Abstract
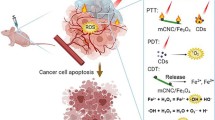
Malignant tumor has always been a complex disease that endangers human health. Traditional treatment methods include surgical resection, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. However, solid tumors are prone to recur. Herein, we developed a hydrogel-based drug-carrying system to prevent postoperative tumor recurrence. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose was modified with dopamine via the N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) and 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbanyl diimide (EDC)-mediated coupling chemistry. The CMC-DA-MnO2/MnO (CDM) hydrogel was prepared by oxidative cross-linking, using KMnO4 as the oxidizing agent. In the hydrogel, the KMnO4 can not only be used as an oxidant to trigger the polymerization and gelation of CMC-DA but also transformed into MnO2 and MnO to afford the T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The fluorescent dye IR808 as a photosensitizer was introduced into the hydrogel system by simply soaking the CDM hydrogel in the IR808 solution. Under the 808 nm laser irradiation, IR808 and PDA endowed the hydrogel with tumor photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT) capacities, respectively. With the proven hemo- and cyto-compatibilities, the CDM hydrogel was successfully used for the PDT and PTT prevention of postoperative tumor recurrence.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xie P, Zhang L, Shen H, Wu H, Zhao J, Wang S, Hu L (2022) Biodegradable MoSe2-polyvinylpyrrolidone nanoparticles with multi-enzyme activity for ameliorating acute pancreatitis. J Nanobiotechnol 20(1):113
Cheng Y, Zheng X, Zhang L, Zhao J, Hu L, Wang S (2023) Enhanced photothermal and chemotherapy of pancreatic tumors by degrading the extracellular matrix. Colloids Surf. B 221:113010
Xie J, Fan T, Kim JH, Xu Y, Wang Y, Liang W, Qiao L, Wu Z, Liu Q, Hu W, Yin N, Yang L, Liu L, Kim JS, Zhang H (2020) Emetine-loaded black phosphorus hydrogel sensitizes tumor to photothermal therapy through inhibition of stress granule formation. Adv Funct Mater 30(43):2003891
Zhou L, Wu Y, Meng X, Li S, Zhang J, Gong P, Zhang P, Jiang T, Deng G, Li W, Sun Z, Cai L (2018) Dye-anchored MnO nanoparticles targeting tumor and inducing enhanced phototherapy effect via mitochondria-mediated pathway. Small 14(36):1801008
Liu P, Peng Y, Zhou Y, Shi X, Li Q, Ding J, Gao Y, Zhou W (2021) Rapamycin as a “One-Stone-Three-Birds” agent for cooperatively enhanced phototherapies against metastatic breast cancer. ACS Appl Mater Inter 13(22):25674–25684
Guo L, Yan DD, Yang D, Li Y, Wang X, Zalewski O, Yan B, Lu W (2014) Combinatorial photothermal and immuno cancer therapy using chitosan-coated hollow copper sulfide nanoparticles. ACS Nano 8(6):5670–5681
Hu J-J, Cheng Y-J, Zhang X-Z (2018) Recent advances in nanomaterials for enhanced photothermal therapy of tumors. Nanoscale 10(48):22657–22672
Leitao MM, de Melo-Diogo D, Alves CG, Lima-Sousa R, Correia IJ (2020) Prototypic heptamethine cyanine incorporating nanomaterials for cancer phototheragnostic. Adv Healthc Mater 9(6):1901665
Park YI, Kim HM, Kim JH, Moon KC, Yoo B, Lee KT, Lee N, Choi Y, Park W, Ling D, Na K, Moon WK, Choi SH, Park HS, Yoon S-Y, Suh YD, Lee SH, Hyeon T (2012) Theranostic probe based on lanthanide-doped nanoparticles for simultaneous in vivo dual-modal imaging and photodynamic therapy. Adv Mater 24(42):5755–5761
