Abstract
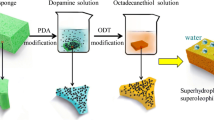
The development of a convenient method for oil-removal is of great significance for environmental protection. Here, we present a simple method for the removal of oils from water surface based on sponges that we fabricated by solution-immersion processes. The sponges exhibited high selectivity and absorption capacities for various kinds of oils when they were employed as absorptive materials. More importantly, the superhydrophobic sponge could be sustained 400 cycles of compressing test without losing their superhydrophobicity, exhibiting the high elasticity, robustness, and durability. To extend application field, superhydrophobic filter paper was used for oil–water separation. Interestingly, tunable wettability was received when oleophobic silica was employed instead of hydrophobic silica. We expected that this low-cost process can be used for oil-spill cleanup.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Su FH, Yao K (2014) Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic surface with excellent mechanical abrasion and corrosion resistance on copper substrate by a novel method. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:8762–8770
Liu CS, Su FH, Liang JZ (2014) Facile fabrication of a robust and corrosion resistant superhydrophobic aluminum alloy surface by a novel method. RSC Adv 4:55556–55564
Kwon G, Kota AK, Li YX, Sohani A, Mabry JM, Tuteja A (2012) On demand separation of oil-water mixtures. Adv Mater 24:3666–3671
Feng L, Zhang ZY, Mai ZH, Ma YM, Liu BQ, Jiang L, Zhu DB (2004) A super-hydrophobic and super-oleophilic coating mesh film for the separation of oil and water. Angew Chem 116:2046–2048
Nguyen DD, Tai NH, Lee SB, Kuo WS (2012) Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties of graphene-based sponges fabricated using a facile dip coating method. Energy Environ Sci 5:7908–7912
Cong HP, Ren XC, Wang P, Yu SH (2012) Macroscopic multifunctional graphene-based hydrogels and aerogels by a metal ion induced self-assembly process. ACS Nano 6:2693–2703
Dong XC, Chen J, Ma YW, Wang J, Chan-Park MB, Liu XM, Wang LH, Huang W, Chen P (2012) Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic hybrid foam of graphene and carbon nanotube for selective removal of oils or organic solvents from the surface of water. Chem Commun 48:10660–10662
Fuertes AB, Marban G, Nevskaia DM (2003) Adsorption of volatile organic compounds by means of activated carbon fibre-based monoliths. Carbon 41:87–96
Adebajo MO, Frost RL, Kloprogge JT, Carmody O, Kokot S (2003) Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: A review of synthesis and absorbing properties. J Porous Mater 10:159–170
Deschamps G, Caruel H, Borredon ME, Bonnin C, Vignoles C (2003) Oil removal from water by selective sorption on hydrophobic cotton fibers. 1. Study of sorption properties and comparison with other cotton fiber-based sorbents. Environ Sci Technol 37:1013–1015
Yuan JK, Liu XG, Akbulut O, Hu JQ, Suib SL, Kong J, Stellacci F (2008) Superwetting nanowire membranes for selective absorption. Nat Nanotechnol 3:332–336
Chu Y, Pan QM (2012) Three-dimensionally macroporous Fe/C nanocomposites as highly selective oil-absorption materials. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 4:2420–2425
Jiang GH, Hu RB, Xi XG, Wang XH, Wang RJ (2013) Facile preparation of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic sponge for fast removal of oils from water surface. J Mater Res 28:651–656
Sun H, Li A, Zhu Z, Liang W, Zhao X, La P, Deng W (2013) Superhydrophobic activated carbon-coated sponges for separation and absorption. ChemSusChem 6:1057–1062
Gui XC, Wei JQ, Wang KL, Cao AY, Zhu HW, Jia Y, Shu QK, Wu DH (2010) Carbon nanotube sponges. Adv Mater 22:617–621
Hu H, Zhao ZB, Wan WB, Gogotsi Y, Qiu JS (2013) Ultralight and highly compressible graphene aerogels. Adv Mater 25:2219–2223
Xiao N, Ling Z, Zhou Y, Qiu JS (2013) Synthesis and structure of carbon belts made of carbon nanofibers supported on carbon foams. Carbon 61:386–394
Xiao N, Zhou Y, Ling Z, Qiu JS (2013) Synthesis of a carbon nanofiber/carbon foam composite from coal liquefaction residue for the separation of oil and water. Carbon 59:530–536
Hu H, Zhao ZB, Wan WB, Gogotsi Y, Qiu JS (2014) Polymer/graphene hybrid aerogel with high compressibility, conductivity, and “sticky” superhydrophobicity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:3242–3249
Tao SY, Wang YC, Shi D, An YL, Qiu JS, Zhao YS, Cao Y, Zhang XF (2014) Facile synthesis of highly graphitized porous carbon monoliths with a balance on crystallization and pore-structure. J Mater Chem A 2:12785–12791
Hu H, Zhao ZB, Gogotsi Y, Qiu JS (2014) Compressible carbon nanotube-graphene hybrid aerogels with superhydrophobicity and superoleophilicity for oil sorption. Environ Sci Technol Lett 1:214–220
Li R, Chen CB, Li J, Xu LM, Xiao GY, Yan DY (2014) A facile approach to superhydrophobic and superoleophilic graphene/polymer aerogels. J Mater Chem A 2:3057–3064
Wu C, Huang XY, Wu XF, Qian R, Jiang PK (2013) Mechanically flexible and multifunctional polymer-based graphene foams for elastic conductors and oil-water separators. Adv Mater 25:5658–5662
Zhu Q, Pan QM, Liu FT (2011) Facile removal and collection of oils from water surfaces through superhydrophobic and superoleophilic sponges. J Phys Chem C 115:17464–17470
Calcagnile P, Fragouli D, Bayer IS, Anyfantis GC, Martiradonna L, Cozzoli PD, Cingolani R, Athanassiou A (2012) Magnetically driven floating foams for the removal of oil contaminants from water. ACS Nano 6:5413–5419
Ge B, Zhang ZZ, Men XH, Zhu XT, Zhou XY (2014) Sprayed superamphiphobic coatings on copper substrate with enhanced corrosive resistance. Appl surface sci 293:271–274
Cassie ABD, Baxter S (1944) Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans Faraday Soc 40:546–551
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51335010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, B., Men, X., Zhu, X. et al. A superhydrophobic monolithic material with tunable wettability for oil and water separation. J Mater Sci 50, 2365–2369 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8756-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8756-4