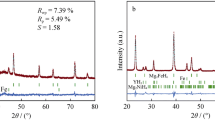
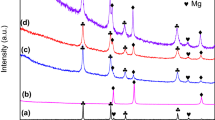
Abstract
The thermodynamics and kinetics of hydrogen absorption–desorption of nfTa2O5–Mg–MgH2—composite (nf stands for nano-flakes) have been studied. The nfTa2O5–Mg composite could absorb hydrogen at room temperature (17 °C). The hydrogen desorption of nfTa2O5–MgH2 composite starts at 200 °C. The remarkably improved hydrogen absorption–desorption of catalyzed Mg–MgH2 could be attributed to the nano-engineered surface by nfTa2O5. The enthalpies of hydrogen absorption–desorption were found to be 80 ± 2, and 76 ± 3 kJ/mol respectively. The activation energy of hydrogen absorption was evaluated as 49 ± 5 kJ/mol which is same as the energy barrier for diffusion of hydrogen in Mg matrix. The apparent activation of hydrogen desorption of nfTa2O5–MgH2 was found to be 74 ± 7 kJ/mol. The nfTa2O5–MgH2 composite has shown cyclic stability up to fifty hydrogen absorption–desorption without significant changes in the kinetics and hydrogen storage capacity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pacesila M, Burcea SG, Colesca SE (2016) Analysis of renewable energies in European Union. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 56:156–170
Wang Y, Lu S, Zhou Z, Zhou W, Guo J, Lan Z (2017) Effect of a transition metal on the hydrogen storage properties Mg–Al alloy. J Mater Sci 52:2392–2399. doi:10.1007/s10853-016-0533-0
Taxak M, Kumar S, Sheelvantra S, Krishnamurthy N (2014) Effect of iron on the solubility of hydrogen in tantalum. J Mater Sci 49:8471–8477. doi:10.1007/s10853-014-8557-9
Zhevago NK (2016) Other methods of the physical storage of hydrogen. Compend Hydrogen Energy 82:189–218
Matysik P, Czujko T, Varin RA (2014) The application of Pettifor structure maps to binary metal hydrides. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:398–405
Kumar S, Tiwari GP, Sagar S, Jain U, Krishnamurthy N (2014) High-performance FeTi-3.1 mass% V alloy for onboard hydrogen storage solution. Energy 75:520–524
Taxak M, Kumar S, Krishnamurthy N (2013) Thermodynamic parameters for the Ta–Cr–H solid solution from equilibrium P–C–T data. J Chem Thermodyn 67:48–54
Kumar S, Tirpude A, Taxak M, Krishnamurthy N (2013) Hydrogen absorption kinetics in powdered V + 80 wt%LaNi5 composite. J Alloys Compd 580:S179–S182
Akiba E (1999) Hydrogen absorbing alloys. Curr Opin Solid Mater Sci 4:267–272
Zuttel A (2004) Hydrogen storage methods. Naturwissenschaften 91:157–172
Zuttel A (2013) Materials for hydrogen storage. Mater Today 6:24–33
Wang H, Lin HJ, Cai WT, Ouyang LZ, Zhu M (2016) Tuning kinetics and thermodynamics of hydrogen storage in light metal element systems—A review of recent progress. J Alloys Compd 658:280–300
Lu J, Choi YJ, Fang ZZ, Sohn HY, Rönnebro E (2010) Hydrogenation of nanocrystalline Mg at room temperature in the presence of TiH2. J Am Chem Soc 132:6616–6617
Eli G, Maya S, Tony S et al (2014) Hydrogen sorption properties of 90 wt% MgH2–10 wt% MeSi2 (Me = Ti, Cr). J Mater Sci 49:2647–2652. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7969-2
Lototskyy M, Yartys VA (2015) Comparative analysis of the efficiencies of hydrogen storage systems utilizing solid state H storage materials. J Alloys Compd 645:S365–S373
Bobet JL, Hhevalier B (2004) Hydrogen Storage Properties of Mg-based mixture elaborated by reactive mechanical grinding. J Mater Sci 39:5243–5246. doi:10.1023/B:JMSC.0000039219.04507.6f
Matar SF (2010) Intermetallic hydrides: a review with ab initio aspects. Prog Solid State Chem 38:1–37
Webb CJ (2015) A review of catalyst-enhanced magnesium hydride as a hydrogen storage materials. J Phys Chem Solids 84:96–106
