Abstract
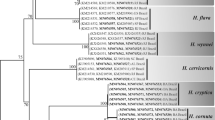
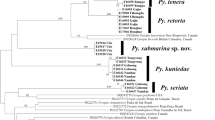
Hypnea musciformis, a red macroalga widely distributed in tropical and subtropical coasts around the world, has great economic importance as a source of carrageenan for industrial production. In this work, the DNA barcode marker COI-5P and the plastid rbcL gene, in addition to morphological studies, were used to investigate this species on the coast of Brazil and compare it with specimens from other countries. A total of 128 sequences were obtained in this study for 100 specimens from Brazil and 15 specimens from other countries, including the type locality in Italy. The divergence between South American sequences and sequences from Italy for H. musciformis was significantly high for both markers, indicating that the specimens found on the Brazilian coast belong to a different species. Considering the data gathered from molecular markers and morphological analysis, the specimens previously identified morphologically as “H. musciformis”, “H ypnea nigrescens”, and “Hypnea valentiae” collected in Brazil were considered morphological variations of the new species described in this paper, named Hypnea pseudomusciformis Nauer, Cassano & M.C. Oliveira, sp. nov. The identification of specimens based only on morphological characteristics proved to be unsatisfactory for reasons that could be attributed to phenotypic plasticity in this species. Thus, the technique of DNA barcoding, especially with respect to the COI-5P marker, was essential for the identification and definition of species, revealing scenarios that would otherwise be ignored by using only morphological analysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott IA (1999) Marine red algae of the Hawaiian Islands. Bishop Museum Press, Honolulu
Agardh JG (1851) Species genera et ordines algarum, seu descriptiones succinctae specierum, generum et ordinum, quibus algarum regnum constituitur. Volumen secundum: algas florideas complectens. Part 2, fasc. 1, 337–506. C.W.K. Gleerup, Lund
Agardh JG (1852) Species genera et ordines Floridearum, seu descriptiones succinctae specierum, generum et ordinum, quibus floridearum classis constituitur. Volumis secundi: Part 2, pp. 337–720. Lundae [Lund]: C.W.K. Gleerup.
Amado-Filho GM, Horta PA, Brasileiro PS, Barreto MBB, Fujii MT (2006) Subtidal benthic marine algae of the Marine State Park of Laje de Santos (São Paulo, Brazil). Braz J Oceanogr 54:225–234
Bangmei X, Yongqiang W (1997) Some species of the genus Hypnea (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) from China. In: Abbott IA (ed) Taxonomy of economic seaweeds, vol 6. California Sea Grant College, University of California, La Jolla, pp 193–206
Børgesen F (1943) Some marine algae from Mauritius. III. Rhodophyceae. Part 2. Gelidiales, Cryptonemiales, Gigartinales. Det Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab. Biol Medd 19(1):1–85
Chiang YM (1997) Species de Hypnea Lamouroux (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) from Taiwan. In: ABBOTT IA (ed) Taxonomy of economic seaweeds, vol 6. California Sea Grant College System, La Jolla, pp 163–177
Cordeiro-Marino M (1977) Rodofíceas bentônicas marinhas do Estado de Santa Catarina. Rickia 7:69–73
Figueiredo MAO, Tâmega FTS (2007) Macroalgas marinhas. In: Biodiversidade marinha da Ilha Grande. In: JC Creed, DO Pires & MAO Figueiredo (orgs). Ministério do Meio Ambiente vol. 23, p. 153–180.
Fredericq S, Hommersand MH (2003) Biogeography of the marine red algae of the South African West Coast: a molecular approach. Proceedings of the 7th International Seaweed Symposium. Oxford University Press, Oxford p. 325–340
Freshwater DW, Rueness J (1994) Phylogenetic relationships of some European Gelidium (Gelidiales, Rhodophyta) species based on rbcL nucleotide sequence analysis. Phycologia 33:187–194
Furtado MR (2004) Desequilíbrio climático abre mercado para novos hidrocolóides. Quím e Deriv 430:1–4
Geraldino PJL, Yang EC, Boo SM (2006) Morphology and molecular phylogeny of Hypnea flexicaulis (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) from Korea. Algae 21:417–423
Geraldino PJL, Yang EC, Kim MS, Boo SM (2009) Systematics of Hypnea asiatica sp. nov. (Hypneaceae, Rhodophyta) based on morphology and nrDNA SSU, plastid rbcL, and mitochondrial cox1. Taxon 58:606–616
Geraldino PJL, Riosmena-Rodriguez R, Liao LM, Boo SM (2010) Phylogenetic relationships within the genus Hypnea (Gigartinales, Rhodophya), with a description of H.caespitosa sp. nov. J Phycol 46:336–345
Guimarães SMPB (2006) A revised checklist of benthic Rhodophyta from the State of Espírito Santo, Brazil. Bol Inst Bot 17:143–194
Guimarães N (2011) Diversidade do gênero Hypnea (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) do Estado de São Paulo baseada em marcadores moleculares e morfologia. Msc. Dissertation. University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 90 p
Guiry MD, Guiry GM (2014) AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 20 February 2014.
