Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RAFLSs) proliferate abnormally and resist apoptosis. Bufalin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. In this study, we explored the effects of bufalin on interleukin-1beta (IL-1β)-induced proliferation and apoptosis of RAFLSs. The cell proliferation and apoptosis were measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide assay and annexin V/propidium iodide staining, respectively. Bufalin dose-dependently inhibited IL-1β-induced RAFLS proliferation. Mechanistically, bufalin decreased the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), both of which are involved in IL-1β-mediated RAFLS proliferation. Moreover, bufalin induced apoptosis and mitochondrial damage of RAFLSs, which was associated with Bcl-2 downregulation, Bax upregulation, mitochondrial cytochrome c release, and enhanced cleavages of caspase-3 and poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Collectively, our results reveal that bufalin suppresses IL-1β-induced proliferation of RAFLSs through MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways and induces RAFLS apoptosis via the mitochondria-dependent pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
18 February 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-023-01794-6
References
Pope, R.M. 2002. Apoptosis as a therapeutic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews Immunology 2: 527–535.
Huang, H., Y. Xiao, H. Lin, D. Fu, Z. Zhan, L. Liang, X. Yang, J. Fan, Y. Ye, L. Sun, and H. Xu. 2011. Increased phosphorylation of ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins contributes to proliferation of rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 50: 1045–1053.
Firestein, G.S. 2003. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 423: 356–361.
Jang, J., D.S. Lim, Y.E. Choi, Y. Jeong, S.A. Yoo, W.U. Kim, and Y.S. Bae. 2006. MLN51 and GM-CSF involvement in the proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research and Therapy 8: R170.
Farahat, M.N., G. Yanni, R. Poston, and G.S. Panayi. 1993. Cytokine expression in synovial membranes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 52: 870–875.
Lim, D.S., and Y.S. Bae. 2011. Metastatic lymph node 51 and fibroblast-like synoviocyte hyperproliferation in rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. Rheumatology International 31: 843–847.
Byun, H.S., J.K. Song, Y.R. Kim, L. Piao, M. Won, K.A. Park, B.L. Choi, H. Lee, J.H. Hong, J. Park, J.H. Seok, Y.J. Lee, S.W. Kang, and G.M. Hur. 2008. Caspase-8 has an essential role in resveratrol-induced apoptosis of rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47: 301–308.
Baier, A., I. Meineckel, S. Gay, and T. Pap. 2003. Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 15: 274–279.
Bai, S., H. Liu, K.H. Chen, P. Eksarko, H. Perlman, T.L. Moore, and R.M. Pope. 2004. NF-kappaB-regulated expression of cellular FLIP protects rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts from tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated apoptosis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 50: 3844–3855.
Perlman, H., L.J. Pagliari, C. Georganas, T. Mano, K. Walsh, and R.M. Pope. 1999. FLICE-inhibitory protein expression during macrophage differentiation confers resistance to fas-mediated apoptosis. Journal of Experimental Medicine 190: 1679–1688.
Schedel, J., R.E. Gay, P. Kuenzler, C. Seemayer, B. Simmen, B.A. Michel, and S. Gay. 2002. FLICE-inhibitory protein expression in synovial fibroblasts and at sites of cartilage and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 46: 1512–1518.
Asahara, H., T. Hasumuna, T. Kobata, H. Yagita, K. Okumura, H. Inoue, S. Gay, T. Sumida, and K. Nishioka. 1996. Expression of Fas antigen and Fas ligand in the rheumatoid synovial tissue. Clinical Immunology and Immunopathology 81: 27–34.
Asahara, H., T. Hasunuma, T. Kobata, H. Inoue, U. Muller-Ladner, S. Gay, T. Sumida, and K. Nishioka. 1997. In situ expression of protooncogenes and Fas/Fas ligand in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Journal of Rheumatology 24: 430–435.
Chou, C.T., J.S. Yang, and M.R. Lee. 2001. Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis—expression of Fas, Fas-L, p53, and Bcl-2 in rheumatoid synovial tissues. Journal of Pathology 193: 110–116.
Hamaguchi, M., Y. Kawahito, A. Omoto, Y. Tsubouchi, M. Kohno, T. Seno, M. Kadoya, A. Yamamoto, H. Ishino, M. Matsuyama, R. Yoshimura, and T. Yoshikawa. 2008. Eicosapentaenoic acid suppresses the proliferation of synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition 43: 126–128.
