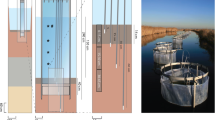
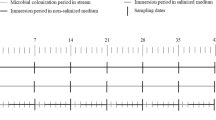
Abstract
Large, pulsed sodium chloride (NaCl) additions can increase mortality of aquatic biota, but longer-term effects from low-level additions are less understood. Small ionic increases may alleviate sodium (Na) limitation or osmoregulatory stress, thereby increasing microbial respiration and macroinvertebrate consumption and growth. We manipulated NaCl levels in microcosms containing just sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua L.) leaves with associated microbes, or leaves, microbes, and one of two macroinvertebrate detritivores (Tipula abdominalis Say in Experiment I and Lirceus sp. in Experiment II). In Experiment I, microcosms had either ambient or elevated NaCl (3 or 7 mg Na l−1, respectively). Contrary to predictions, microbial respiration did not significantly differ between treatments after 4 weeks. However, after 2 weeks, T. abdominalis marginally decreased leaf consumption in elevated treatments without change in growth. Experiment II had three NaCl treatments: low (ambient), medium, and high (3, 14, and 140 mg Na l−1, respectively). After 6 weeks, microbial respiration averaged 15% lower in medium and 29% lower in high than in low treatments. Throughout, Lirceus sp. ate and grew similarly in low and medium treatments. However, Lirceus sp. growth was 12% slower in high than in low treatments. Lirceus sp. ate 74% more leaves in high than medium treatments, but growth and assimilation did not differ. Therefore, we infer possible osmoregulatory stress. Even low-level NaCl inputs may negatively impact some detritivores, which could alter stream processes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlocher, F., 1985. The role of fungi in the nutrition of stream macroinvertebrates. Botanical Journal of Linnean Society 91: 83–94.
Baxter, C. V., K. D. Fausch & W. C. Saunders, 2005. Tangled webs: reciprocal flows of invertebrate prey link streams and riparian zones. Freshwater Biology 50: 201–220.
Benbow, M. E. & R. W. Merritt, 2004. Road-salt toxicity of select Michigan wetland macroinvertebrates under different testing conditions. Wetlands 24: 68–76.
Benke, A. C., 1993. Concepts and patterns of invertebrate production in running waters. Proceedings-International Association of Theoretical and Applied Limnology 25: 15.
Birge, W. J., J. A. Black, A. G. Westerman, T. M. Short, S. B. Taylor, D. M. Bruser & E. D. Wallingford, 1985. Recommendations on numerical values for regulating iron and chloride concentrations for the purpose of protecting warmwater species of aquatic life in the commonwealth of Kentucky. School of Biological Sciences and Graduate Center for Toxicology, University of Kentucky, Kentucky Natural Resources and Environmental Protection Cabinet.
Blasius, B. J. & R. W. Merritt, 2002. Field and laboratory investigations on the effects of road salt (NaCl) on stream macroinvertebrate communities. Environmental Pollution 120: 219–231.
Bordalo, A. A., 1993. The effects of salinity on bacterioplankton; field and microcosm experiments. The Journal of Applied Bacteriology 75: 393–398.
Brooks, S. J., D. Platvoet & C. L. Mills, 2008. Cation regulation and alteration of water permeability in the amphipod Dikerogammarus villosus: an indicator of invasion potential. Fundamental and Applied Limnology/Archiv für Hydrobiologie 172: 183–189.
Brose, U., R. J. Williams & N. D. Martinez, 2006. Allometric scaling enhances stability in complex food webs. Ecology Letters 9: 1228–1236.
Burke, V. & L. A. Baird, 1931. Fate of fresh water bacteria in the sea. Journal of Bacteriology 21: 287.
Camp, A. A., D. H. Funk & D. B. Buchwalter, 2014. A stressful shortness of breath: molting disrupts breathing in the mayfly Cloeon dipterum. Freshwater Science 33: 695–699.
Cañedo-Argüelles, M., M. Bundschuh, C. Gutiérrez-Cánovas, B. J. Kefford, N. Prat, R. Trobajo & R. B. Schäfer, 2014. Effects of repeated salt pulses on ecosystem structure and functions in a stream mesocosm. Science of the Total Environment 476–477: 634–642.
Cañedo-Argüelles, M., M. Sala, G. Peixoto, N. Prat, M. Faria, A. M. Soares, C. Barata & B. Kefford, 2016. Can salinity trigger cascade effects on streams? A mesocosm approach. Science of the Total Environment 540: 3–10.
Cardinale, B. J., D. S. Srivastava, J. E. Duffy, J. P. Wright, A. L. Downing, M. Sankaran & C. Jouseau, 2006. Effects of biodiversity on the functioning of trophic groups and ecosystems. Nature 443: 989–992.
Chadwick, M. A., D. R. Dobberfuhl, A. C. Benke, A. D. Huryn, K. Suberdropp & J. E. Thiele, 2006. Urbanization affects stream ecosystem functions by altering hydrology, chemistry, and biotic richness. Ecological Applications 16: 1796–1807.
