Abstract
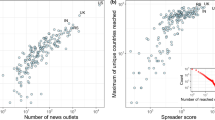
Along with the rapid development of online news production and consumption, information spreads rapidly among news portals through reprinting and re-posting. Understanding the dissemination process of online news has important implications for policy making, crisis management, and brand imaging. As the frequency of news reprinting between two news portals expresses the social relationship between them, the topological properties of complex networks of news portals indicate the dynamic patterns of online news dissemination. This research is the first study that examines patterns and organizational structure of online news networks based on historical data collected from more than one thousand Chinese news portals. Main findings reveal that information can spread widely and rapidly through online news portals. Specifically, some major news portals exchange information with each other frequently and they exchange information with small news portals directly, implying that hot-spot events, even they are first reported by a small news portal, can be re-posted by many major news portals in a short time and then spread over the Internet quickly. The dense connections between many major news portals ensure that the spread will not be influenced greatly by the refusal to report typical events of a small part of major news portals.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, R., & Barabási, A.-L. (2002). Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Reviews of Modern Physics, 74(1), 47–97.
Barabasi, A., & Albert, R. (1999). Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science, 286(5439), 509.
Barrat, A., Barthelemy, M., Pastor-Satorras, R., & Vespignani, A. (2004). The architecture of complex weighted networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101(11), 3747–3752.
Barrat, A., Barthlemy, M., & Vespignani, A. (2008). Dynamical processes on complex networks. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Barthélemy, M., Barrat, A., Pastor-Satorras, R., & Vespignani, A. (2005). Dynamical patterns of epidemic outbreaks in complex heterogeneous networks. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 235(2), 275–288.
Boczkowski, P. J. (2002). The development and use of online newspapers: What research tells us and what we might want to know. In L. Lievrouw and S. Livingstone (Eds.), The handbook of new media (pp. 270–286). London: Sage.
Borgatti, S. P., & Everett, M. G. (2000). Models of core/periphery structures. Social Networks, 21(4), 375–395.
Bustamante, E. (2004). Cultural industries in the digital age: some provisional conclusions. Media, Culture & Society, 26(6), 803.
Chyi, H., & Sylvie, G. (1998). Competing with whom? Where? And how? A structural analysis of the electronic newspaper market. Journal of Media Economics, 11(2), 1–18.
CNNIC. (2012). the 29th China Internet Development Status Survey Report. http://www.cnnic.cn/research/bgxz/tjbg/201201/P020120116330880247967.pdf. Accessed 1.18 2012.
Cohen, R., & Havlin, S. (2003). Scale-free networks are ultrasmall. Physical Review Letters, 90(5), 58701.
Crucitti, P., Latora, V., Marchiori, M., & Rapisarda, A. (2003). Efficiency of scale-free networks: error and attack tolerance. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 320, 622–642. doi:10.1016/s0378-4371(02)01545-5.
Dasgupta, N., Mandl, K. D., & Brownstein, J. S. (2009). Breaking the news or fueling the epidemic? Temporal association between news media report volume and opioid-related mortality. PLoS ONE, 4(11), e7758. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007758.
Deuze, M. (2003). The web and its journalisms: considering the consequences of different types of newsmedia online. New Media & Society, 5(2), 203.
Dorogovtsev, S. N., Goltsev, A. V., & Mendes, J. F. F. (2006). k-core organization of complex networks. Physical Review Letters, 96(4), 040601.
Fan, W., & Yeung, K. H. (2011). Online social networks—Paradise of computer viruses. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 390, 189–197. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2010.09.034.
Flaounas, I., Turchi, M., Ali, O., Fyson, N., De Bie, T., Mosdell, N., et al. (2010). The structure of the EU mediasphere. PLoS One, 5(12), e14243. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014243.
Gonçalves, B., Perra, N., & Vespignani, A. (2011). Modeling users’ activity on twitter networks: validation of Dunbar’s number. PLoS One, 6(8), e22656. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022656.
Harwit, E., & Clark, D. (2001). Shaping the internet in China: evolution of political control over network infrastructure and content. Asian Survey, 41(3), 377–408.
Herbert, J., & Thurman, N. (2007). Paid content strategies for news websites. Journalism Practice, 1(2), 208–226.
Hindman, M. (2007). A mile wide and an inch deep: measuring media diversity online and offline. Media diversity and localism: Meaning and metrics, 40(2), 327–348.
Hindman, M. (2009). The myth of digital democracy. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press.