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Harvey WH (1834) Notice of a collection of algae, communicated to Dr. Hooker by the late Mrs. Charles Telfair, from “Cap Malheureux”, in the Mauritius; with descriptions of some new and little known species. J of Bot [Hooker] 1:147–157, pls CXXV, CXXVI
Horta PA (2000) Macroalgas do infralitoral do sul e sudeste do Brasil. PhD Thesis. University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil. 301 p.
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MrBayes: Bayesian inference of phylogeny. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Jesus PB (2012) O gênero Hypnea J.V. Lamouroux (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) no litoral do estado da Bahia, Brasil: aspectos morfológicos e anatômicos Msc. Dissertation. State University of Feira de Santana, Bahia, Brazil. 195 p.
Jesus PB, Schnadelbach AS, Nunes JMC (2014) O gênero Hypnea (Cystocloniaceae, Rhodophyta) no litoral do estado da Bahia, Brasil. Sitientibus Ser Cien Biol 13:1–21
Joly AB (1965) Flora marinha do litoral norte do Estado de São Paulo e regiões circunvizinhas. Bol Fac Fil Ciênc Let Univ São Paulo Ser Bot 21:1–393
Knutsen SH, Murano E, Damato M, Toffanin R, Rizzo R, Paoletti S (1995) Modified procedures for extraction and analysis of carrageenans applied to the red alga Hypnea musciformis (Wulfen) Lamouroux. J Appl Phycol 7:12
Lamouroux JV, (1813). Essai sur les genres de la famille des Thalassiophytes non articulées. Annales du Muséum d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris 20: 21–47, 115–139, 267–293, pls 7–13.
Lane CE, Lindstrom SC, Saunders GW (2007) A molecular assessment of northeast Pacific Alaria species (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae) with reference to the utility of DNA barcoding. Mol Phylogenet Evol 44:634–648
Lewmanomont K (1997) Species of Hypnea from Thailand. In: Abbott IA (ed) Taxonomy of economic seaweeds, vol 6. California Sea Grant College System, La Jolla, pp 179–190
Lyra GM, Santos ACC, Nunes JMC (2007) Rodofíceas bentônicas das praias da Concha e Engenhoca, Município de Itacaré - Bahia, Brasil. Acta Bot Mal 32:41–47
Masuda M, Yamagishi Y, Chiang YM, Lewmanomont K, Xia B (1997) Overview of Hypnea (Rhodophyta, Hypneaceae). In: Abbott IA (ed) Taxonomy of economic seaweeds, vol 6. California Sea Grant College System, La Jolla, pp 127–133
Montagne CJ (1841) Plantae celulares. In: Barker-Webb P & Berthelot S. Histoire naturelle de Iles Canaries. Vol 3. Paris
Mshigeni KE, Chapman DJ (1994) Hypnea (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). In: Akatsuka I (ed) Biology of economic algae. SPB Academic Publishing, The Hague, pp 245–281
Nunes JMC (2005) Rodofíceas marinhas bentônicas do estado da Bahia, Brasil. PhD Thesis. University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil. 410 p.
Nylander JAA (2004) Bayesian phylogenetics and the evolution of gall wasps. Comprehensive Summaries of Uppsala Dissertations from the Faculty of Science and Technology, 34 p.
Oliveira-Filho EC (1977) Algas marinhas bentônicas do Brasil. Thesis. University of São Paulo, São Paulo, 406 p
Oliveira-Filho EC, Berchez FAS (1987) Ensayos sobre el cultivo del alga roja Hypnea musciformis (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) en São Paulo, Brasil. In: Verret JA, Carillo M, Zanuy S, Huisman EA (eds.) Procedimientos del trabajo sobre acuicultura en America Latina. International Foundation for Science p. 399–409.
Pereira SMB, Oliveira-Carvalho MF, Angeiras J.A, Bandeira-Pedrosa ME, Oliveira NMB, Torres J, Gestinari LMS, Cocentino ALM, Santos MD, Nascimento PRF, Cavalcanti DR (2002) Algas marinhas bentônicas do Estado de Pernambuco In: Tabarelli M & Silva JMC (Org.). Diagnóstico da Biodiversidade de Pernambuco, p. 97–124. Massangana.
