Abstract
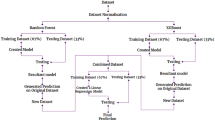
Mould level fluctuation (MLF) is one of the main reasons for surface defects in continuously cast slabs. In these study first, large scale mould level fluctuations has been categorized in three different cases based on actual plant data. Moreover, theoretical formulation has been investigated to better understand the underlying physics of flow. Next, exploratory data analysis is used for preliminary investigation into the phenomenon based on actual plant data. Finally, different classification algorithms were used to classify non-mould level fluctuation cases from MLF cases for two different scenarios- one where all mould level fluctuation cases are considered and in another where only a particular case of mould level fluctuation is considered. Classification algorithm such as recursive partitioning, random forest etc. has been used to identify different casting parameters affecting the phenomenon of mould level fluctuation. 70 % of the dataset used as training dataset and rest 30 % as the testing dataset. Prediction accuracy of these different classification algorithms along with an ensemble model has been compared on a completely unseen test set. Ladle change operation and superheat temperature has been identified as process parameters influencing the phenomenon of large scale mould level fluctuations.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, C., Liaw, A., & Breiman, L. (2004). Using Random Forest to learn imbalanced data. Berkeley: Department of Statistics, University of California. 12.
Colla, V., Matarese, N., & Nastasi, G. (2011). Prediction of under pickling defects on steel strip surface. International Journal of Soft Computing and Software Engineering, 1(1), 9–17. doi:10.7321/jscse.v1.n1.2.
de Beer, P. G., & Craig, K. J. (2008). Continuous cast width control using a data mining approach. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 35(3), 213–220. doi:10.1179/030192307X233052.
Furtmueller, C., del Re, L., Bramerdorfer, H., & Moerwald, K. (2005). Periodic disturbance suppression in a steel plant with unstable internal feedback and delay. In Proceedings of 5th international conference on technology and automation, ICTA (vol. 5, pp. 1–6).
Galili, T. (2015). dendextend: an R package for visualizing, adjusting, and comparing trees of hierarchical clustering. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 31(22), 3718–3720. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv428.
Girase, N. U., Basu, S., & Choudhary, S. K. (2007). Development of indices for quantification of nozzle clogging during continuous slab casting. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 34(6), 506–512. doi:10.1179/174328107X168075.
Gursoy, K. A. (2014). Quantifying the effect of flow rate controllers on liquid steel flow in continuous casting mold using CFD modeling. Middle East Technical University.
Hajari, A., & Meratian, M. (2010). Surface turbulence in a physical model of a steel thin slab continuous caster. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 17(6), 697–703. doi:10.1007/s12613-010-0376-7.
Javurek, M. (2008). Lingotamento Continuo-Continuous Casting.png. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lingotamento_Continuo-Continuous_Casting.png.
Kant, S., Jha, P. K., & Kumar, P. (2013). Investigation of effect of dam on intermixing during ladle changeover in six strand billet caster tundish. Ironmaking & Steelmaking. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1179/1743281211Y.0000000007#.VtQQ6Pl97cc. Accessed 29 February 2016.
Kumar, D. S., Rajendra, T., Sarkar, A., Karande, A. K., & Yadav, U. S. (2007). Slab quality improvement by controlling mould fluid flow. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 34(2), 185–191. doi:10.1179/174328107X155330.
Lee, P. D., Ramirez-Lopez, P. E., Mills, K. C., & Santillana, B. (2012). Review: The “butterfly effect” in continuous casting. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 39(4), 244–253. doi:10.1179/0301923312Z.00000000062.
Liaw, A., & Wiener, M. (2002). Classification and regression by randomForest. R News, 2(3), 18–22. http://cran.r-project.org/doc/Rnews/
Liu, R., Sengupta, J., Crosbie, D., Yavuz, M. M., & Thomas, B. G. (2011). Effects of stopper rod movement on mold fluid flow at ArcelorMittal Dofasco’s No. 1 continuous Caster AISTech 2011 proceedings (vol I(1), pp. 1619–1631).
Liu, R., Thomas, B. G., Kalra, L., Bhattacharya, T., & Dasgupta, A. (2013). Slidegate dithering effects on transient flow and mold level fluctuations. In AISTech 2013 proceedings (pp. 1351–1364).
