffer layer acts as a protective layer to prevent the photoactive layer interface by UV light from oxidation. Besides, it reduces the energy barrier to easily transfer electrons between the collecting electrode and the organic acceptor lowest unoccupied molecular orbital level. The buffer layer block holes in P3HT from recombining with electrons in the collecting electrode. The X-ray diffraction analysis show that the constant orientation of the grains according to the c-axis perpendicular to the substrate surface. The optical measurements indicated that all samples have a transmission higher than 60 % in the visible range. A slight shift of the absorption edge toward the small wavelengths was observed as the thickness increased to over 250 nm. The electrical measurements depended on thickness. The resistivity decreased from 5.45 to 4.98 × 10−3 Ω.cm, and the mobility increased from 1.66 to 1.71 × 10−1 cm2/Vs when the thickness increased from 65.6 nm to 107.0 nm. This behavior was explained by the crystallinity pattern. The optimization of the ZnO buffer layer caused the short circuit current density to vary from 0.287 to 1.599 mA/cm2 and the fill factor to range between 19.08 and 24.55 %. This result increased the power conversion efficiency from 0.007 to 0.043 %. The photovoltaic performance of inverted structure OSCs is strongly dependent on the ZnO buffer layer thickness.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Gholamkhass, N.M. Kiasari, P. Servati, An efficient inverted organic solar cell with improved ZnO and gold contact layers. Org. Electron. 13, 945–953 (2012)
S. Schumann, R. Da Campo, B. Illy, A.C. Cruickshank, M.A. McLachlan, M.P. Ryan, D.J. Riley, D.W. McComb, T.S. Jones, Inverted organic photovoltaic devices with high efficiency and stability based on metal oxide charge extraction layers. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 2381–2386 (2011)
J. Weickert, R.B. Dunbar, H.C. Hesse, W. Wiedemann, L. Schmidt-Mende, Nanostructured organic and hybrid solar cells. Adv. Mater. 23, 1810–1828 (2011)
N. Espinosa, H.F. Dam, D.M. Tanenbaum, J.W. Andreasen, M. Jørgensen, F.C. Krebs, Roll-to-roll processing of inverted polymer solar cells using hydrated vanadium (V) oxide as a PEDOT:PSS replacement. Materials 4, 169–182 (2011)
M. Jørgensen, K. Norrman, F.C. Krebs, Stability/degradation of polymer solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 92, 686–714 (2008)
M. Jørgensen, K. Norrman, S.A. Gevorgyan, T. Tromholt, B. Andreasen, F.C. Krebs, Stability of polymer solar cells. Adv. Mater. 24, 580 (2012)
T. Kuwabara, Y. Kawahara, T. Yamaguci, K. Takahaski, Characterization of inverted type organic solar cells with a ZnO layer as the electron collection electrode by ac impedance spectroscopy. Acs Appl. Mater. 1, 2107–2110 (2009)
J.L. Delgado, P.A. Bouit, S. Filippone, M.A. Herranz, N. Martin, Organic photovoltaics: a chemical approach. Chem. Commun. 46, 4853–4865 (2010)
M.S. White, D.C. Olson, S.E. Shaheen, N. Kopidakis, D.S. Ginley, Inverted bulk- heterojunction organic photovoltaic device using a solution-derived ZnO underlayer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 1435171–1435173 (2006)
M.F. Malek, M.H. Mamat, M.Z. Sahdan, M.Z. Musa, Z. Khusaimi, M. Rusop, Influence of various sol concentrations on stress/strain and properties of ZnO thin films synthesised by sol-gel technique. Thin Solid Films 527, 102–109 (2013)
M.F. Malek, M.Z. Sahdan, M.H. Mamat, M.Z. Musa, Z. Khusaimi, S.S. Husairi, N.D. Md Sin, M. Rusop, A novel fabrication of MEH-PPV/Al:ZnO nanorod arrays based ordered bulk heterojunction hybrid solar cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. 275, 75–83 (2013)
A.K.K. Kyaw, X.W. Sun, C.Y. Jiang, G.Q. Lo, D.W. Zhao, D.L. Kwong, An inverted organic solar cell employing a sol-gel derived ZnO electron selective layer and thermal evaporated MoO3 hole selective layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 221107–221101–221107-221103 (2008)
Y.-J. Noh, S.-I. Na, S.-S. Kim, Inverted polymer solar cells including ZnO electron transport layer fabricated by facile spray pyrolysis. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 117, 139–144 (2013)
R. Lampande, G.W. Kim, D.C. Choe, J.H. Kong, J.H. Kwon, Solution processed n-type mixed metal oxide layer for electron extraction in inverted polymer solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 125, 276–282 (2014)
X. Yu, X. Yu, J. Zhang, G. Zhao, J. Ni, H. Cai, Y. Zhao, Efficiency boosting of inverted polymer solar cells with a polyvinylpyrrolidone-modified Al-doped ZnO electron transport layer. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 128, 307–312 (2014)
M. Thambidurai, J.Y. Kim, C.M. Kang, N. Muthukumarasamy, H.J. Song, J. Song, Y. Ko, D. Velauthapillai, C. Lee, Enhanced photovoltaic performance of inverted organic solar cells with In-doped ZnO as an electron extraction layer. Renew. Energy 66, 433–442 (2014)
A. Baumann, T.J. Savenije, D.H.K. Murthy, M. Heeney, V. Dyakonov, C. Deibel, Influence of phase segregation on recombination dynamics in organic bulk heterojunction solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 1687–1692 (2011)
F. Zhang, X. Xu, W. Tang, J. Zhang, Z. Zhuo, J. Wang, J. Wang, Z. Xu, Y. Wang, Recent development of the inverted configuration organic solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 95, 1785–1799 (2011)
