Abstract
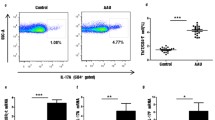
The aim of this study is to explore the dynamic changes in IL-17-expressing T cells (Th17)/Treg expression in monophasic experimental autoimmune uveitis (mEAU). mEAU was induced in Lewis rats with IRBP1177–1191 peptide and evaluated clinically and pathologically on days 9, 13, 18, 23, 28, 35, and 48. Lymphocytes isolated from inguinal lymph nodes were subjected to flow cytometry to analyze the frequency of Th17/Treg cells. The levels of cytokines (IL-17, IL-6, IL-10, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β) in serum were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-PCR) was used for measuring the levels of IL-17, IL-6, TGF-β, and Foxp3. Clinical and histopathologic assessment showed that mEAU began on day 9, peaked on day 13, and decreased to normal on day 18. The frequency of Th17 cells increased obviously on day 9, peaking on day 13, while the frequency of Treg cells increased on day 13, peaked on day 18, and remained at a high level until day 48. In the serum, the levels of IL-17 and IL-6 peaked on day 9 and gradually decreased to normal on day 28. The level of TGF-β increased on day 9, peaked on day 13, and decreased to normal on day 35. Meanwhile, the level of IL-10 increased on day 9 and stayed at a high level until day 48. Additionally, the above results were further confirmed by RT-PCR. The imbalance between Th17 and Treg cells contributes to the onset and progression of mEAU, and a compartmental imbalance of Treg over Th17 exists in the recovery phase of mEAU.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durrani, O.M., C.A. Meads, and P.I. Murray. 2004. Uveitis: A potentially blinding disease. Ophthalmologica 218: 223–236.
He, Y., S.B. Jia, W. Zhang, and J.M. Shi. 2013. New options for uveitis treatment. International Journal of Ophthalmology 6: 702–707.
Nussenblatt, R.B. 1991. Proctor lecture. Experimental autoimmune uveitis: Mechanisms of disease and clinical therapeutic indications. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 32: 3131–3141.
Wildner, G., M. Diedrichs-Mohring, and S.R. Thurau. 2008. Rat models of autoimmune uveitis. Ophthalmic Research 40: 141–144.
Camelo, S., L. Lajavardi, A. Bochot, B. Goldenberg, M.C. Naud, N. Brunel, et al. 2009. Protective effect of intravitreal injection of vasoactive intestinal peptide-loaded liposomes on experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Journal of Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics 25: 9–21.
Zou, W., Z. Wu, X. Xiang, S. Sun, and J. Zhang. 2014. The expression and significance of T helper cell subsets and regulatory T cells CD4 +CD25 + in peripheral blood of patients with human leukocyte antigen B27-positive acute anterior uveitis. Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology 252: 665–672.
Ma, L., H.B. Xue, X.H. Guan, C.M. Shu, F. Wang, J.H. Zhang, et al. 2014. The imbalance of Th17 cells and CD4(+)CD25(high)Foxp3(+)Treg cells in patients with atopic dermatitis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 28: 1079–1086.
Chen, Z., J. Ding, N. Pang, R. Du, W. Meng, Y. Zhu, et al. 2013. The Th17/Treg balance and the expression of related cytokines in Uygur cervical cancer patients. Diagnostic Pathology 8: 61.
Sun, M., P. Yang, L. Du, H. Zhou, X. Ren, X. Lin, et al. 2010. Increased regulatory T cells in spleen during experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Ocular Immunology and Inflammation 18: 38–43.
Song, X., H. Gao, and Y. Qian. 2014. Th17 differentiation and their pro-inflammation function. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 841: 99–151.
Mc Geachy, M.J., and D.J. Cua. 2008. Th17 cell differentiation: The long and winding road. Immunity 28: 445–453.
Toussirot, E. 2012. The IL23/Th17 pathway as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammatory diseases. Inflammation & Allergy Drug Targets 11: 159–168.
Yang, L., D.E. Anderson, C. Baecher-Allan, W.D. Hastings, E. Bettelli, M. Oukka, et al. 2008. IL-21 and TGF-beta are required for differentiation of human T(H)17 cells. Nature 454: 350–352.