Clay, N. A., S. P. Yanoviak & M. Kaspari, 2014. Short-term sodium inputs attract microbi-detritivores and their predators. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 75: 248–253.
Collins, S. J. & R. W. Russell, 2009. Toxicity of road salt to Nova Scotia amphibians. Environmental Pollution 157: 320–324.
Cook, L. J. & S. N. Francoeur, 2013. Effects of simulated short-term road salt exposure on lotic periphyton function. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 28: 211–223.
Cummins, K. W., 1973. Trophic relations of aquatic insects. Annual Review of Entomology 18: 183–206.
Davis, J. M., A. D. Rosemond, S. L. Eggert, W. F. Cross & J. B. Wallace, 2010. Nutrient enrichment differentially affects body sizes of primary consumers and predators in a detritus-based stream. Limnology and Oceanography 55: 2305–2316.
Dudgeon, D., A. H. Arthington, M. O. Gessner, Z. Kawabata, D. J. Knowler, C. Leveque, R. J. Naiman, A. H. Prieur-Richard, D. Soto, M. L. Stiassny & C. A. Sullivan, 2006. Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 81: 163–182.
Duncan, R. A., M. G. Bethune, T. Thayalakumaran, E. W. Christen & T. A. McMahon, 2008. Management of salt mobilisation in the irrigated landscape-a review of selected irrigation regions. Journal of Hydrology 351: 238–252.
EIA, 2011. Annual Energy Outlook. Energy Information Administration. United States Department of Energy, Washington, D.C.
El-Ashry, M. T., J. van Schilfgaarde & S. Schiffman, 1985. Salinity pollution from irrigated agriculture. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 40: 48–52.
Emmerson, M. C. & D. Raffaelli, 2004. Predator-prey body size, interaction strength and the stability of a real food web. Journal of Animal Ecology 73: 399–409.
Ferreira, V., V. Gulis & M. A. S. Graça, 2006. Whole-stream nitrate addition affects litter decomposition and associated fungi but not invertebrates. Oecologia 149: 718–729.
Freitas, E. C. & O. Rocha, 2011. Acute and chronic effects of sodium and potassium on the tropical freshwater cladoceran Pseudosida ramosa. Ecotoxicology 20: 88–96.
Fuller, C. L., M. A. Evans-White & S. A. Entrekin, 2015. Growth and stoichiometry of a common aquatic detritivore respond to changes in resource stoichiometry. Oecologia 177: 837–848.
Gleick, P. H., 1996. Basic water requirements for human activities: meeting basic needs. Water International 21: 83–92.
Goetsch, P. A. & C. G. Palmer, 1997. Salinity tolerances of selected macroinvertebrates of the Sabie River, Kruger National Park, South Africa. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 32: 32–41.
Graça, M. A. S., 2001. The role of invertebrates on leaf litter decomposition in streams - a review. International Review of Hydrobiology 86: 383–393.
Graça, M. A. S., R. C. F. Ferreira & C. N. Coimbra, 2001. Litter processing along a stream gradient: the role of invertebrates and decomposers. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 20: 408–420.
Griffith, M. B., 2014. Natural variation and current reference for specific conductivity and major ions in wadeable streams of the conterminous USA. Freshwater Science 33: 1–17.
Gulis, V. & K. Suberkropp, 2003. Leaf litter decomposition and microbial activity in nutrient-enriched and unaltered reaches of a headwater stream. Freshwater Biology 48: 123–134.
Hagen, E. M., J. R. Webster & E. F. Benfield, 2006. Are leaf breakdown rates a useful measure of stream integrity along an agricultural landuse gradient? Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25: 330–343.
Hall, R. O., J. B. Wallace & S. L. Eggert, 2000. Organic matter flow in stream food webs with reduced detrital resource base. Ecology 81: 3445–3463.
Hart, B. T., P. Bailey, R. Edwards, K. Hortle, K. James, A. McMahon, C. Meredith & K. Swadling, 1991. A review of the salt sensitivity of the Australian freshwater biota. Hydrobiologia 210: 105–144.
Hassell, K. L., B. J. Kefford & D. Nugegoda, 2006. Sub-lethal and chronic salinity tolerances of three freshwater insects: Cloeon sp. and Centroptilum sp. (Ephemeroptera: Baetidae) and Chironomus sp. (Diptera: Chironomidae). Journal of Experimental Biology 209: 4024–4032.
Johnson, B. R., P. C. Weaver, C. T. Nietch, J. M. Lazorchak, K. A. Struewing & D. H. Funk, 2015. Elevated major ion concentrations inhibit larval mayfly growth and development. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 34: 167–172.
Kaspari, M., S. P. Yanoviak, R. Dudley, M. Yuan & N. A. Clay, 2009. Sodium shortage as a constraint on the carbon cycle in an inland tropical rainforest. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106: 19405–19409.