Liu, R., Thomas, B. G., & Sengupta, J. (2012). Simulation of transient fluid flow in mold region during steel continuous casting. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 33, 012015. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/33/1/012015.
Matsumiya, T. (2006). Recent topics of research and development in continuous casting. ISIJ International, 46(12), 1800–1804. doi:10.2355/isijinternational.46.1800.
Nastasi, G., Colla, V., Cateni, S., & Campigli, S. (2016). Implementation and comparison of algorithms for multi-objective optimization based on genetic algorithms applied to the management of an automated warehouse. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-016-1198-x.
Ordieres-Meré, J., Martínez-de-Pisón-Ascacibar, F. J., González-Marcos, A., & Ortiz-Marcos, I. (2008). Comparison of models created for the prediction of the mechanical properties of galvanized steel coils. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 21(4), 403–421. doi:10.1007/s10845-008-0189-y.
R Core Team. (2014). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria. http://www.r-project.org/
Rackers, K. G. & Thomas, B. G. (1995). Clogging in continuous casting nozzles. In: 78th steelmaking conference proceedings (vol. 78, pp. 723–734).
Ridgeway, G. (2015). gbm: Generalized boosted regression models. https://cran.r-project.org/package=gbm
Sharafi, S. M., & Esmaeily, H. R. (2010). Applying data mining methods to predict defects on steel surface. Journal of Theoretical & Applied Information Technology, 20, 87–92.
Shaver, J. W. (2002). Measurement of metal/slag interfacial phenomena in thin slab caster. Retrieved from http://ccc.illinois.edu/PDFFiles/Theses/2002_SHAVER_Joseph_MSThesis.pdf.
Singh, A. K., Pardeshi, R., & Goyal, S. (2011). Integrated modeling of tundish and continuous caster to meet quality requirements of cast steels. In Proceedings of the first world congress on integrated computational materials engineering (vol. 1, pp. 81–85).
Singh, V., Ajmani, S. K., Pal, A. R., Singh, S. K., & Denys, M. B. (2012). Single strand continuous caster tundish furniture comparison for optimal performance. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 39(3), 171–179. doi:10.1179/1743281211Y.0000000065.
Suzuki, D. (2004). Formulation of mold level control model by molten steel flow analysis method. Nippon Steel Technical Report, 89, 46–49.
Tang, L., Liu, W., & Liu, J. (2005). A neural network model and algorithm for the hybrid flow shop scheduling problem in a dynamic environment. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 16(3), 361–370. doi:10.1007/s10845-005-7029-0.
Therneau, T., Atkinson, B., & Ripley, B. (2014). rpart: Recursive partitioning and regression trees. http://cran.r-project.org/package=rpart
Thomas, B. G. (2001). Continuous casting of steel. Modelling for Casting and Solidification Processing. doi:10.1049/sqj.1963.0042.
Thomas, B. G. (2013). Fluid flow in the mold (pp. 1–41). http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.503.5487&rep=rep1&type=pdf.
Torgo, L. (2010). Data mining with R, learning with case studies. London: Chapman and Hall/CRC. http://www.dcc.fc.up.pt/~ltorgo/DataMiningWithR
Wang, H., & Wu, K. (2003). Modeling and analysis for multi-period, multi-product and multi-resource production scheduling. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 14(3), 297–309. doi:10.1023/A:1024645608673.
Wehrens, R., & Buydens, L. M. C. (2007). Self- and super-organizing maps in R?: The kohonen package. Journal of Statistical Software, 21(5), 1–19. doi:10.18637/jss.v021.i05.
Zhang, L., Yang, S., Cai, K., Li, J., Wan, X., & Thomas, B. G. (2007). Investigation of fluid flow and steel cleanliness in the continuous casting strand. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B: Process Metallurgy and Materials Processing Science, 38(February), 63–83. doi:10.1007/s11663-006-9007-0.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the TSCR Caster Automation, Electrical and Operations team, for their support and expert guidance on the subject matter which greatly assisted in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha Roy, P.D., Tiwari, P.K. Knowledge discovery and predictive accuracy comparison of different classification algorithms for mould level fluctuation phenomenon in thin slab caster. J Intell Manuf 30, 241–254 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-016-1242-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-016-1242-x