Mangan, P.R., L.E. Harrington, D.B. O’Quinn, W.S. Helms, D.C. Bullard, C.O. Elson, et al. 2006. Transforming growth factor-beta induces development of the T(H)17 lineage. Nature 441: 231–234.
Veldhoen, M., R.J. Hocking, C.J. Atkins, R.M. Locksley, and B. Stockinger. 2006. TGFbeta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity 24: 179–189.
del Rosario Espinoza Mora, M., M. Böhm, and A. Link. 2014. The Th17/Treg imbalance in patients with cardiogenic shock. Clinical Research in Cardiology 103: 301–313.
Leung, S., X. Liu, L. Fang, X. Chen, T. Guo, and J. Zhang. 2010. The cytokine milieu in the interplay of pathogenic Th1/Th17 cells and regulatory T cells in autoimmune disease. Cellular & Molecular Immunology 7: 182–189.
Chen, L., P. Yang, H. Zhou, H. He, X. Ren, W. Chi, et al. 2008. Diminished frequency and function of CD4 + CD25high regulatory T cells associated with active uveitis in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 49: 3475–3482.
Talaat, R.M., S.F. Mohamed, I.H. Bassyouni, and A.A. Raouf. 2015. Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cytokine imbalance in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients: Correlation with disease activity. Cytokine 72: 146–153.
Zhang, R., A. Tian, J. Wang, X. Shen, G. Qi, and Y. Tang. 2015. miR26a modulates Th17/Treg balance in the EAE model of multiple sclerosis by targeting IL6. Neuromolecular Medicine 17: 24–34.
Jia, X., M. Hu, C. Wang, C. Wang, F. Zhang, Q. Han, et al. 2011. Coordinated gene expression of Th17- and Treg-associated molecules correlated with resolution of the monophasic experimental autoimmune uveitis. Molecular Vision 17: 1493–507.
Jha, P., B. Manickam, B. Matta, P.S. Bora, and N.S. Bora. 2009. Proteolytic cleavage of type I collagen generates an autoantigen in autoimmune uveitis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 284: 31401–31411.
Fang, C.B., D.X. Zhou, S.X. Zhan, Y. He, Z. Lin, C. Huang, et al. 2013. Amelioration of experimental autoimmune uveitis by leflunomide in Lewis rats. PloS One 8: e62071.
Fang, I.M., C.H. Yang, and C.M. Yang. 2014. Chitosan oligosaccharides attenuate ocular inflammation in rats with experimental autoimmune anterior uveitis. Mediators of Inflammation 2014: 827847.
Tian, Q., H. Bi, Y. Cui, D. Guo, X. Xie, W. Su, et al. 2012. Qingkailing injection alleviates experimental autoimmune uveitis in rats via inhibiting Th1 and Th17 effector cells. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 35: 1991–1996.
Peng, Y., G. Han, H. Shao, Y. Wang, H.J. Kaplan, and D. Sun. 2007. Characterization of IL-17+ interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein-specific T cells in experimental autoimmune uveitis. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 48: 4153–4161.
Sun, M., P. Yang, L. Du, H. Zhou, X. Ren, and A. Kijlstra. 2010. Contribution of CD4+CD25+T cells to the regression phase of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 51: 383–389.
Mai, J., H. Wang, and X.F. Yang. 2010. Th17 cells interplay with Foxp3+ Tregs in regulation of inflammation and autoimmunity. Frontiers in Bioscience (Landmark Ed) 15: 986–1006.
Park, T.Y., S.D. Park, J.Y. Cho, J.S. Moon, N.Y. Kim, K. Park, et al. 2014. RORγt-specific transcriptional interactomic inhibition suppresses autoimmunity associated with TH17 cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 111: 18673–18678.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81373826, 81403438) and the Development Project of Science and Technology of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Shandong Province (2013ZDZK-083).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lian Zhang and Fangzhu Wan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Wan, F., Song, J. et al. Imbalance Between Th17 Cells and Regulatory T Cells During Monophasic Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis. Inflammation 39, 113–122 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0229-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0229-7