Abstract
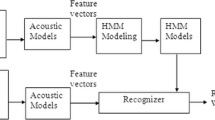
In this paper, a Standard Yorùbá speech-to-text system capable of recognizing isolated words spoken by the users based on previously stored data was designed and implemented. This system adopted syllable-based approach, and carefully-selected words were recorded, analyzed and annotated, using Praat software. An experimental database of six native speakers was taken, each speaking 25 bi-syllabic and 25 tri-syllabic words, under an acoustically-controlled room. The meaningful spectral coefficients were successfully extracted using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients technique and Hidden Markov Model Toolkit was used to implement the system. A graphical user interface was also developed to make the system accessible and more interactive. Furthermore, the system was tested and evaluated based on the perception of native speakers of the language. The overall accuracy for bi-syllabic and tri-syllabic words was 76 and 84 % respectively. These results obtained for both bi and tri-syllabic words showed that this system was a promising approach that could be adopted for Standard Yorùbá continuous speech recognition system as this will make the system useable for the foreign speaker.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Wahab, F. A., Shahrul, A. M. Y., & Hariharan, M. (2013). Yorùbá Automatic speech recognition: A review. In International conference of rural ICT development, Melaka, Malaysia (pp. 116–121).
Adeniran, W. (2015). Will the Yoruba language survive beyond the 21st century? A lecture delivered at the Yoruba day celebration in Stockholm, Sweden. Retrieved November 07, 2015.
Afolabi, A. O., & Wahab, A. J. (2013). Implementation of Yoruba text-to-speech E-learning system. International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology, 2(11), 1055–1064.
Ahmad, M. A., Gunawan, T. S., & Khalifa, O. O. (2010). English digits speech recognition system based on hidden Markov models. In International Islamic University Malaysia, international conference on computer and communication engineering (ICCCE), 11–13, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Corporation and Cambridge University Engineering Department.
Bamgboṣe, A. (1969). Yorùbá. In Elizabeth Dunstan (Ed.), Twelve Nigerian languages (p. 166). New York: Africana Publishing Corp.
Cini, K., & Balakrishnan, K. (2012). Continuous speech recognition system for Malayalam language using PLP cepstral coefficient. International Journal of Computing and Business Research (IJCBR), 3(1).
Das, R., & Das, P. K. (2013). Design and implementation of monophones and triphones based speech recognition systems for Spanish language. Bharati International Journal of Information Technology (BIJIT), 2(3), 237–253.
Dopamu, P. (2004). Understanding Yorùbá life and culture. Trenton, NJ: Africa World Press Inc.
Dua, M., Aggarwal, R. K., Kadyan, V, & Dua, S. (2013). Punjabi continuous speech recognition using HTK, Department of Computer Engineering, NIT, India.
Gales, M. J. F., Kim, D. Y., Woodland, P. C., Chan, R. H. Y., Mrva, D., Sinha, R., et al. (2006). Progress in the CU-HTK broadcast news transcription system. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 14(5), 1513–1525.
Graham, W. (2014). Syllabic consonants-speech and language therapy information. Retrieved December 13, 2015 from http://www.sltinfo.com/syllabic-consonants/.
Ishizuka, K., & Nakatani, T. (2006). Study of noise robust voice activity detection based on periodic component to aperiodic component ratio. In Statistical and perceptual audition (SAPA) (pp. 65–70). Retrieved from ISCA Archive http://www.isca-speech.org/archive.
Kumolalo, F. O., Adagunodo, E. R., & Odejobi, O. A. (2010). Development of a Syllabicator for Yorùbá Language. Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria Proceedings of OAU TekConf.
Majdalawieh, O., Gu, J., & Meng, M. (2004). An HTK-developed Hidden Markov Model (hmm) for a voice-controlled robotic system. In IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Sendai, Japan (pp. 4050–4055).
Manadhar, S., Ziolko, B., Wilson, R. C., & Galka, J. (2008). Application of HTK to the Polish language. International Conference on Audio, Language and Image Processing, 2(1), 234–245.
Maya, M., Elizabeth, S., & Varghese, W. S. (2010). Malayalam word identification for speech recognition system. Kerala: Indian Institute of Information Technology and Management (IIITM-K).
Mohri, M. (2002). Edit-distance of weighted automata: General definitions and algorithms. International Journal of Foundations of Computer Science, 14(6), 957–982.
Odéjobí, O. A. (2008). Recognition of tones in Yoruba speech: Experiments with artificial neural networks. In B. Prasad & S. R. M. Prasanna (Eds.), Studies Computational Intelligence (SCI) (vol. 83, pp. 23–47).
Oloruntoyin, S. T. (2014). Development of Yorùbá language text-to-speech E-learning system. International Journal of Scholarly Research Gate, 2(1), 345–367.
Oyekanmi, E. O., Oluwadare, S. A., & Alese, B. K. (2013). Intelligent system learning and understanding of Yorùbá language. International Journal of Computer and Information Technology, 2(5), 993–997.
Paul, D. B. (2010). A Tutorial of HMM Tool Kit (HTK): A power point presentation at the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Binghamton University.
Rabiner, L. R., & Juang, B. H. (1993). Fundamentals of speech recognition. Englewood Cliff, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Saini, P., Kaur, P., & Dua, M. (2013). Automatic speech segmentation for Hindi language using HTK. International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT), 4(6), 2451–2555.
Williamson, K., & Blench, R. (2000). Niger-Congo. African languages: An introduction (pp. 1–42).
Young, S., Evermann, G., Gales, M., Hain, T., Kershaw, D., Liu, X., Moore, G., Odell, J., Ollason, D., Povey, D., Valtchev, V., & Woodland, P. (2002). The HTK book, Microsoft. Cambridge University Engineering Department.
Zhang, G., Yin, J., Liu, Q., & Yang, C. (2011). The fixed-point optimization of Mel frequency cepstrum coefficients for speech recognition. School of Applied Sciences, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin, China.
Funding
Self sponsored.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adetunmbi, O.A., Obe, O.O. & Iyanda, J.N. Development of Standard Yorùbá speech-to-text system using HTK. Int J Speech Technol 19, 929–944 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-016-9380-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-016-9380-2