Xu J, Han W, Yang P, Jia T, Dong S, Bi H, Gulzar A, Yang D, Gai S, He F, Lin J, Li C (2018) Tumor microenvironment-responsive mesoporous MnO2-coated upconversion nanoplatform for self-enhanced tumor theranostics. Adv Funct Mater 28(36):1803804
Escudero A, Carrillo-Carrion C, Castillejos MC, Romero-Ben E, Rosales-Barrios C, Khiar N (2021) Photodynamic therapy: photosensitizers and nanostructures. Mater Chem Front 5(10):3788–3812
Cheng Y, Cheng H, Jiang C, Qiu X, Wang K, Huan W, Yuan A, Wu J, Hu Y (2015) Perfluorocarbon nanoparticles enhance reactive oxygen levels and tumour growth inhibition in photodynamic therapy. Nat Commun 6:8785
Li X, Kwon N, Guo T, Liu Z, Yoon J (2018) Innovative strategies for hypoxic-tumor photodynamic therapy. Angew Chem Int Edit 57(36):11522–11531
Yang J-C, Shang Y, Li Y-H, Cui Y, Yin X-B (2018) An “all-in-one” antitumor and anti-recurrence/metastasis nanomedicine with multi-drug co-loading and burst drug release for multi-modality therapy. Chem Sci 9(36):7210–7217
Liu J, Zhao X, Nie W, Yang Y, Wu C, Liu W, Zhang K, Zhang Z, Shi J (2021) Tumor cell-activated “Sustainable ROS Generator” with homogeneous intratumoral distribution property for improved anti-tumor therapy. Theranostics 11(1):379–396
Lan M, Zhao S, Liu W, Lee C-S, Zhang W, Wang P (2019) Photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Adv Healthc Mater 8(13):1900132
Wang C, Wang X, Dong K, Luo J, Zhang Q, Cheng Y (2016) Injectable and responsively degradable hydrogel for personalized photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 104:129–137
Wu L, Ishigaki Y, Zeng W, Harimoto T, Yin B, Chen Y, Liao S, Liu Y, Sun Y, Zhang X, Liu Y, Liang Y, Sun P, Suzuki T, Song G, Fan Q, Ye D (2021) Generation of hydroxyl radical-activatable ratiometric near-infrared bimodal probes for early monitoring of tumor response to therapy. Nat Commun 12(1):6145
Hai J, Zeng X, Zhu Y, Wang B (2019) Anions reversibly responsive luminescent nanocellulose hydrogels for cancer spheroids culture and release. Biomaterials 194:161–170
Chen Z, Wu H, Wang H, Zaldivar-Silva D, Aguero L, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Yin Y, Qiu B, Zhao J, Lu X, Wang S (2021) An injectable anti-microbial and adhesive hydrogel for the effective noncompressible visceral hemostasis and wound repair.Mater Sci Eng C 129:112422
Wang T, Yi W, Zhang Y, Wu H, Fan H, Zhao J, Wang S (2023) Sodium alginate hydrogel containing platelet-rich plasma for wound healing. Colloids Surf. B 222:113096
Du H, Liu W, Zhang M, Si C, Zhang X, Li B (2019) Cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils based hydrogels for biomedical applications. Carbohyd Polym 209:130–144
Teixeira MA, Paiva MC, Amorim MTP, H.P. (2020) Felgueiras, Electrospun nanocomposites containing cellulose and its derivatives modified with specialized biomolecules for an enhanced wound healing. Nanomaterials 10(3):557
Chiang C-W, Hsiao Y-C, Jheng P-R, Chen C-H, Manga YB, Lekha R, Chao K-M, Ho Y-C, Chuang E-Y (2021) Strontium ranelate-laden near-infrared photothermal-inspired methylcellulose hydrogel for arthritis treatment. Mater Sci Eng C 123:111980
Samyn P (2021) Polydopamine and cellulose: two biomaterials with excellent compatibility and applicability. Polym Rev 61(4):814–865
Xu Q, Chang M, Zhang Y, Wang E, Xing M, Gao L, Huan Z, Guo F, Chang J (2020) PDA/Cu bioactive hydrogel with “Hot Ions Effect” for inhibition of drug-resistant bacteria and enhancement of infectious skin wound healing. ACS Appl Mater Inter 12(28):31255–31269
