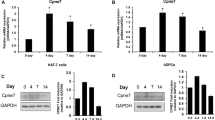
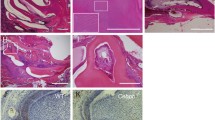
Abstract
Our previous research has shown that the extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) is expressed during and may function in the early development of tooth germs. In the present study, we observed the specific expression of EMMPRIN in ameloblasts and odontoblasts during the middle and late stages of tooth germ development using immunohistochemistry. Furthermore, to extend our understanding of the function of EMMPRIN in odontogenesis, we used an anti-EMMPRIN function-blocking antibody to remove EMMPRIN activity in tooth germ culture in vitro. Both the formation and mineralisation of dental hard tissues were suppressed in the tooth germ culture after the abrogation of EMMPRIN. Meanwhile, significant reductions in VEGF, MMP-9, ALPL, ameloblastin, amelogenin and enamelin expression were observed in antibody-treated tooth germ explants compared to control and normal serum-treated explants. The current results illustrate that EMMPRIN may play a critical role in the processing and maturation of the dental matrix.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal SM, Yong VW (2011) The many faces of EMMPRIN—roles in neuroinflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812(2):213–219. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.07.018
Berditchevski F, Chang S, Bodorova J, Hemler ME (1997) Generation of monoclonal antibodies to integrin associated proteins. Evidence that α3β1 complexes with EMMPRIN/basigin/OX47/M6. J Biol Chem 272(46):29174–29180
Biswas C, Nugent MA (1987) Membrane association of collagenase stimulatory factor(s) from B-16 melanoma cells. J Cell Biochem 35(3):247–258. doi:10.1002/jcb.240350307
Biswas C, Zhang Y, DeCastro R, Guo H, Nakamura T, Kataoka H, Nabeshima K (1995) The human tumor cell-derived collagenasestimulatory factor (renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of theimmunoglobulin superfamily. Cancer Res 55(2):434–439
Bougatef F, Quemener C, Kellouche S, Naïmi B, Podgorniak MP, Millot G, Gabison EE, Calvo F, Dosquet C, Lebbé C, Menashi S, Mourah S (2009) EMMPRIN promotes angiogenesis through hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha-mediated regulation of soluble VEGF isoforms and their receptor VEGFR-2. Blood 114(27):5547–5556. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-04-217380
Cao Z, Xiang J, Li C (2009) Expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer and enhancement of the production of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38(8):880–885. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.03.004
Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M, Fahrig M, Vandenhoeck A, Harpal K, Eberhardt C, Declercq C, Pawling J, Moons L, Collen D, Risau W, Nagy A (1996) Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature 380(6573):435–439. doi:10.1038/380435a0
Caudroy S, Polette M, Tournier JM, Burlet H, Toole B, Zucker S, Birembaut P (1999) Expression of the extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) and the matrix metalloproteinase-2 in bronchopulmonary and breast lesions. J Histochem Cytochem 47(12):1575–1580. doi:10.1177/002215549904701209
Chen X, Chen G, Feng L, Jiang Z, Guo W, Yu M, Tian W (2014) Expression of Nfic during root formation in first mandibular molar of rat. J Mol Histol (Epub ahead of print). doi:10.1007/s10735-014-9588-x
Ellis SM, Nabeshima K, Biswas C (1989) Monoclonal antibody preparation and purification of a tumor cell collagenase-stimulatory factor. Cancer Res 49(12):3385–3391
Emingil G, Tervahartiala T, Mãntylã P, Määttä M, Sorsa T, Atilla G (2006) Gingival crevicular fluid matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-7, extracellular MMP inducer, and tissue inhibitor of MMP-1 levels in periodontal disease. J Periodontol 77(12):2040–2050. doi:10.1902/jop.2006.060144
Fadool JM, Linser PJ (1993) Differential glycosylation of the 5A11/HT7 antigen by neural retina and epithelial tissues in the chicken. J Neurochem 60(4):1354–1364. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03296.x
Fan QW, Kadomatsu K, Uchimura K, Muramatsu T (1998) Embigin/basigin subgroup of the immunoglobulin superfamily: different modes of expression during mouse embryogenesis and correlated expression with carbohydrate antigenic markers. Dev Growth Differ 40(3):277–286. doi:10.1046/j.1440-169X.1998.t01-1-00003.x