M.Z. Sahdan, M.F. Malek, M.S. Alias, S.A. Kamaruddin, C.A. Norhidayah, N. Sarip, N. Nafarizal, M. Rusop, Fabrication of inverted bulk heterojunction organic solar cells based on conjugated P3HT:PCBM using various thicknesses of ZnO buffer layer. Optik 126, 645–648 (2015)
M.J. Alam, D.C. Cameron, Preparation and properties of transparent conductive aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films by sol–gel process. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 19, 1642–1646 (2001)
B.D. Cullity, S.R. Stock, Elements of X-ray Diffraction (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1978)
M.Z. Sahdan, M.H. Mamat, M. Salina, Z. Khusaimi, U.M. Noor, M. Rusop, Heat treatment effects on the surface morphology and optical properties of ZnO nanostructures. Phys. Status Solidi C 7, 2286–2289 (2010)
E.F. Keskenler, M. Tomakin, S. Doğan, G. Turgut, S. Aydın, S. Duman, B. Gürbulak, Growth and characterization of Ag/n-ZnO/p-Si/Al heterojunction diode by sol–gel spin technique. J. Alloys Compd. 550, 129–132 (2013)
B.D. Cullity, S.R. Stock, Elements of X-ray Diffraction (Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 2001)
T.P. Rao, M.C. Santhoshkumar, Effect of thickness on structural, optical and electrical properties of nanostructured ZnO thin films by spray pyrolysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 4579–4584 (2009)
O. Lupan, T. Pauporte´, L. Chow, B. Viana, F. Pelle´, L.K. Ono, B. Roldan Cuenya, H. Heinrich, Effects of annealing on properties of ZnO thin films prepared by electrochemical deposition in chloride medium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 1895–1907 (2010)
Selected Powder Diffraction Data for Metals and Alloys, vol.1 (JCPDS, USA, 1978), p. 108
R. Ghosh, D. Basak, S. Fujihara, Effect of substrate-induced strain on the structural, electrical, and optical properties of polycrystalline ZnO thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 96, 2689–2692 (2004)
V. Gupta, A. Mansingh, Influence of postdeposition annealing on the structural and optical properties of sputtered zinc oxide film. J. Appl. Phys. 80, 1063–1073 (1996)
X.J. Ping, S.S. Bo, L. Lan, Z.X. Song, W.Y. Xin, C.X. Ming, Effects of annealing temperature on structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films. Chin. Phys. Lett. 27, 047803 (2010)
Y.G. Wang, S.P. Lau, H.W. Lee, S.F. Yu, B.K. Tay, X.H. Zhang, K.Y. Tse, H.H. Hng, Comprehensive study of ZnO films prepared by filtered cathodic vacuum arc at room temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 1597–1604 (2003)
M.F. Malek, M.H. Mamat, M.Z. Musa, Z. Khusaimi, M.Z. Sahdan, A.B. Suriani, A. Ishak, I. Saurdi, S.A. Rahman, M. Rusop, Thermal annealing-induced formation of ZnO nanoparticles: minimum strain and stress ameliorate preferred c-axis orientation and crystal-growth properties. J. Alloys Compd. 610, 575–588 (2014)
J. Rodríguez-Báez, A. Maldonado, G. Torres-Delgado, R. Castanedo-Pérez, M. de la, L. Olvera, Influence of the molar concentration and substrate temperature on fluorine-doped zinc oxide thin films chemically sprayed. Mater. Lett. 60, 1594–1598 (2006)
M.F. Malek, M.H. Mamat, Z. Khusaimi, M.Z. Sahdan, M.Z. Musa, A.R. Zainun, A.B. Suriani, N.D. Md Sin, S.B. Abd Hamid, M. Rusop, Sonicated sol-gel preparation of nanoparticulate ZnO thin films with various deposition speeds: the highly preferred c-axis (0 0 2) orientation enhances the final properties. J. Alloys Compd. 582, 12–21 (2014)
H. Hoppe, N.S. Sariciftci, Organic solar cells: an overview. J. Mater. Res. 19, 1924–1945 (2004)
J. Rostalski, D. Meissner, Photocurrent spectroscopy for the investigation of charge carrier generation and transport mechanisms in organic p/n-junction solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 63, 37–47 (2000)
H.P. Kim, A.R.M. Yusoff, H.M. Kim, H.J. Lee, G.J. Seo, J. Jang, Inverted organic photovoltaic device with a new electron transport layer. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 150–150 (2014)
T.-H. Lai, S.-W. Tsang, J.R. Manders, S. Chen, F. So, Properties of interlayer for organic photovoltaics. Mater. Today 16, 424–432 (2013)
H. Kim, K. Lee, Role of interpenetrating networks in the device performance of polymer-fullerene photovoltaic cells. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 42, 183–186 (2003)
H. Sun, J. Weickert, H.C. Hesse, L. Schmidt-Mende, UV light protection through TiO2 blocking layers for inverted organic solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 95, 3450–3454 (2011)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Ministry of Education Malaysia for the financial support through FRGS grant Vote No. 1093 and the Program Ahli Sains dan Penyelidik Muda (PSPM) scholarship under the Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM) and the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) Malaysia. We also acknowledge Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM) for the technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahdan, M.Z., Malek, M.F., Alias, M.S. et al. Metamorphosis of the ZnO buffer layer thicknesses on the performance of inverted organic solar cells. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 12891–12902 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5425-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5425-1