Poinard B, Neo SZY, Yeo ELL, Heng HPS, Neoh KG, Kah JCY (2018) Polydopamine nanoparticles enhance drug release for combined photodynamic and photothermal therapy. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10(25):21125–21136
Zhang Y, Zhu C, Zhang Z, Zhao J, Yuan Y, Wang S (2021) Oxidation triggered formation of polydopamine-modified carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel for anti-recurrence of tumor. Colloids Surf. B 207:112025
Huang H, Feng W, Chen Y (2021) Two-dimensional biomaterials: material science, biological effect and biomedical engineering applications. Chem Soc Rev 50:11381–11485
Zhong Y, Wang J, Yuan Z, Wang Y, Xi Z, Li L, Liu Z, Guo X (2019) A mussel-inspired carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel with enhanced adhesiveness through enzymatic crosslinking. Colloids Surf. B 179:462–469
Guo L, Liu W, Niu G, Zhang P, Zheng X, Jia Q, Zhang H, Ge J, Wang P (2017) Polymer nanoparticles with high photothermal conversion efficiency as robust photoacoustic and thermal theranostics. J Mater Chem B 5(15):2832–2839
Yang X, Wang S, Zhang X, Ye C, Wang S, An X (2022) Development of PVA-based microsphere as a potential embolization agent. Mater Sci Eng C 135:112677
Deng X, Huang B, Wang Q, Wu W, Coates P, Sefat F, Lu C, Zhang W, Zhang X (2021) A mussel-inspired antibacterial hydrogel with high cell affinity, toughness, self-healing, and recycling properties for wound healing. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 9(8):3070–3082
Huang W, Cheng S, Wang X, Zhang Y, Chen L, Zhang L (2021) Noncompressible hemostasis and bone regeneration induced by an absorbable bioadhesive self-healing hydrogel. Adv Funct Mater 31(22):2009189
Li K-C, Chu H-C, Lin Y, Tuan H-Y, Hu Y-C (2016) PEGylated copper nanowires as a novel photothermal therapy agent. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8(19):12082–12090
Gao S, Zhou H, Cui S, Shen H (2018) Bottom-up synthesis of MoS2 nanospheres for photothermal treatment of tumors. Photochem Photobiol Sci 17(10):1337–1345
Yu B, Wang C (2020) Tunable synthesis of mesoporous prussian blue@calcium phosphate nanoparticles for synergic chemo-photothermal cancer therapy. ChemistrySelect 5(35):10841–10847
Tang Z, Miao Y, Zhao J, Xiao H, Zhang M, Liu K, Zhang X, Huang L, Chen L, Wu H (2021) Mussel-inspired biocompatible polydopamine/carboxymethyl cellulose/polyacrylic acid adhesive hydrogels with UV-shielding capacity. Cellulose 28(3):1527–1540
Cai X, Jia X, Gao W, Zhang K, Ma M, Wang S, Zheng Y, Shi J, Chen H (2015) A versatile nanotheranostic agent for efficient dual-mode imaging guided synergistic chemo-thermal tumor therapy. Adv Funct Mater 25(17):2520–2529
Tsai Y-C, Vijayaraghavan P, Chiang W-H, Chen H-H, Liu T-I, Shen M-Y, Omoto A, Kamimura M, Soga K, Chiu H-C (2018) Targeted delivery of functionalized upconversion nanoparticles for externally triggered photothermal/photodynamic therapies of brain glioblastoma. Theranostics 8(5):1435
Funding
This study was funded by Key cultivation projects of Gastroenterology, SHBY201904 (Yangbei Zhu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Yaroslava Yingling.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Zhang, Y., Wu, H. et al. An oxidative polymerized carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel for the combined anti-tumor recurrence. J Mater Sci 58, 369–382 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-08046-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-08046-2