Liagre, B., P. Vergne-Salle, C. Corbiere, J.L. Charissoux, and J.L. Beneytout. 2004. Diosgenin, a plant steroid, induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes with cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression. Arthritis Research and Therapy 6: R373–R383.
Xu, Z., G. Wu, X. Wei, X. Chen, Y. Wang, and L. Chen. 2013. Celastrol induced DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis in human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synovial cells. American Journal of Chinese Medicine 41: 615–628.
Li, L., C. Liu, M. Liu, L. Shi, Q. Liu, H. Guan, and P. Li. 2013. Taurochenodeoxycholic acid induces apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. European Journal of Pharmacology 706: 36–40.
Takai, N., N. Kira, T. Ishii, T. Yoshida, M. Nishida, Y. Nishida, K. Nasu, and H. Narahara. 2012. Bufalin, a traditional oriental medicine, induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention 13: 399–402.
Krenn, L., and B. Kopp. 1998. Bufadienolides from animal and plant sources. Phytochemistry 48: 1–29.
Bartok, B., and G.S. Firestein. 2010. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunology Reviews 233: 233–255.
Choy, E.H., and G.S. Panayi. 2001. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine 344: 907–916.
Arnett, F.C., S.M. Edworthy, D.A. Bloch, D.J. McShane, J.F. Fries, N.S. Cooper, L.A. Healey, S.R. Kaplan, M.H. Liang, H.S. Luthra, et al. 1988. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 31: 315–324.
Hochberg, M.C., R.W. Chang, I. Dwosh, S. Lindsey, T. Pincus, and F. Wolfe. 1992. The American College of Rheumatology 1991 revised criteria for the classification of global functional status in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 35: 498–502.
Nikitopoulou, Il., N. Oikonomou, E. Karouzakis, I. Sevastou, N. Nikolaidou-Katsaridou, Z. Zhao, V. Mersinias, M. Armaka, Y. Xu, M. Masu, G.B. Mills, S. Gay, G. Kollias, and V. Aidinis. 2012. Autotaxin expression from synovial fibroblasts is essential for the pathogenesis of modeled arthritis. Journal of Experimental Medicine 209(5): 925–933.
Foxwell, B., K. Browne, J. Bondeson, C. Clarke, R. Demartin, and F. Brennan. 1998. Efficient adenoviral infection with IκBα reveals that macrophage tumor necrosis factor α production in rheumatoid arthritis is NF-κB dependent. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 95: 8211–8215.
Schett, G., M. Tohidast-Akrad, J.S. Smolen, B.J. Schmid, C.W. Steiner, P. Bitzan, P. Zenz, K. Redlich, Q. Xu, and G. Steiner. 2000. Activation, differential localization, and regulation of the stress-activated protein kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-JUN N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, in synovial tissue and cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 43: 2501–2512.
Inoue, H., M. Takamori, N. Nagata, T. Nishikawa, H. Oda, S. Yamamoto, and Y. Koshihara. 2001. An investigation of cell proliferation and soluble mediators induced by interleukin 1beta in human synovial fibroblasts: comparative response in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation Research 50: 65–72.
Chueh, F.S., Y.Y. Chen, A.C. Huang, H.C. Ho, C.L. Liao, J.S. Yang, C.L. Kuo, and J.G. Chung. 2014. Bufalin-inhibited migration and invasion in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells is carried out by suppression of the matrix metalloproteinase-2, ERK, and JNK signaling pathways. Environmental Toxicology 29: 21–29.
Jiang, Y., Y. Zhang, J. Luan, H. Duan, F. Zhang, K. Yagasaki, and G. Zhang. 2010. Effects of bufalin on the proliferation of human lung cancer cells and its molecular mechanisms of action. Cytotechnology 62: 573–583.
Perlman, H., C. Georganas, L.J. Pagliari, A.E. Koch, K. Haines 3rd, and R.M. Pope. 2000. Bcl-2 expression in synovial fibroblasts is essential for maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis and cell viability. Journal of Immunology 164: 5227–5235.
Zamzami, N., C. Brenner, I. Marzo, S.A. Susin, and G. Kroemer. 1998. Subcellular and submitochondrial mode of action of Bcl-2-like oncoproteins. Oncogene 16: 2265.
Basañez, G., L. Soane, and J.M. Hardwick. 2012. A new view of the lethal apoptotic pore. PLoS Biology 10: e1001399.