Price JH, John DM, Lawson GW (1992) Seaweeds of the western coast of tropical Africa and adjacent islands: a critical assessment. IV. Rhodophyta (Florideae) 3. Genera H-K. Bull Br Mus Nat Hist (Bot) 22:123–146
Reis RP, Yoneshigue-Valentin Y (1998) Variação espaço-temporal de populações de Hypnea musciformis (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) na Baía de Sepetiba e Armação dos Búzios, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Acta Bot Bras 12:465–483
Reis RP, Leal MCR, Yoneshigue-Valentin Y, Belluco F (2003) Efeito de fatores bióticos no crescimento de Hypnea musciformis (Rhodophyta - Gigartinales). Acta Bot Bras 17:279–286
Reis RP, Caldeira AQ, Miranda APS, Barros Barreto MB (2006) Potencial para maricultura da carragenófita Hypnea musciformis (Wulfen) J.V. Lamour. (Giagartinales - Rhodophyta) na Ilha da Marambaia, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Acta Bot Bras 20:763–769
Saunders GW (2005) Applying DNA barcoding to red macroalgae: a preliminary appraisal holds promise for future applications. Phil Trans R Soc B 360:1879–1888
Schenkman RPF (1986) Cultura de Hypnea (Rhodophyta) in vitro como subsídio para estudos morfológicos, reprodutivos e taxonômicos. PhD Thesis. University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil. 81 p.
Schneider CW, Searles RB (1991) Seaweeds of the Southeastern United States: Cape Hatteras to Cape Canaveral. Duke University Press, Durham, NC, p 554
Tamura N, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10:512–526
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thiers B (2014) Index Herbariorum: a global directory of public herbaria and associated staff. New York Botanical Garden’s Virtual Herbarium. http://www.nybg.org/bsci/ih/ih.html. [continuously updated].
Tsiamis K, Verlaque M (2011) A new contribution to the alien red macroalgal flora of Greece (Eastern Mediterranean) with emphasis on Hypnea species. Crypt Algol 32:393–410
Turner D (1809) Fuci sive plantarum fucorum generi a botanicis ascriptarum icones descriptiones et historia. Fuci, or coloured figures and descriptions of the plants referrred by botanists to the genus Fucus. Vol. 2. Londini [London], [i], 164, [2] p., pl. 72–134 (col. copp. W.J. Hooker).
Womersley HBS (1994) The marine benthic flora of Southern Australia. Part III-A. Bangiophyceae and Florideophyceae (Acrochaetiales, Nemaliales, Gelidiales, Hildenbrandiales and Gigartinales sensu lato). Australian Biological Resources Study, Camberra
Yamagishi Y, Masuda M (1997) Species de Hypnea from Japan. In: Abbott IA (ed) Taxonomy of economic seaweeds, vol 6. California Sea Grant College System, La Jolla, pp 135–162
Yamagishi Y, Masuda M (2000) A taxonomic revision of a Hypnea charoides-valentiae complex (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) in Japan, with a description of Hypnea flexicaulis sp. nov. Phycol Res 48:27–35
Yamagishi Y, Masuda M, Abe T, Uwai S, Kogami K, Kawagushi S, Phang SM (2003) Taxonomic notes on marine algae from Malaysia. XI. Four species of Rhodophyceae. Bot Mar 46:534–547
Yoneshigue Y (1985) Taxonomie et ecologie des algues marines dans la region de Cabo Frio (Rio de Janeiro, Bresil). PhD Thesis - Faculté dês Sciences de Luminy Université d’Aix – Marseille II, Marseille, France. 466 p
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Fabio Rindi and M. Hommersand for sending samples of H. musciformis. We also greatly thank Michael Wynne for comments and exchange of relevant information on the taxonomy of species of Hypnea. We are grateful for the support from FAPESP (Biota 2013-11833-3), CNPq (Br BOL-564945-2010-2, 301491/2013-5), CAPES (Proex), and NP-BioMar. We also thank all members of the Marine Algae Laboratories (LAM), University of São Paulo, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Detailed list of data collection of specimens analyzed in this work. GB – GenBank accession numbers, − not sequenced. (DOCX 54 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nauer, F., Cassano, V. & Oliveira, M.C. Description of Hypnea pseudomusciformis sp. nov., a new species based on molecular and morphological analyses, in the context of the H. musciformis complex (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). J Appl Phycol 27, 2405–2417 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0488-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0488-y