Abstract
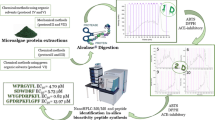
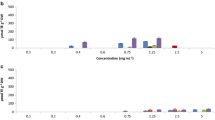
The genus Caulerpa consists of over than 100 members. This genus is famous because of its invasive members in the Mediterranean Sea. Although many eradication methods have been applied on these seaweeds, no validated method exists in the literature on these aliens. Research on the biotechnological utilization of these seaweeds are limited. This paper proposes an alternative in silico evaluation method for identifying possible utilization of these seaweeds. In the present study, bioactive peptides in the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) of 28 Caulerpa species were investigated by using in silico tools. According to the results, RuBisCO in Caulerpa cylindracea, Caulerpa taxifolia, Caulerpa racemosa var. lamourouxii, and Caulerpa racemosa f. occidentalis showed the best potential for bioactive peptides. In conclusion, exotic alien Caulerpa genus members could be evaluated in the food industry as alternative sources of bioactive peptides instead of attempting eradication methods.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa M, Valentão P, Andrade PB (2014) Bioactive compounds from macroalgae in the new millennium: implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Mar Drugs 12:4934–4972
Belton GS, Reine WF, Huisman JM, Draisma SG, Gurgel D, Frederico C (2014) Resolving phenotypic plasticity and species designation in the morphologically challenging Caulerpa racemosa–peltata Complex (Chlorophyta, Caulerpaceae). J Phycol 50:32–54
Cavazos A, de Mejia EG (2013) Identification of bioactive peptides from cereal storage proteins and their potential role in prevention of chronic diseases. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 12:364–380
Cengiz S, Cavas L, Yurdakoc K (2010) Alpha-amylase inhibition kinetics by caulerpenyne. Med Mar Sci 11:93–104
Cengiz S, Cavas L, Yurdakoc K, Pohnert G (2011) The sesquiterpene caulerpenyne from Caulerpa spp. is a lipoxygenase inhibitor. Mar Biotechnol 13:321–326
Cheung IW, Nakayama S, Hsu MN, Samaranayaka AG, Li-Chan EC (2009) Angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory activity of hydrolysates from oat (Avena sativa) proteins by in silico and in vitro analyses. J Agr Food Chem 57:9234–9242
Desiere F, German B, Watzke H, Pfeifer A, Saguy S (2001) Bioinformatics and data knowledge: the new frontiers for nutrition and foods. Trends Food Sci Tech 12:15–229
de Souza ET, de Lira DP, de Queiroz AC, da Silva DJ, de Aquino AB, Mella EA, Lorenzo VP, de Miranda GE, de Araújo-Júnior JX, Chaves MC, Barbosa-Filho JM, de Athayde-Filho PF, Santos BV, Alexandre-Moreira MS (2009) The antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of caulerpin, a bisindole alkaloid isolated from seaweeds of the genus Caulerpa. Mar Drugs 7:689–704
di Bernardini R, Mullen AM, Bolton D, Kerry J, O’Neill E, Hayes M (2012) Assessment of the angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE-I) inhibitory and antioxidant activities of hydrolysates of bovine brisket sarcoplasmic proteins produced by papain and characterisation of associated bioactive peptidic fractions. Meat Sci 90:226–235
Dumas M, Nadal-Wollbold F, Gaussem P, Perez M, Mirault T, Létienne R, Bourbon T, Grelac F, Le Grand B, Bachelot-Loza C (2012) Antiplatelet and antithrombotic effect of F 16618, a new thrombin proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR1) antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 165:1827–1835
Elias RJ, Kellerby SS, Decker EA (2008) Antioxidant activity of proteins and peptides. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 48:430–441
Fu Y, Wu W, Zhu M, Xiao Z (2015) In silico assessment of the potential of patatin as a precursor of bioactive peptides. J Food Biochem 40:366–370