Kaushal, S. S., P. M. Groffman, G. E. Likens, K. T. Belt, W. P. Stack, V. R. Kelly, L. E. Band & G. T. Fisher, 2005. Increased salinization of fresh water in the northeastern United States. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102: 13517–13520.
Kefford, B. J., P. J. Papas, L. Metzeling & D. Nugegoda, 2004. Do laboratory salinity tolerances of freshwater animals correspond with their field salinity? Environmental Pollution 129: 355–362.
Kelly, V. R., G. M. Lovett, K. C. Weathers, S. Findlay, D. Strayer, D. J. Burns & G. E. Likens, 2008. Long-term sodium chloride retention in a rural watershed: legacy effects of road salt on streamwater concentration. Environmental Science and Technology 42: 410–415.
Marshall, W. S. & M. Grosell, 2006. Ion transport, osmoregulation, and acid-base balance. The physiology of fishes 3: 177–230.
Moore, D. J., R. H. Reed & D. P. Stewart, 1985. Responses of Cyanobacteria to low level osmotic stress: implications for the use of buffers. Microbiology 131: 1267–1272.
Musto, A. L., 2013. Trace elements and macroinvertebrate community structure across a gradient of shale gas extraction. University of Central Arkansas.
Nimiroski, M. T. & M. C. Waldren, 2002. Sources of sodium and chloride in the Scituate Reservoir drainage, Rhode Island. US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey.
Odum, E. P., J. T. Finn & E. H. Franz, 1979. Perturbation theory and the subsidy-stress gradient. Bioscience 29: 349–352.
Olmstead, S. M., L. A. Muehlenbachs, J. S. Shih, Z. Y. Chu & A. J. Krupnick, 2012. Shale gas development impacts on surface water quality in Pennsylvania. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 110: 4962–4967.
Raven, J. A., 1982. The energetics of freshwater algae; energy requirements for biosynthesis and volume regulation. New Phytologist 92: 1–20.
Rose, S., 2007. The effects of urbanization on the hydrochemistry of base flow within the Chattahoochee River Basin (Georgia, USA). Journal of Hydrology 341: 42–54.
Rossi, L., E. A. Fano & A. Basset, 1983. Sympatric coevolution of the trophic niche of two detrivorous isopods, Asellus aquaticus and Proasellus coxalis. Oikos 40: 208–215.
Scheibener, S. A., V. S. Richardi & D. B. Buchwalter, 2015. Comparative sodium transport patterns provide clues for understanding salinity and metal responses in aquatic insects. Aquatic Toxicology 171: 20–29.
Sleator, R. D. & C. Hill, 2001. Bacterial osmoadaptation: the role of osmolytes in bacterial stress and virulence. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 26: 49–71.
Smith, R. A., R. B. Alexander & M. G. Wolman, 1987. Water-quality trends in the nation’s rivers. Science 235: 1607–1615.
Strayer, D. L. & D. Dudgeon, 2010. Freshwater biodiversity conservation: recent progress and future challenges. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 29: 344–358.
Swan, C. M. & M. A. Palmer, 2006. Preferential feeding by an aquatic consumer mediates non-additive decomposition of speciose leaf litter. Oecologia 149: 107–114.
Sweeney, B. W. & R. L. Vannote, 1978. Size variation and the distribution of hemimetabolous aquatic insects: two thermal equilibrium hypotheses. Science 200: 444–446.
Tank, J. L., E. J. Rosi-Marshall, N. A. Griffiths, S. A. Entrekin & M. L. Stephen, 2010. A review of allochthonous organic matter dynamics and metabolism in streams. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 29: 118–146.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), 2004. Evaluation of impacts to underground sources of drinking water by hydraulic fracturing of coalbed methane reservoirs study, Vol. 2010. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Washington, D.C.
US EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), 2013. National Rivers and Streams Assessment 2008–2009 results.
Wallace, J. B., J. R. Webster & T. F. Cuffney, 1982. Stream detritus dynamics - regulation by invertebrate consumers. Oecologia 53: 197–200.
Wesner, J. S., J. M. Kraus, T. S. Schmidt, D. M. Walters & W. H. Clements, 2014. Metamorphosis enhances the effects of metal exposure on the mayfly, Centroptilum triangulifer. Environmental Science & Technology 48: 10415–10422.
Woodward, G. & P. Warren, 2007. Body Size and Predatory Interaction in Freshwaters: Scaling from Individuals to Communities. In Hildrew, A. G., D. G. Raffaelli & R. Edmonds-Brown (eds), Body size: The structure and function of aquatic ecosystems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Acknowledgments
Lucy Baker, David Costello, Chris Fuller, Brittany Furtado, Brent Johnson, Katherine Larson, Stephanie Stoughton, Manuel Graça, Raelyn Rowland, and two anonymous reviewers contributed valuable comments that improved the experimental design and the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Verónica Jacinta Lopes Ferreira
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tyree, M., Clay, N., Polaskey, S. et al. Salt in our streams: even small sodium additions can have negative effects on detritivores. Hydrobiologia 775, 109–122 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2718-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2718-6