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O’Shea KS, Powell-Braxton L, Hillan KJ, Moore MW (1996) Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature 380(6573):439–442. doi:10.1038/380439a0
Halestrap AP (2012) The monocarboxylate transporter family—structure and functional characterization. IUBMB Life 64(1):1–9. doi:10.1002/iub.573
Huang Z, Wang C, Wei L, Wang J, Fan Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Chen T (2008) Resveratrol inhibits EMMPRIN expression via P38 and ERK1/2 pathways in PMA-induced THP-1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374(3):517–521. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.07.058
Huang Z, Hu X, Lin C, Chen S, Huang F, Zhang Y (2014) Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in human embryonic tooth germ. J Mol Histol (Epub ahead of print). doi:10.1007/s10735-014-9580-5
Igakura T, Kadomatsu K, Kaname T, Muramatsu H, Fan QW, Miyauchi T, Toyama Y, Kuno N, Yuasa S, Takahashi M, Senda T, Taguchi O, Yamamura K, Arimura K, Muramatsu T (1998) A null mutation in basigin, an immunoglobulin superfamily member, indicates its important roles in peri-implantation development and spermatogenesis. Dev Biol 194(2):152–165. doi:10.1006/dbio.1997.8819
Kanyenda LJ, Verdile G, Boulos S, Krishnaswamy S, Taddei K, Meloni BP, Mastaglia FL, Martins RN (2011) The dynamics of CD147 in Alzheimer’s disease development and pathology. J Alzheimers Dis 26(4):593–605. doi:10.3233/JAD-2011-110584
Kero D, Kalibovic Govorko D, Vukojevic K, Cubela M, Soljic V, Saraga-Babic M (2014) Expression of cytokeratin 8, vimentin, syndecan-1 and ki-67 during human tooth development. J Mol Histol 45(6):627–640. doi:10.1007/s10735-014-9592-1
Kirk P, Wilson MC, Heddle C, Brown MH, Barclay AN, Halestrap AP (2000) CD147 is tightly associated with lactate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 and facilitates their cell surface expression. EMBO J 19(15):3896–3904. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.15.3896
Lee S, Jilani SM, Nikolova GV, Carpizo D, Iruela-Arispe ML (2005) Processing of VEGF-A by matrix metalloproteinases regulates bioavailability and vascular patterning in tumors. J Cell Biol 169(4):681–691. doi:10.1083/jcb.200409115
Lei H, Liu H, Ding Y, Ge L (2014) Immunohistochemical localization of Pax6 in the developing tooth germ of mice. J Mol Histol 45(4):373–379. doi:10.1007/s10735-014-9564-5
Li R, Huang L, Guo H, Toole BP (2001) Basigin (murine EMMPRIN) stimulates matrix metalloproteinase production by fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol 186(3):371–379. doi:10.1002/1097-4652(2000)9999:999<000:AID-JCP1042>3.0.CO;2-8
Line SR (2003) Variation of tooth number in mammalian dentition: connecting genetics, development, and evolution. Evol Dev 5(3):295–304. doi:10.1046/j.1525-142X.2003.03036.x
Liu L, Li C, Cai X, Xiang J, Cao Z, Dong W (2010) The temporal expression and localization of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) during the development of periodontitis in an animal model. J Periodontal Res 45(4):541–549. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0765.2010.01269.x
Määttä M, Tervahartiala T, Kaarniranta K, Tang Y, Yan L, Tuukkanen J, Sorsa T (2006) Immunolocalization of EMMPRIN (CD147) in the human eye and detection of soluble form of EMMPRIN in ocular fluids. Curr Eye Res 31(11):917–924. doi:10.1080/02713680600932290
Mishra B, Kizaki K, Sato T, Ito A, Hashizume K (2012) The role of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) in the regulation of bovine endometrial cell functions. Biol Reprod 87(6):149. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.112.102152
Mitsiadis TA, Smith MM (2006) How do genes make teeth to order through development? J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 306(3):177–182. doi:10.1002/jez.b.21104
Mitsiadis TA, Muramatsu T, Muramatsu H, Thesleff I (1995) Midkine (MK), a heparin-binding growth/differentiation factor, is regulated by retinoic acid and epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the developing mouse tooth, and affects cell proliferation and morphogenesis. J Cell Biol 129(1):267–281. doi:10.1083/jcb.129.1.267
Miwa Y, Fujita T, Sunohara M, Sato I (2008) Immunocytochemical localization of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 of the human deciduous molar tooth germ development in the human fetus. Ann Anat 190(3):246–251. doi:10.1016/j.aanat.2007.11.006
Nabeshima K, Suzumiya J, Nagano M, Ohshima K, Toole BP, Tamura K, Iwasaki H, Kikuchi M (2004) Emmprin, a cell surface inducer of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), is expressed in T-cell lymphomas. J Pathol 202(3):341–351. doi:10.1002/path.1518