Hoffman, L. (2006). Is Internet content different after all? A content analysis of mobilizing information in online and print newspapers. Journalism and Mass Communication Quarterly, 83(1), 58.
Holme, P. (2005). Core-periphery organization of complex networks. Physical Review E, 72, 046111.
Journalism.org (2010). The state of the news media 2010: Online: Audience behavior. http://www.stateofthemedia.org/2010/online_audience.php. Accessed 2010.06.10.
Kaye, B. K., & Johnson, T. J. (2003). From here to obscurity?: media substitution theory and traditional media in an on-line world. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 54(3), 260–273. doi:10.1002/Asi.10212.
Kohut, A., Doherty, D., & Dimock, M. (2008). Key news audiences now blend online and traditional sources. Washington, D.C.: The Pew Research Center for the People and the Press.
Latora, V., & Marchiori, M. (2001). Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Physical Review Letters, 87(19), 198701.
Lee, A., & Carpini, M. (2010). News consumption revisited: Examining the power of habits in the 21st century.
Leskovec, J., Krause, A., Guestrin, C., Faloutsos, C., VanBriesen, J., & Glance, N. (2007). Cost-effective outbreak detection in networks. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 13th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, San Jose, California, USA.
Moore, C., & Newman, M. E. J. (2000). Epidemics and percolation in small-world networks. Physical Review E, 61(5), 5678.
Newman, M. E. (2001). The structure of scientific collaboration networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(2), 404–409.
Newman, M. E. J. (2003). The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Review, 45(2). doi:10.1137/s003614450342480.
Newman, M. E. J., Forrest, S., & Balthrop, J. (2002). Email networks and the spread of computer viruses. Physical Review E, 66(3), 035101.
Ni, S., Weng, W., & Zhang, H. (2011). Modeling the effects of social impact on epidemic spreading in complex networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 390(23–24), 4528–4534. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2011.07.042.
Panzarasa, P., Opsahl, T., & Carley, K. (2009). Patterns and dynamics of users’ behavior and interaction: network analysis of an online community. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 60(5), 911–932.
Paulussen, S. (2006). Online news production in Flanders: how Flemish online journalists perceive and explore the internet’s potential. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 9(4).
Peng, F., Tham, N., & Xiaoming, H. (1999). Trends in online newspapers: a look at the US web. Newspaper Research Journal, 20(2).
Quandt, T. (2008). (NO) News on the world wide web? Journalism Studies, 9(5), 717–738.
Scott, J. (2007). Social network analysis: A handbook. London, UK: Sage.
Singer, J. (2003). Who are these guys?: the online challenge to the notion of journalistic professionalism. Journalism, 4(2), 139.
Thelwall, M. (2004). Link analysis: An information science approach. Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Pub Ltd.
Varian, H. R., Farrell, J., & Shapiro, C. (2004). The economics of information technology. Boston: Cambridge University Press.
Wan, X., & Yang, J. (2007). Learning information diffusion process on the web. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 16th international conference on World Wide Web, Banff, Alberta, Canada.
Wang, Y., Zeng, D., Zheng, X., & Wang, F. (2009a). Internet news media analysis based on complex network theory. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 6(3), 11–21.
Wang, Y., Zeng, D., Zheng, X., & Wang, F. (2009b). Propagation of online news: dynamic patterns. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE international conference on Intelligence and security informatics, Richardson, Texas, USA.
Watts, D. J., & Strogatz, S. H. (1998). Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature, 393(6684), 440–442.
Weber, M., & Monge, P. (2011). The flow of digital news in a network of sources, authorities, and hubs. Journal of Communication, 61(6), 1062–1081.
Weldon, M. (2008). Everyman news: The changing American front page. Columbia, MO: University of Missouri Press.
Zhang, X. (2007). Breaking news, media coverage and ‘citizen’s right to know’in China. Journal of Contemporary China, 16(53), 535–545.
Zhang, J., Cao, X.-B., Du, W.-B., & Cai, K.-Q. (2010). Evolution of Chinese airport network. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 389(18), 3922–3931. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2010.05.042.
Zheng, X., Zeng, D., Li, H., & Wang, F. (2008). Analyzing open-source software systems as complex networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 387(24), 6190–6200. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2008.06.050.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge research support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 71103180, 71025001, 91124001, 91024030, 90924302, and 70890084.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zeng, D., Zhu, B. et al. Patterns of news dissemination through online news media: A case study in China. Inf Syst Front 16, 557–570 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-012-9358-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-012-9358-9