Abstract
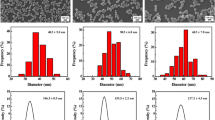
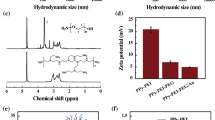
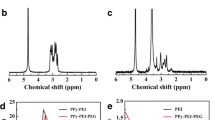
PPY nanoparticles, as one of the important organic photothermal agents has been attracted great attention due to their good biocompatibility, high photothermal efficiency, and low cost. In order to further evaluate the size-dependent photothermal effect, PPY nanoparticles with two different sizes have been prepared with a facile method. The near infrared absorption and photothermal effect of the two size PPY nanoparticles were compared. The PPY nanoparticle with small size shows better photothermal effect at the same condition. The photostability, stability, and cytotoxicity in biologic system have also been investigated. In addition, the PPY nanoparticles with small size can kill the cancer cells effectively under the irradiation of 808 nm laser with a low-power density. These findings may provide better information for the application of the PPY nanoparticles on the photothermal ablation of cancer cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Tian Q, Jiang F, Zou R, Liu Q, Chen Z, Zhu M, Yang S, Wang J, Wang J, Hu J (2011) Hydrophilic Cu9S5 nanocrystals: a photothermal agent with a 25.7 % heat conversion efficiency for photothermal ablation of cancer cells in vivo. ACS Nano 5:9761–9771
Chen WR, Adams RL, Carubelli R, Nordquist RE (1997) Laser-photosensitizer assisted immunotherapy: a novel modality for cancer treatment. Cancer Lett 115:25–30
Skrabalak SE, Chen J, Au L, Lu X, Li X, Xia Y (2007) Gold nanocages for biomedical applications. Adv Mater 19:3177–3184
Huang X, Tang S, Mu X, Dai Y, Chen G, Zhou Z, Ruan F, Yang Z, Zheng N (2011) Freestanding palladium nanosheets with plasmonic and catalytic properties. Nat Nano 6:28–32
Xu R, Ma J, Sun X, Chen Z, Jiang X, Guo Z, Huang L, Li Y, Wang M, Wang C, Liu J, Fan X, Gu J, Chen X, Zhang Y, Gu N (2009) Ag nanoparticles sensitize IR-induced killing of cancer cells. Cell Res 19:1031–1034
Hessel CM, Pattani VP, Rasch M, Panthani MG, Koo B, Tunnell JW, Korgel BA (2011) Copper selenide nanocrystals for photothermal therapy. Nano Lett 11:2560–2566
Robinson JT, Tabakman SM, Liang Y, Wang H, Sanchez Casalongue H, Vinh D, Dai H (2011) Ultrasmall reduced graphene oxide with high near-infrared absorbance for photothermal therapy. J Am Chem Soc 133:6825–6831
Yang K, Zhang S, Zhang G, Sun X, Lee S-T, Liu Z (2010) Graphene in mice: ultrahigh in vivo tumor uptake and efficient photothermal therapy. Nano Lett 10:3318–3323
Zha Z, Yue X, Ren Q, Dai Z (2013) Uniform polypyrrole nanoparticles with high photothermal conversion efficiency for photothermal ablation of cancer cells. Adv Mater 25:777–782
Chen M, Fang X, Tang S, Zheng N (2012) Polypyrrole nanoparticles for high-performance in vivo near-infrared photothermal cancer therapy. Chem Commun 48:8934–8936
Yang K, Xu H, Cheng L, Sun C, Wang J, Liu Z (2012) In vitro and in vivo near-infrared photothermal therapy of cancer using polypyrrole organic nanoparticles. Adv Mater 24:5586–5592
Kim S, Oh W-K, Jeong YS, Hong J-Y, Cho B-R, Hahn J-S, Jang J (2011) Cytotoxicity of, and innate immune response to, size-controlled polypyrrole nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Biomaterials 32:2342–2350
Roper DK, Ahn W, Hoepfner M (2007) Microscale heat transfer transduced by surface plasmon resonant gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 111:3636–3641
Tian Q, Hu J, Zhu Y, Zou R, Chen Z, Yang S, Li R, Su Q, Han Y, Liu X (2013) Sub-10 nm Fe3O4@Cu2–xS core–shell nanoparticles for dual-modal imaging and photothermal therapy. J Am Chem Soc 135:8571–8577
Tian Q, Tang M, Sun Y, Zou R, Chen Z, Zhu M, Yang S, Wang J, Wang J, Hu J (2011) Hydrophilic flower-like CuS superstructures as an efficient 980 nm laser-driven photothermal agent for ablation of cancer cells. Adv Mater 23:3542–3547
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the Shanghai Municipal Nature Science Foundation (Grant No. 13ZR1433300), the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology, China (Grant No. 11JC1410400), the Shanghai Jiao Tong University Biomedical Engineering (Physical) Crossover Foundation (Grant No. YG2011MS57), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21171035 and 51302035), the Key Grant Project of Chinese Ministry of Education (Grant No. 313015), the PhD Programs Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (Grant Nos. 20110075110008 and 20130075120001), the National 863 Program of China (Grant No. 2013AA031903), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No. 13ZR1451200), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (Grant No. IRT1221), the Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (Grant No. B603), and the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (No. 111-2-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wang, J., Lv, G. et al. Facile synthesis of hydrophilic polypyrrole nanoparticles for photothermal cancer therapy. J Mater Sci 49, 3484–3490 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8061-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8061-2