Pispa J, Thesleff I (2003) Mechanisms of ectodermal organogenesis. Dev Biol 262(2):195–205. doi:10.1016/S0012-1606(03)00325-7
Rocha CA, Cestari TM, Vidotti HA, de Assis GF, Garlet GP, Taga R (2014) Sintered anorganic bone graft increases autocrine expression of VEGF, MMP-2 and MMP-9 during repair of critical-size bone defects. J Mol Histol 45(4):447–461. doi:10.1007/s10735-014-9565-4
Sameshima T, Nabeshima K, Toole BP, Yokogami K, Okada Y, Goya T, Koono M, Wakisaka S (2000) Glioma cell extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) (CD147) stimulates production of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases and activated gelatinase A in co-cultures with brain-derived fibroblasts. Cancer Lett 157(2):177–184. doi:10.1016/S0304-3835(00)00485-7
Sangboonruang S, Thammasit P, Intasai N, Kasinrerk W, Tayapiwatana C, Tragoolpua K (2014) EMMPRIN reduction via scFv-M6-1B9 intrabody affects α3β1-integrin and MCT1 functions and results in suppression of progressive phenotype in the colorectal cancer cell line Caco-2. Cancer Gene Ther 21(6):246–255. doi:10.1038/cgt.2014.24
Schwab W, Harada H, Goetz W, Nowicki M, Witt M, Kasper M, Barth K (2007) Immunocytochemical and biochemical detection of EMMPRIN in the rat tooth germ: differentiation-dependent co-expression with MMPs and co-localization with caveolin-1 in membrane rafts of dental epithelial cells. Histochem Cell Biol 128(3):195–203. doi:10.1007/s00418-007-0313-7
Su J, Chen X, Kanekura T (2009) A CD147-targeting siRNA inhibits the proliferation, invasiveness, and VEGF production of human malignant melanoma cells by down-regulating glycolysis. Cancer Lett 273(1):140–147. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.07.034
Sun J, Hemler ME (2001) Regulation of MMP-1 and MMP-2 production through CD147/extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer interactions. Cancer Res 61(5):2276–2281
Tang W, Chang SB, Hemler ME (2004) Links between CD147 function, glycosylation, and caveolin-1. Mol Biol Cell 15(9):4043–4050. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-05-0402
Tang Y, Nakada MT, Rafferty P, Laraio J, McCabe FL, Millar H, Cunningham M, Snyder LA, Bugelski P, Yan L (2006) Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by EMMPRIN via the PI3 K-Akt signaling pathway. Mol Cancer Res 4(6):371–377. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-06-0042
Tang R, Wang Q, Du J, Yang P, Wang X (2013) Expression and localization of Nell-1 during murine molar development. J Mol Histol 44(2):175–181. doi:10.1007/s10735-012-9472-5
Taylor PM, Woodfield RJ, Hodgkin MN, Pettitt TR, Martin A, Kerr DJ, Wakelam MJ (2002) Breast cancer cell-derived EMMPRIN stimulates fibroblast MMP2 release through a phospholipase A(2) and 5-lipoxygenase catalyzed pathway. Oncogene 21(37):5765–5772. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205702
Wang B, Li H, Liu Y, Lin X, Lin Y, Wang Y, Hu X, Zhang Y (2014) Expression patterns of WNT/β-CATENIN signaling molecules during human tooth development. J Mol Histol 45(5):487–496. doi:10.1007/s10735-014-9572-5
Wilson MC, Meredith D, Fox JE, Manoharan C, Davies AJ, Halestrap AP (2005) Basigin (CD147) is the target for organomercurial inhibition of monocarboxylate transporter isoforms 1 and 4: the ancillary protein for the insensitive MCT2 is EMBIGIN (gp70). J Biol Chem 280(29):27213–27221. doi:10.1074/jbc.M411950200
Xie M, Jiao T, Chen Y, Xu C, Li J, Jiang X, Zhang F (2010) EMMPRIN (basigin/CD147) is involved in the morphogenesis of tooth germ in mouse molars. Histochem Cell Biol 133(5):585–594. doi:10.1007/s00418-010-0697-7
Yurchenko V, Pushkarsky T, Li JH, Dai WW, Sherry B, Bukrinsky M (2005) Regulation of CD147 cell surface expression: involvement of the proline residue in the CD147 transmembrane domain. J Biol Chem 280(17):17013–17019. doi:10.1074/jbc.M412851200
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30900848), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai (Grant No. 09DZ2271100), and the Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (Grant No. T0202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, M., Xing, G., Hou, L. et al. Functional role of EMMPRIN in the formation and mineralisation of dental matrix in mouse molars. J Mol Hist 46, 21–32 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-014-9603-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-014-9603-2