Abstract
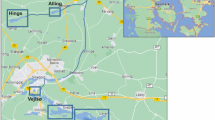
The effect on bottom organisms of periodic freezing of the upper layer of intertidal sediments during abnormal cold winters has been studied for a long time in seas of a moderate climatic zone. However, the effect of ice cover every year on intertidal communities in polar seas is still poorly investigated. Seasonal and long-term variation in the structure of intertidal soft-bottom communities in two small bights in the White Sea with annual ice cover was studied for over two decades. Sampling was carried out four times a year, in the hydrological spring, summer, autumn, and winter. It was found that bottom macrobenthic communities at upper and lower horizons of the intertidal distinctly differed in the studied sites. Periodic changes caused by the effect of abnormal ice conditions, including the partial removal by ice of sediment with in situ organisms, were discovered. Recovery of communities after disturbance normally took less than half a year. Communities at the lower and upper horizons of the intertidal zone were more stable than intermediate communities, which led to periodic shifts of the biological border between lower and upper intertidal assemblages.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Recently, this index is often referred to as the Bray–Curtis similarity.
References
Babkov, A. I., 1982. A short hydrological characteristics of the Chupa Inlet of the White Sea. Ecological Investigations of the Possible Objects from the Fauna of the White Sea for the Mariculture, Leningrad: 3–16. (In Russian).
Babkov, A. I. & V. V. Lukanin, 1985. Spring’s alterations of salinity and temperature of surface waters of the White Sea and its influence on distribution littoral and sublittoral organisms. Biocenoses of the Chupa Inlet of the White Sea and their seasonal dynamics, Nauka Publishers, Leningrad: 84–88. (In Ruusuan).
Beukema, J. J., 1985. Zoobenthos survival during sever winters on high and low tidal flats in the Dutch Wadden Sea. In Gray, J. S. & M. E. Christiansen (eds), Marine Biology of Polar Regions and Effects of Stress on Marine Organisms. Wiley, New York: 351–361.
Beukema, J. J., 1992a. Long-term and recent changes in the benthic macrofauna living on tidal flats in the Western part of the Wadden Sea. Netherlands Institute for Sea Research Publication Series 20: 135–141.
Beukema, J. J., 1992b. Expected changes in the Wadden Sea benthos in warmer word: lessons from with mild winters. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 30: 73–79.
Beukema, J. J., R. Dekker, K. Essink & H. Michaelis, 2001. Synchronized reproductive success of the main bivalve species in the Wadden Sea: causes and consequences. Marine Ecology Progress Series 211: 143–155.
Denisenko, S. G., 2006. Shannon information measuring and its application to estimation of a biodiversity (on example of marine zoobenthos). In Sirenko B. I. & S. V. Vasilenko (eds), Marine Invertebrates of Arctic, Antarctic and Subantarctic, Saint Petersburg: 35–46. (In Russian).
Dörjes, J., H. Michaelis & D. Rhode, 1986. Long-term studies of macrozoobenthos in intertidal and shallow subtidal habitats near the island of Norderney (East Frisian coast, Germany). Hydrobiologia 142: 217–232.
Fedyakov, V. V. & A. M. Sheremetevsky, 1991. General features of mud-sandy biotopes of the intertidal zone near Kartesh Point (Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea). In Naumov A. D. & V. V. Fedyakov (eds), Benthos of the White Sea: Populations, Communities, Fauna, Leningrad: 148–157. (In Russian).
Ibanez, F. & J.-C. Dauvin, 1988. Long-term changes (1977–1987) in a muddy fine sand Abra alba – Melinna palmata community from Western English Channel: multivariate time-series analysis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 49: 65–81.
Kuznetzov, V. V., 1960. The White Sea and Biological Peculiarities of its Flora and Fauna. Academy of Sciences Publishers, Moscow. (In Russian).
Maximovich, N. V. & A. V. Guerassimova, 2003. Life history characteristics of the clam Mya arenaria in the White Sea. Helgoland Marine Research 57: 91–99.
McCook, L. J. & R. O. Chapman, 1991. Community succession following massive ice-scour on an exposed rocky shore: effects of Fucus canopy algae and of mussels during late succession. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 154: 137–169.
Naumov, A. D., 1991. On the macrobenthos communities investigation. In Naumov A. D. & V. V. Fedyakov (eds), Benthos of the White Sea: Populations, Communities, Fauna, Leningrad: 127–147. (In Russian).
Naumov, A. D., 2007. Long-term investigations of the littoral benthos of the White Sea in the Chupa Guba (Kandalaksha Bay): seasonal and long-term dynamics of the biomass of the eelgrass Zostera marina. Complex Investigations of Processes, Characteristics and Recourses of Russian Seas of North European Basin 2, Apatity: 493–502. (In Russian).
Naumov, A. D., 2011. Abnormal Casting Ashore of Starfishes in the Dvina Bay in 1990. St. Petersburg. (In Russian).
Naumov, A. D., V. V. Khalaman & M. V. Fokin, 2009. Long-term dynamics of the abundance of several intertidal polychaetes in two inlets of Kandalaksha Bay (White Sea). Russian Journal of Marine Biology 35: 381–387.
Pesenko, Yu. A., 1982. Principals of numeric analysis in faunistic investigations. Nauka Publishers, Moscow. (In Russian).
Petraitis, P. S., E. T. Methratta, E. C. Rhile, N. A. Vidargas & S. R. Dudgeon, 2009. Experimental confirmation of multiple states in a marine ecosystem. Oecologia 161: 139–148.
Scrosati, R. & K. L. Eckersley, 2007. Thermal insulation of the intertidal zone by the ice foot. Journal of Sea Research 58: 331–334.
Shannon, C. E., 1948. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana.
Varfolomeeva M. & A. Naumov, 2012. Long-term temporal and spatial variation of macrobenthos in the intertidal soft-bottom flats of two small bights (Chupa Inlet, Kandalaksha Bay, White Sea). doi:10.1007/s10750-012-1341-4.
Warwick, R. M., 1986. A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthos communities. Marine Biology 92: 557–562.
Warwick, R. M., T. H. Pearson & Ruswahyuni, 1987. Detection of pollution effects on marine macrobenthos: further evaluation of the species abundance/biomass method. Marine Biology 95: 193–200.
Acknowledgments
The material was mainly collected by three people: Dr. V.V. Fedaykov participated in the work between 1987 and 1999, Dr. M.V. Fokin between 2000 and 2009, and the author since 1989 to the present. I am very grateful to both named scientists for their longstanding collaboration. Our colleagues Dr. K.V. Galaktionov, Dr. K.E. Nikolaev, and Dr. I.A. Levakin kindly helped us in winter fieldwork over the last 10 years. I acknowledge their invaluable assistance. I thank numerous students of Saint Petersburg State University for their help with fieldwork. I am very grateful to anonymous reviewers and Guest Editor for their useful comments. This study was funded from different sources: as a scheduled research topic of the Zoological Institute RAS, by the research grant from the Commission of the European Communities INCO-Copernicus-II ICA2-CT-2000-10053, and by the program of fundamental research of the Branch of Biological Sciences Russian Academy of Sciences “Biological resources of Russia: estimation of state and essential principles of monitoring” and by the program of fundamental research of the Presidium of the Russian Academy of Sciences “Biological diversity”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editor: A. A. Sukhotin / Long-term research on marine ecosystems in the White Sea, Russia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naumov, A.D. Long-term fluctuations of soft-bottom intertidal community structure affected by ice cover at two small sea bights in the Chupa Inlet (Kandalaksha Bay) of the White Sea. Hydrobiologia 706, 159–173 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1339-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1339-y