Abstract
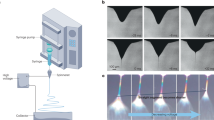
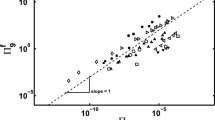
This work explores how in electrospinning, mass deposition rate and electric current relate to applied voltage and electrode separation, factors giving a range of applied electric fields. Mass deposition rate was measured by quantifying the rate of dry fibre deposited over time. Electric current was measured using a current feedback from the high voltage supply. The deposition of fibre was observed to occur at a constant rate for deposition times of up to 30 min. Both the mass deposition rate and electric current were found to vary with the applied voltage according to a power law. The relationship between the electric current and mass deposition rate was found to be linear for all combinations of applied voltage and electrode separation. This means that for all combinations of applied voltage and electrode separation, hence for all applied electric field conditions, there is a constant charge density of 96.1 C/kg for poly(vinyl alcohol).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramakrishna S, Fujihara K, Teo W, Lim T, Ma Z (2006) An introduction to electrospinning and nanofibers. World Scientific, Singapore
Doshi J, Reneker DH (1995) J Electrost 35:151
Reznik SN, Yarin AL, Theron A, Zussman E (2004) J Fluid Mech 516:349
Reneker DH, Yarin AL, Fong H, Koombhongse S (2000) J Appl Phys 87(9):4531
Patra SN, Lin RJT, Bhattacharyya D (2010) J Mater Sci 45(14):3938. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4459-7
Zhang S, Shim W, Kim J (2009) Mater Des 30(9):3659
Stanger J (2008) Charge transfer mechanisms in electrospinning. University of Canterbury, Christchurch
Demir MM, Yilgor I, Yilgor E, Erman B (2002) Polymer 43(11):3303
Theron SA, Zussman E, Yarin AL (2004) Polymer 45:2017
Fallahi D, Rafizadeh M, Mohammadi N, Vahidi B (2008) Polym Int 57(12):1363
Tripatanasuwan S, Reneker DH (2009) Polymer 50(8):1835
Yarin AL, Koombhongse S, Reneker DH (2001) J Appl Phys 89(5):3018
Kowalewski TA, Barral S, Kowalczyk T (2005) Bull Pol Acad Sci: Tech Sci 53(4):385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanger, J., Tucker, N., Fullick, S. et al. Insights into the power law relationships that describe mass deposition rates during electrospinning. J Mater Sci 47, 1113–1118 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5959-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5959-9