García MC, Puchalska P, Esteve C, Marina ML (2013) Vegetable foods: a cheap source of proteins and peptides with antihypertensive, antioxidant, and other less occurrence bioactivities. Talanta 106:328–349
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, Ivanyi I, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2003) ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucl Acids Res 31:3784–3788
Gu Y, Majumder K, Wu J (2011) QSAR-aided in silico approach in evaluation of food proteins as precursors of ACE inhibitory peptides. Food Res Int 44:2465–2474
Algae Base. Caulerpa J.V. Lamouroux, 1809. http://www.algaebase.org/search/genus/detail/?genus id=bce5aa03b730bef59 Accessed 22 Jan 2015
Hegde AN, Upadhya SC (2011) Role of ubiquitin–proteasome-mediated proteolysis in nervous system disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1809:128–140
Holton TA, Vijayakumar V, Khaldi N (2013) Bioinformatics: current perspectives and future directions for food and nutritional research facilitated by a food-wiki database. Trends Food Sci Tech 34:5–17
Je JY, Cho YS, Gong M, Udenigwe CC (2015) Dipeptide Phe-Cys derived from in silico thermolysin-hydrolysed RuBisCO large subunit suppresses oxidative stress in cultured human hepatocytes. Food Chem 171:287–291
Juillerat-Jeanneret L (2013) Dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its inhibitors: therapeutics for type 2 diabetes and what else? J Med Chem 57:2197–2212
Kitts DD, Weiler K (2003) Bioactive proteins and peptides from food sources. Applications of bioprocesses used in isolation and recovery. Curr Pharm Des 9:1309–1323
Klein J, Verlaque M (2008) The Caulerpa racemosa invasion: a critical review. Mar Poll Bull 56:205–225
de Kloet AD, Krause EG, Woods SC (2010) The renin angiotensin system and the metabolic syndrome. Physiol Behav 100:525–534
Korhonen H, Pihlanto A (2006) Bioactive peptides: production and functionality. Int Dairy J 16:945–960
Kuda T, Ikemori T (2009) Minerals, polysaccharides and antioxidant properties of aqueous solutions obtained from macroalgal beach-casts in the Noto peninsula, Ishikawa, Japan. Food Chem 112:575–581
Kumar M, Gupta V, Kumari P, Reddy CRK, Jha B (2011) Assessment of nutrient composition and antioxidant potential of Caulerpaceae seaweeds. J Food Comp Anal 24:270–278
Lacroix IM, Li-Chan EC (2012) Evaluation of the potential of dietary proteins as precursors of dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-IV inhibitors by an in silico approach. J Funct Foods 4:403–422
Lafarga T, O’Connor P, Hayes M (2015) In silico methods to identify meat-derived prolyl endopeptidase inhibitors. Food Chem 175:337–343
Lafarga T, Aluko RE, Rai DK, O’Connor P, Hayes M (2016) Identification of bioactive peptides from a papain hydrolysate of bovine serum albumin and assessment of an antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Res Int 81:91–99
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Li GH, Le GW, Shi YH, Shrestha S (2004) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins and their physiological and pharmacological effects. Nutr Res 24:469–486
Lin HC, Chou ST, Chuang MY, Liao TY, Tsai WS, Chiu TH (2012) The effects of Caulerpa microphysa enzyme-digested extracts on ACE-inhibitory activity and in vitro anti-tumour properties. Food Chem 134:2235–2241
Liu DQ, Mao SC, Zhang HY, Yu XQ, Feng MT, Wang B, Feng LH, Guo YW (2013) Racemosins A and B, two novel bisindole alkaloids from the green alga Caulerpa racemosa. Fitoterapia 91:15–20
Long AN, Dagogo-Jack S (2011) Comorbidities of diabetes and hypertension: mechanisms and approach to target organ protection. J Clin Hypertens 13:244–251
Löw P (2011) The role of ubiquitin–proteasome system in ageing. Gen Comp Endocrinol 172:39–43
Majumder K, Wu J (2010) A new approach for identification of novel antihypertensive peptides from egg proteins by QSAR and bioinformatics. Food Res Int 43:1371–1378
