Abstract
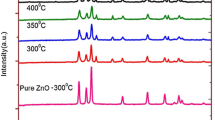
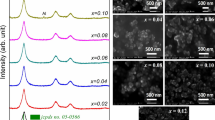
The undoped and Al-doped ZnO (AZO) nanostructures were synthesized by using simple hydrothermal process with two different pH values 6 and 10. The structural and optical properties of the ZnO and 0.5 % AZO nano particles were investigated using field emission scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, transmission electron microscope, atomic force microscope, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Ultraviolet–visible (UV) spectroscopy and photoluminescence (PL). It is observed from XRD results; on aluminium doping the crystalline size reduces significantly. It can be clearly seen from the FESEM images that Al doping causes the crystalline structure of ZnO to agglomerated small grain nano particles and TEM confirms that the particles are of nanometer size. The UV absorption indicates that blue shift of the samples increases the optical band gap, and decreases the average crystallite size. In the PL spectra, undoped ZnO exhibit an excitonic peak in the UV region and a defect-related peak in the visible region, whereas Al doping leads to a suppression of c lattice parameter and blue shift of luminescence with blue and green emission.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
U. Ozgur, Y.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M.M. Reshchikov, S. Dogan, V. Avrutin, S.J. Cho, H. Morkoc, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 86 (2005)
C. Klingshirn, Chem. Phys. Chem. 8, 782 (2007)
V. Musat, A.M. Rego, R. Monteiro, E. Forttunato, Thin Solid Films 516, 1512–1515 (2008)
T. Minami, S. Ida, T. Yao, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 75, 190–198 (2000)
Ting-Jen Hsueh, Cheng-Liang Hsu, Sens. Actuators B Chem. 131(2), 572–576 (2008)
K. Momeni, G.M. Odegard, R.S. Yassar, Acta Mater. 60, 5117–5124 (2012)
S. Choopun, R.D. Vispute, W. Noch, A. Balasamo, R.P. Sharma, T. Venkatesan, A. Lliadies, D.C. Look, Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 3947–3949 (1999)
B.J. Jin, S. Im, S.Y. Lee, Thin Solid Films 366, 107–110 (2000)
K. Vanheusden, W.L. Warren, C.H. Seager, D.R. Tallant, J.A. Voigt, B.E. Gnade, J. Appl. Phys. 79, 7983 (1996)
L.E. Greene, M. Law, J. Goldberger, F. Kim, J.C. Johnson, Y. Zhang, R.J. Saykally, P. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 3031–3034 (2003)
Y.W. Heo, D.P. Norton, S.J. Pearton, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 1–6 (2005)
S.A. Studenikin, N. Golego, M. Cocivera, J. Appl. Phys. 84, 2287 (1998)
R.G. Gordon, Criteria for choosing transparent conductors. MRS Bull. 25, 52–57 (2000)
M. Benhaliliba, C.E. Benouis, M.S. Aida, A.S. Juarez, F. Yakuphanoglu, A.T. Silver, J. Alloys Compd. 506, 548–553 (2010)
L. Grigorjeva, D. Millers, K. Smits, C. Monty, J. Kouam, L. ElMir, Solid State Phenom. 128, 141–146 (2007)
Suresh C. Pillai, John M. Kelly, Raghavendra Ramesh, Declan E. McCormackad, J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 3268–3271 (2013)
A.M. Marijn, D.V. Versteegh, J.I. Dijkhuis, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 157402 (2012)
K. Ueda, H. Tabata, T. Kawai, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 988 (2001)
L. Yan, C.K. Ong, X.S. Rao, J. Appl. Phys. 96, 508 (2004)
Z.L. Wang, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16, R829–R858 (2004)
K. Shirouzu, T. Ohkusa, M. Hotta, N. Enomoto, J. Hojo, J. Ceram. Soc. Japan 115, 254–258 (2007)
B. Houng, C.-L. Huang, S.-Y. Tsai, J. Cryst. Growth 307, 328–333 (2007)
H. Agura, A. Suzuki, T. Matsushita, T. Aoki, M. Okuda, Thin Solid Films 445, p263–p267 (2003)
K. Sambath, M. Saroja, M. Venkatachalam, K. Rajendran, N. Muthukumarasamy, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 431–436 (2012)
C.-C. Lin, S.-Y. Chen, S.-Y. Cheng, H.-Y. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 5040–5042 (2004)
J. Jolivet, S. Cassaignon, C. Chaneac, D. Chiche, O. Durupthy, D. Portehault, C. R. Chim. 13, 40–51 (2010)
D.S. Rana, D.K. Chaturvedi, J.K. Quamara, J. Optoelectron Adv. Mater. 11(5), 705–712 (2009)
S. Suwanboon, P. Amornpitoksuk, A. Sukolrat, Dependence of optical properties on doping metal, crystallite size and defect concentration of M-doped ZnO nano powders (M = Al, Mg, Ti). Ceram. Int. 37, 1359–1365 (2011)
T. Takagahara, K. Takeda, Theory of the quantum confinement effect on excitons in quantum dots of in direct-gap materials. Phys. Rev. B 46, 15578 (1992)
S. Fung, W.M. Kwok, W.K. Chan, D.L. Phillips, L. Ding, W.K. Ge, Defects in ZnO nanorods prepared by a hydrothermal method. Phys. Chem. B 110, 20865–20871 (2006)
C.H. Ahn, Y.Y. Kim, D.C. Kim, S.K. Mohanta, H.K. Cho, A comparative analysis of deep level emission in ZnO layers deposited by various methods. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 089901–089902 (2009)
J.L. Driscoll, N. Khare, Y. Liu, M.E. Vickers, Adv. Mater. 19, 2925–2929 (2007)
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to the Department of Bio-Sciences, Sri Krishna Arts and Science College, Coimbatore for providing the laboratory facilities and Centre for Nano science and technology of Sathyabama University, Chennai to carry out characterization for this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj Mohan, R., Sambath, K. & Rajendran, K. Experimental investigation on structural and optical properties of ZnO: AZO nano particles by hydrothermal synthesis. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 1748–1755 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2603-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2603-x