Abstract
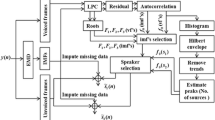
Speech separation is an essential part of any voice recognition system like speaker recognition, speech recognition and hearing aids etc. When speech separation is applied at the front-end of any voice recognition system increases the performance efficiency of that particular system. In this paper we propose a system for single channel speech separation by combining empirical mode decomposition (EMD) and multi pitch information. The proposed method is completely unsupervised and requires no knowledge of the underlying speakers. In this method we apply EMD to short frames of the mixed speech for better estimation of the speech specific information. Speech specific information is derived through multi pitch tracking. To track multi pitch information from the mixed signal we apply simple-inverse filtering tracking and histogram based pitch estimation to excitation source information along with estimating the number of speakers present in the mixed signal.































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bofill, P. (2008). Identifying single source data for mixing matrix estimation in instantaneous blind source separation. Proceedings of the ICANN, 5163, 759–767.
Boldt, J. B., & Ellis, D. P. W. (2009) A simple correlation based model of intelligibility for nonlinear speech enhancement and separation. Columbia university academic commons, http://hdl.handle.net/10022/AC:P:13660.
Digital Speech Processing Course (2015). Time domain methods in speech processing. http://www.ece.ucsb.edu/Faculty/Rabiner/ece259/speech20course.html.
Douglas, S. C., Sawada, H., & Makino, S. (2005). Natural gradient Multichannel blind deconvolution and speech separation using causal FIR filters. IEEE Transactions on Speech Audio Processing, 13(1), 92–104.
Ellis, D. (2006). Model based scene analysis. In D. Wang & G. Brown (Eds.), Computational auditory scene analysis: Principles, algorithms and applications. New York: Wiley.
Fevotte, C., & Godsill, S. J. (2006). A baysean approach for blind separation of sparse sources. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 14(6), 2174–2188.
Gao, B., Woo, W. L., & Dlay, S. S. (2011). Single channel source separation using EMD sub band variable regularized sparse features. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 19(4), 961–976.
Gao, B., Woo, W. L., & Dlay, S. S. (2013). Unsupervised single Channel separation of non stationary signals using Gammatone filter bank and Itakura-Satio nonnegative matrix two-dimensional factorizations. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 60(3), 662–675.
Greenwood M., & Kinghorn, A. (1999). SUVing: Automatic Silence/Unvoiced/Voiced Classification of Speech. Undergraduate Coursework, Department of Computer Science, The University of Sheffield, http://www.dcs.shef.ac.uk/mark/uni/.
Hershey, J.R., Olsen, P.A., Rennie, S. J., & Aron, A. (2011). Audio Alchemy: Getting computers to understand overlapping speech. Scientific American Online, http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/speech-gettingcomputersunderstand-overlapping.
Huang, N. E., Shen, Z., & Long, S. R. (1998). The empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceedings of Royal Society of London, 454, 903–995.
Jang, G. J., & Lee, T. W. (2003). A maximum likelihood approach to single channel source separation. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 4, 1365–1392.
Karhunen, J., & Oja, E. (2001). Independent component analysis. New York: John Wiley Sons.
Kristjansson, T., Attias, H., & Hershey, J. (2004) Single microphone source separation using high resolution signal reconstruction. In Proceedings of International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing, (ICASSP’04, (Vol. 2, pp. 817–820). Montreal, QC.
Kumaraswamy, R., Yegnanarayana, B., & Sri ramamurty, K. (2009). Determining mixing parameters from multi speaker data using speech specific information. IEEE Transactions on Audio Speech and Language Processing, 17(6), 1196–1207.
Li, Y., Amari, S., & Cichocki, A. (2006a). Underdetermined blind source separation based on sparse representation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 54(2), 423–437.
Li, P., Guan, Y., & Xu, B. (2006b). Monaural speech separation based on computational auditory scene analysis and objective quality assessment of speech. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 14(6), 2014–2023.
Linear Prediction Analysis (2015) http://iitg.vlab.co.in/?sub=59&brch=164&sim=616&cnt=1108.
Litvin, Y., & Cohen, I. (2009). Single channel source separation of audio signals using Bark Scale Wavlet Packet Decomposition. IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing, 65(3), 339–9350.
Mijovic, Bogdan, & De Vos, Maarten. (2010). Source separation from single channel recordings by combining empirical mode decomposition and independent component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 57(9), 2188–2196.
Molla, M. K., & Hirose, K. (2007). Single mixture audio source separation by subspace decomposition of Hilbert spectrum. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 15(3), 893–900.
Ozerov, A., & Fevotte, C. (2010). Multichannel non-negative Matrix factorization in convolutive mixtures for audio source separation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 18(3), 550–563.
Philipos, C. (2011). Loizou. Speech Quality Assessment, Multimedia Analysis, Processing & Communications, 346, 623–654.
Reys, M. J., Ellis, D., & Jojic, N. (2004). Multiband audio modelling for single channel acoustic source separation. In Proceedings of International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing (ICASSP’04) (Vol. 5, pp. 641–644). Montreal, QC.
Schmidt, M. N., & Olsson, R. K. (2006). Single channel speech separation using sparse non negative matrix factorization”, In Proceedings of International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (INTERSPEECH), (pp. 2614–2617). Pittsburgh, PA.
Schobben, D., Torkkola, K., & Smaragdis, P. (1999). Evaluation of blind signal separation methods. In Proceedings of ICA BSS, Aussois.
Stark, Michael, Wohlmayr, Michael, & Pernkopf, Franz. (2011). Source filter based single channel speech separation using pitch information. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 19(2), 242–254.
Tengtrairat, N., Gao, B., & Woo, W. L. (2013). Single channel Blind separation using pseudo stereo mixture and complex 2-D histogram. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 24(11), 1722–1735.
Vincent, E., & Bertin, N. (2014). From Blind to guided audio source separation. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 31(3), 107–115.
Vincent, E., Gribonval, R., & Fevotte, C. (2006). Performance measurement in blind audio source separation. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing., 14(4), 1462–1469.
Virtanen, T. (2007). Monaural sound source separation by non negative matrix factorization with temporal continuity and sparseness criteria. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 15(3), 1066–1074.
Wang, Y. H., Yeh, C. H., & Young, H. W. (2014). On the Computational complexity of the empirical mode decomposition algorithm. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 400(15), 159–167.
Wu, K-H., & Chen, C-P., & Yeh, B-F. (2011). Noise-robust speech feature processing with empirical mode decomposition. EURASIP journal on audio, speech and music processing, http://asmp.eurasipjournals.com/content/2011/1/9.
Yilmaz, O., & Rickard, S. (2004). Blind separation of speech mixtures via time-frequency masking. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 52(7), 1830–1847.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasanna Kumar, M.K., Kumaraswamy, R. Single-channel speech separation using empirical mode decomposition and multi pitch information with estimation of number of speakers. Int J Speech Technol 20, 109–125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-016-9392-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-016-9392-y