Yang, J., X. Liu, K. Bhalla, C.N. Kim, A.M. Ibrado, J. Cai, T.I. Peng, D.P. Jones, and X. Wang. 1997. Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 275: 1129–1132.
Kluck, R.M., E. Bossy-Wetzel, D.R. Green, and D.D. Newmeyer. 1997. The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science 275: 1132–1136.
Hardwick, J.M., Y.B. Chen, and E.A. Jonas. 2012. Multipolar functions of BCL-2 proteins link energetics to apoptosis. Trends in Cell Biology 22: 318–328.
Martinou, J.C., and R.J. Youle. 2011. Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Developmental Cell 21: 92–101.
Rossé, T., R. Olivier, L. Monney, M. Rager, S. Conus, I. Fellay, B. Jansen, and C. Borner. 1998. Bcl-2 prolongs cell survival after Bax-induced release of cytochrome c. Nature 391: 496–499.
Zou, H., W.J. Henzel, X. Liu, A. Lutschg, and X. Wang. 1997. Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3. Cell 90: 405–413.
Marek, Ł. 2013. The role of the apoptosome in the activation of procaspase-9. Postȩpy Higieny i Medycyny Doświadczalnej (Online) 67: 54–64.
Zhao, C.Q., Y.H. Zhang, S.D. Jiang, L.S. Jiang, and L.Y. Dai. 2010. Both endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria are involved in disc cell apoptosis and intervertebral disc degeneration in rats. Age (Dordrecht, Netherlands) 32: 161–177.
Graziani, G., and C. Szabo. 2005. Clinical perspectives of PARP inhibitors. Pharmacological Research 52: 109–118.
Qi, F., Y. Inagaki, B. Gao, X. Cui, H. Xu, N. Kokudo, A. Li, and W. Tang. 2011. Bufalin and cinobufagin induce apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Fas- and mitochondria-mediated pathways. Cancer Science 102: 951–958.
Huang, W.W., J.S. Yang, S.J. Pai, P.P. Wu, S.J. Chang, F.S. Chueh, M.J. Fan, S.M. Chiou, H.M. Kuo, C.C. Yeh, P.Y. Chen, M. Tsuzuki, and J.G. Chung. 2012. Bufalin induces G(0)/G(1) phase arrest through inhibiting the levels of cyclin D, cyclin E, CDK2 and CDK4, and triggers apoptosis via mitochondrial signaling pathway in T24 human bladder cancer cells. Mutation Research 732: 26–33.
Tas, S.W., M.J. Vervoordeldonk, N. Hajji, M.J. May, S. Ghosh, and P.P. Tak. 2006. Local treatment with the selective IkappaB kinase beta inhibitor NEMO-binding domain peptide ameliorates synovial inflammation. Arthritis Research and Therapy 8: R86.
Rong ,X., Ni, W., Liu, Y., Wen, J., Qian, C., Sun, L., Wang, J, 2014. Bufalin, a bioactive component of the Chinese Medicine Chansu, inhibits inflammation and invasion of human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflammation. doi:10.1007/s10753-014-9828-y.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant (13ZR1442500) from the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
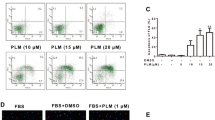
DMOS does not affect IL-1β-induced RAFLS proliferation. Human RAFLSs were cultured with 1 ng/ml IL-1β in the presence or absence of DMSO (0.01 %, v/v) for 72 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. The absorbance was measured at a 490-nm wavelength. Data are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments performed in triplicates. **P < 0.01 versus control RAFLSs. (GIF 6 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
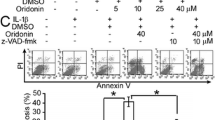
DMSO has no effects on RAFLS apoptosis. Human RAFLSs were cultured in the presence or absence of DMSO (0.01 %, v/v) for 72 h. Cell apoptosis was measured by annexin V and PI double staining. a Apoptotic cells are localized in the lower right (early apoptosis) and upper right (late apoptosis) quadrants of the dot-plot graph. b Quantitative analysis of annexin V positive cells by flow cytometry. The graphs represent typical results of cellular apoptosis. Values represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments in triplicates. (GIF 21 kb)
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Yw., Zhao, Yf., Cao, Yl. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Bufalin Exerts Inhibitory Effects on IL-1β-Mediated Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Human Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Inflammation 37, 1552–1559 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9882-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9882-5