Abstract
Purpose
Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation (AF) requires utilizing multiple venous femoral sheaths in conjunction with aggressive periprocedural anticoagulation, which can lead to increased risk of vascular access complications. The objective of this study is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the “figure-of-eight” (“F-8”) suture technique for femoral venous hemostasis while on therapeutic doses of intravenous anticoagulation at the time of sheath removal.
Methods
In this case-control analysis, 376 consecutive patients underwent AF ablation while on uninterrupted oral anticoagulation and received intraprocedural heparin. In the first 253 patients (the control group), manual pressure was used for femoral venous hemostasis after reversal of heparin effects. The subsequent 123 patients (the F-8 group) had femoral venous hemostasis using the F-8 suture technique and while under therapeutic heparin effects.
Results
The F-8 subcutaneous suture technique achieved adequate venous hemostasis in 98.4 % of patients. As compared to the control group, there was significantly less frequent utilization of the FemoStop compression assist device (1.2 vs. 16.8 %, p < 0.0001) and in a significantly shorter interval (6.8 ± 5.7 vs. 50.7 ± 12.2 min, p < 0.0001). Vascular access complications and thromboembolic events occurred in 9.8 % in the F-8 group vs. 13.0 % in the control group (p = 0.678).
Conclusions
Immediate hemostasis of the femoral venous access sites after insertion of multiple sheaths for AF ablation in the presence of anticoagulation can be safely and effectively achieved using the F-8 suture technique. This technique helps minimize the period of inadequate anticoagulation immediately following ablation and shortens the time required to achieve adequate hemostasis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deshmukh, A., Patel, N. J., Pant, S., Shah, N., Chothani, A., Mehta, K., Grover, P., et al. (2013). In-hospital complications associated with catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in the United States between 2000 and 2010: analysis of 93 801 procedures. Circulation, 128(19), 2104–2112.
Issa, Z. F., Miller, J. M., & Zipes, D. P. (2012). Atrial fibrillation. In Z. F. Issa, J. M. Miller, & D. P. Zipes (Eds.), Clinical arrhythmology and electrophysiology: a companion to Braunwald’s heart disease (2nd ed., pp. 290–374). Philadelphia: Saunders.
Gopinath, D., Lewis, W. R., Di Biase, L., & Natale, A. (2011). Pulmonary vein antrum isolation for atrial fibrillation on therapeutic coumadin: special considerations. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22(2), 236–239.
Bassiouny, M., Saliba, W., Rickard, J., Shao, M., Sey, A., Diab, M., Martin, D. O., et al. (2013). Use of dabigatran for periprocedural anticoagulation in patients undergoing catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Circulation. Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology, 6(3), 460–466.
Lakkireddy, D., Reddy, Y. M., Di Biase, L., Vanga, S. R., Santangeli, P., Swarup, V., Pimentel, R., et al. (2012). Feasibility and safety of dabigatran versus warfarin for peri- procedural anticoagulation in patients undergoing radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation: results from a multicenter prospective registry. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 59, 1168–1174.
Ellis, E. R., Culler, S. D., Simon, A. W., & Reynolds, M. R. (2009). Trends in utilization and complications of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in Medicare beneficiaries. Heart Rhythm, 6(9), 1267–1273.
Page, S. P., Siddiqui, M. S., Finlay, M., Hunter, R. J., Abrams, D. J., Dhinoja, M., Earley, M. J., et al. (2011). Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation on uninterrupted warfarin: can it be done without echo guidance? Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22(3), 265–270.
Wazni, O. M., Beheiry, S., Fahmy, T., Barrett, C., Hao, S., Patel, D., Di Biase, L., et al. (2007). Atrial fibrillation ablation in patients with therapeutic inter-national normalized ratio: comparison of strategies of anticoagulation management in the periprocedural period. Circulation, 116, 2531–2534.
Gautam, S., John, R. M., Stevenson, W. G., Jain, R., Epstein, L. M., Tedrow, U., Koplan, B. A., et al. (2011). Effect of therapeutic INR on activated clotting times, heparin dosage, and bleeding risk during ablation of atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22(3), 248–254.
Ozawa, A., Chaturvedi, R., Lee, K. J., & Benson, L. (2007). Femoral vein hemostasis in children using a suture-mediated closure device. Journal of Interventional Cardiology, 20(2), 164–167.
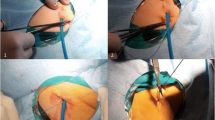
Cilingiroglu, M., Salinger, M., Zhao, D., & Feldman, T. (2011). Technique of temporary subcutaneous “Figure-of-Eight” sutures to achieve hemostasis after removal of large-caliber femoral venous sheaths. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 78(1), 155–160.
Morgan, G. J., Waragai, T., Eastaugh, L., Chaturvedi, R. C., Lee, K. J., & Benson, L. (2012). The fellows stitch: large caliber venous hemostasis in pediatric practice. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 80(1), 79–82.
Mehmet, C., Michael, S., Zhao, D., & Feldman, T. (2011). Technique of temporary subcutaneous “figure-of-eight” sutures to achieve hemostasis after removal of large- caliber femoral venous sheaths. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 78, 155–160.
Bagai J., Zhao D. (2008). Subcutaneous “figure-of-eight” stitch to achieve hemostasis after removal of large- caliber femoral venous sheaths. Cardiac Interventions Today. 22–23.
Zhou, Y., Guo, Z., Bai, Y., Zhao, X., Qin, Y., Chen, S., Wu, H., et al. (2014). Femoral venous hemostasis in children using the technique of “figure-of-eight” sutures. Congenital Heart Disease, 9(2), 122–125.
Hamid, T., Rajagopal, R., Pius, C., Clarke, B., & Mahadevan, V. S. (2013). Preclosure of large-sized venous access sites in adults undergoing transcatheter structural interventions. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 81(4), 586–590.
Mahadevan, V. S., Jimeno, S., Benson, L. N., McLaughlin, P. R., & Horlick, E. M. (2008). Pre-closure of femoral venous access sites used for large-sized sheath insertion with the Perclose device in adults undergoing cardiac intervention. Heart, 94, 571–572.
Mylonas, I., Sakata, Y., Salinger, M., Sanborn, T. A., & Feldman, T. (2006). The use of percutaneous suture-mediated closure for the management of 14 French femoral venous access. Journal of Invasive Cardiology, 18, 299–302.
Shaw, J. A., Dewire, E., Nugent, A., & Eisenhauer, A. C. (2004). Use of suture-mediated vascular closure devices for the management of femoral vein access after transcatheter procedures. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 63, 439–443.
Coto, H. A. (2002). Closure of the femoral vein puncture site after transcatheter procedures using Angio-Seal. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 55, 16–19.
Tanaka-Esposito, C. C., Chung, M. K., Abraham, J. M., Cantillon, D. J., Abi-Saleh, B., & Tchou, P. J. (2013). Real-time ultrasound guidance reduces total and major vascular complications in patients undergoing pulmonary vein antral isolation on therapeutic warfarin. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 37(2), 163–168.
Disclosures
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
(MPG 40282 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Issa, Z.F., Amr, B.S. Venous hemostasis postcatheter ablation of atrial fibrillation while under therapeutic levels of oral and intravenous anticoagulation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 44, 97–104 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-015-0036-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-015-0036-y