Aguey-Zinsou KF, Ares Fernadez JR, Klassen T, Borman R (2007) Effect of Nb2O5 on MgH2 properties during mechanical milling. Int J Hydrogen Energy 32:2400–2407
Barkhoradarian G, Klassen T, Bormann R (2003) Fast hydrogen sorption kinetics of nanocrystalline Mg using Nb2O5 as Catalyst. Scr Mater 49:213–217
Stephen DH, John JV, Chai R, Angus AR, Ian MR (2015) Effect of ball milling duration and dehydrogenation on the morphology, microstructure and catalyst dispersion in Ni-catalyzed MgH2 hydrogen storage materials. Acta Mater 86:55–68
Imamura H, Tanaka K, Kitazawa I, Sumi T, Sakata Y, Nakayama N, Ooshima S (2009) Hydrogen storage properties of nanocrystalline MgH 2 and MgH 2/Sn nanocomposite synthesized by ball milling. J Alloys Compd 484:939–942
Kecik D, Aydinol MK (2009) Density functional and dynamics study of the dissociative adsorption of hydrogen on Mg (0001) surface. Surf Sci 603:304–310
Mamula BP, Novaković JG, Radisavljević I, Ivanović N, Novaković N (2014) Electronic structure and charge distribution topology of MgH 2 doped with 3d transition metals. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:5874–5887
Pozzo M, Alfe M (2009) Hydrogen dissociation and diffusion on transition metal (Ti, Zr, V, Fe, Ru Co, Rh, Ni, Pd, Cu, Ag)-doped Mg (00001) surfaces. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:1922–1930
Guo L, Yang Y (2013) Theoretical investigation of hydrogen molecular absorption and dissociation on AlnV (n = 1–13) clusters. Int J Hydrogen Energy 38:3640–3649
Germanand E, Gebauer R (2016) Improvement of hydrogen vacancy diffusion kinetics in MgH2 by niobium- and zirconium-doping for hydrogen storage applications. J Phys Chem C 120(9):4806–4812. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b12092
Leng H, Pan Y, Li Q, Chou KC (2014) Effect of LiH on hydrogen storage property of MgH2. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:13622–13627
Chen BH, Chuang YS, Cha-o-Kuang C (2016) Improving the hydrogenation properties of MgH2 at room temperature by doping with nano-size ZrO2 catalyst. J Alloys Compd 655:21–27
Malka IE, Czujko T, Bystrzycki J (2010) The Catalytic effect of halide additives ball milled with magnesium hydride. Int J of Hydrogen Energy 35:1706–1712
Krishnamurthy N, Kumar S, Awasthi A (2009) Preparation of binary alloys of refractory metals by co-reduction: group V metals alloys. In: Proceedings of International Symposium 17th PLANSEE, (Plansee-17), Austria 2009, vol 1, RM30/1-RM30/10, pp 1–10
Tien HY, Tanniru M, Wu CY, Ebrahimi F (2009) Effect of hydride nucleation rate on the hydrogen capacity of Mg. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:6343–6349
Kumar S, Tiwari GP, Krishnamurthy N (2015) Tailoring the hydrogen desorption thermodynamics of V2H by alloying additives. J Alloys Compounds 645(2015):S252–S256
Kumar S, Taxak M, Krishnamurthy N (2013) Synthesis and hydrogen absorption in V4Ti4Cr alloy. J Therm Anal Calorim 112(1):51–57
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledged the useful technical discussions with Professor N. Krishnamurthy, of Bhabha Atomic Research Centre and Professor D.K Ross of Salford University-Manchester, UK. The authors appreciate the keen interest and motivation shown by Professor G. K Dey, Director Materials Group during the investigations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest for this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Tiwari, G.P. Thermodynamics and kinetics of MgH2–nfTa2O5 composite for reversible hydrogen storage application. J Mater Sci 52, 6962–6968 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0928-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0928-6