Minkiewicz P, Dziuba J, Michalska J (2011) Bovine meat proteins as potential precursors of biologically active peptides—a computational study based on the BIOPEP database. Food Sci Technol Int 17:39–45
Minkiewicz P, Dziuba J, Iwaniak A, Dziuba M, Darewicz M (2008) BIOPEP database and other programs for processing bioactive peptide sequences. J AOAC Int 91:965–980
Mollo E, Cimino G, Ghiselin MT (2015) Alien biomolecules: a new challenge for natural product chemists. Biol Invasions 17:941–950
Mooney C, Haslam NJ, Pollastri G, Shields DC (2012) Towards the improved discovery and design of functional peptides: common features of diverse classes permit generalized prediction of bioactivity. PLoS One 7(10):e45012
Nelson DL, Cox MM (2008) Lehninger principles of biochemistry, 5th edn. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York (Chapter 20)
Nongonierma AB, Le Maux S, Dubrulle C, Barre C, FitzGerald RJ (2015) Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) protein hydrolysates with in vitro dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory and antioxidant properties. J Cereal Sci 65:112–118
Ryan JT, Ross RP, Bolton D, Fitzgerald GF, Stanton C (2011) Bioactive peptides from muscle sources: meat and fish. Nutrients 3:765–791
Richter P, Schubert G, Schaible AM, Cavas L, Werz O, Pohnert G (2014) Caulerpenyne and related bis-enol esters are novel-type inhibitors of human 5-lipoxygenase. ChemMedChem 9:1655–1659
Roberts PR, Burney JD, Black KW, Zaloga GP (1999) Effect of chain length on absorption of biologically active peptides from the gastrointestinal tract. Digestion 60:332–337
Sharma BR, Rhyu DY (2014) Anti-diabetic effects of Caulerpa lentillifera: stimulation of insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells and enhancement of glucose uptake in adipocytes. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 4:575–580
The UniProt Consortium (2011) Reorganizing the protein space at the universal protein resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res 40:D71–D75
Udenigwe CC, Gong M, Wu S (2013) In silico analysis of the large and small subunits of cereal RuBisCO as precursors of cryptic bioactive peptides. Process Biochem 48:1794–1799
Udenigwe CC (2014) Bioinformatics approaches, prospects and challenges of food bioactive peptide research. Trends Food Sci Tech 36:137–143
Verdecchia P, Angeli F, Mazzotta G, Gentile G, Reboldi G (2008) The renin angiotensin system in the development of cardiovascular disease: role of aliskiren in risk reduction. Vasc Health Risk Manag 4:971–981
Verlaque M, Durand C, Huisman JM, Boudouresque CF, Le Parco Y (2003) On the identity and origin of the Mediterranean invasive Caulerpa racemosa (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta). Eur J Phycol 38:325–339
Wang JS, Zhao MM, Zhao QZ, Jiang YM (2007) Antioxidant properties of papain hydrolysates of wheat gluten in different oxidation systems. Food Chem 101:1658–1663
Wilson J, Hayes M, Carney B (2011) Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme and prolyl endopeptidase inhibitory peptides from natural sources with a focus on marine processing by-products. Food Chem 129:235–244
Wostrikoff K, Stern DB (2009) Rubisco. In: The chlamydomonas source book, Stern DB, Harris E (eds), vol 2, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego p 302–332
Yang P, Liu DQ, Liang TJ, Li J, Zhang HY, Liu AH, Guo YW, Mao SC (2015) Bioactive constituents from the green alga Caulerpa racemosa. Bioorg Med Chem 23:38–45
Yang S, Yunden J, Sonoda S, Doyama N, Lipkowski AW, Kawamura Y, Yoshikawa M (2001) Rubiscolin, a δ selective opioid peptide derived from plant rubisco. FEBS Lett 509:213–217
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agirbasli, Z., Cavas, L. In silico evaluation of bioactive peptides from the green algae Caulerpa . J Appl Phycol 29, 1635–1646 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-1045-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-1045-7