Abstract
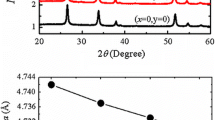
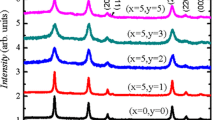
In this work, the dielectric and magnetic properties of (Co, Ni) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles were studied using ac impedance spectroscopy and magnetic properties measurement system or quantum design superconducting quantum interference device. Results showed that dielectric constant (ε r ), dielectric loss (ε″), and ac electrical conductivity (σ AC ) are strongly frequency dependent. A decrease in frequency was accompanied with an increase in ε r and ε″ values, whereas, a decrease in the dielectric constant was observed with the increase of Ni co-doping concentration. It was found that the dielectric constant and dielectric loss values decrease, whilst AC electrical conductivity increases with increase in co-doping concentration. Magnetization measurements revealed that the Ni co-doped SnO2 samples exhibits room temperature ferromagnetism. The results illustrate that (Co, Ni) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles have an excellent dielectric, magnetic properties, and high electrical conductivity than those of co-doped samples reported previously, indicating that these (Co, Ni) co-doped SnO2 materials can be suitable for the purpose of high frequency device and spintronic applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.A. Prinz, Magnetoelectronics. Science 282, 1660 (1998)
W. Prellier, A. Fouchet, B. Mercey, Oxide-diluted magnetic semiconductors: a review of the experimental status. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 15, R1583 (2003)
N.N. Lathiotakis, A.N. Andriotis, M. Menon, Codoping: a possible pathway for inducing ferromagnetism in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 78, 193311 (2008)
J.M.D. Coey, K. Wongsaprom, J. Alaria, M. Venkatesan, Charge-transfer ferromagnetism in oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 134012 (2008)
R. Khan, S. Fashu, Y. Zaman, Magnetic and dielectric properties of (Co, Zn) co-doped SnO2 diluted magnetic semiconducting nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10854-016-4517-2
R. Khan, Zulfiqar, Y. Zaman, Effect of annealing on structural, dielectric, transport and magnetic properties of (Zn, Co) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 4003–4010 (2016)
K. Nomura, J. Okabayashi, K. Okamura, Y. Yamada, Magnetic properties of Fe and Co codoped SnO2 prepared by sol–gel method. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 083901 (2011)
S.B. Ogale, R.J. Choudhary, J.P. Buban, S.E. Lofland, S.R. Shinde, S.N. Kale, V.N. Kulkarni, J. Higgins, C. Lanci, J.R. Simpson, N.D. Browning, S. Das Sarma, H.D. Drew, R.L. Greene, T. Venkatesan, High temperature ferromagnetism with a giant magnetic moment in transparent Co-doped SnO2−δ . Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 077205 (2003)
J.M.D. Coey, A.P. Douvalis, C.B. Fitzgerald, M. Venkatesan, Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped SnO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1332 (2004)
J.D. Bryan, S.M. Heald, S.A. Chambers, D.R. Gamelin, Strong room-temperature ferromagnetism in Co2+-doped TiO2 made from colloidal nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 11640 (2004)
F.H. Aragón, J.A.H. Coaquira, P. Hidalgo, S.L.M. Brito, D. Gouvea, R.H.R. Castro, Structural and magnetic properties of pure and nickel doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 22, 496003 (2010)
D.H. Kim, S.I. Woo, S.H. Moon, H.D. Kim, B.Y. Kim, J.H. Cho, Y.G. Joh, E.C. Kim, Effect of Co/Fe co-doping in TiO2 rutile prepared by solid state reaction. Solid State Commun. 136, 554 (2005)
K. Nomura, C.A. Barrero, K. Kuwano, Y. Yamada, T. Saito, E. Kuzmann, 57Fe Mössbauer study of sol–gel synthesized Sn1−x−yFexSbyO2−δ powders. Hyperfine Interact. 191, 25 (2009)
R. Adnan, N.A. Razana, I.A. Rahman, M.A. Farrukh, Synthesis and characterization of high surface area tin oxide nanoparticles via the sol–gel method as a catalyst for the hydrogenation of styrene. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 57, 222 (2010)
Y.H. Xiao, S.H. Ge, L. Xi, Y. Zuo, X.Y. Zhou, L. Zhang, G. Wang, X.F. Han, Z.C. Wen, Structure, optical, and magnetic properties of rutile Sn1−x Mn x O2 thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 7981 (2009)
P.I. Archer, P.V. Radovanovic, S.M. Heald, D.R. Gamelin, Low-temperature activation and deactivation of high-Curie-temperature ferromagnetism in a new diluted magnetic semiconductor: Ni2+-doped SnO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 14479 (2005)
Y.F. Li, R. Deng, Y.F. Tian, B. Yao, T. Wu, Role of donor–acceptor complexes and impurity band in stabilizing ferromagnetic order in Cu-doped SnO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 172402 (2012)
X.S. Fang, C.H. Ye, L.D. Zhang, T. Xie, Twinning mediated growth of Al2O3 nanobelts and their enhanced dielectric responses. Adv. Mater. 17, 1661–1665 (2005)
J.G. Han, Z.Y. Zhu, S. Ray, A.K. Azad, W.L. Zhang, M.X. He, S.H. Li, Y.P. Zhao, Optical and dielectric properties of ZnO tetrapod structures at terahertz frequencies. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 031107 (2006)
F. Gu, S.F. Wang, M.K. Lü, G.J. Zhou, D. Xu, D.R. Yuan, Photoluminescence properties of SnO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel method. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 8119–8123 (2004)
P.S. Szu, Y.C. Lin, AC impedance studies of copper doped silica glass. Phys. Chem. Mater. 82, 295–300 (2003)
O. Pakma, N. Serinl, T. Serin, S. Altında, Influence of frequency and bias voltage on dielectric properties and electrical conductivity of Al/TiO2/p-Si/p+ (MOS) structures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 215103 (2008)
C.H. Ho, C.D. Liu, C.H. Hsieh, K.H. Hsieh, S.N. Lee, High dielectric constant polyaniline/poly(acrylic acid) composites prepared by in situ polymerization. Synth. Metals 158, 630–637 (2008)
H. Zhang, D. Wang, V. Hu, X. Kang, H. Liu, Synthesis and magnetic properties of Sn1−x Co x O2 nanostructures and their application in gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B 184, 288–294 (2013)
K. Nomura, J. Okabayashi, K. Okamura, Y. Yamada, Magnetic properties of Fe and Co codoped SnO2 prepared by sol–gel method. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 083901 (2011)
J. Hays, A. Punnoose, R. Baldner, M.H. Engelhard, J. Peloquin, K.M. Reddy, Relationship between the structural and magnetic properties of Co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 72, 075203 (2005)
Acknowledgments
Rajwali Khan and Zulfiqar would like thankful to the Department of Physics, Islamia College Peshawar China; Abdul Wali Khan University, Mardan, Pakistan, and Harare Institute of Technology, Harare, Zimbabwe for providing some experimental facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, R., Zulfiqar, Fashu, S. et al. Effects of Ni co-doping concentrations on dielectric and magnetic properties of (Co, Ni) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 7725–7730 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4759-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4759-z