Abstract
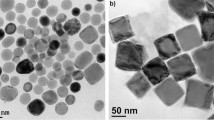
Iron nanoparticles were synthesized without a chilling device in a condensation system of gases vaporized from iron pentacarbonyls as starting precursors. The size distribution of the synthesized iron particles was wider, namely, ranging from 10 to 100 nm, than that of the particles rapidly cooled on the surface of a chiller. The oxide shell thicknesses were analyzed quantitatively in synthesized powders, along with their microstructures and magnetic properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Yao, Y.D., Chen, Y.Y., Lee, S.F., et al., Magnetic and Thermal Studies of Nano-Size Co and Fe Particles, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2002, vol. 239, pp. 249–251.
Choi, C.J., Dong, X.L., and Kim, B.K., Characterization of Fe and Co Nanoparticles Synthesized by Chemical Vapor Condensation, Scr. Mater., 2001, vol. 44, pp. 2225–2229.
Dong, X.L., Choi, C.J., and Kim, B.K., Structural and Magnetic Characterization of Fe Nanoparticles Synthesized by Chemical Vapor Condensation Process, J. Appl. Phys., 2002, vol. 92, pp. 5380–5385.
Choi, C.J., Tolochko, O.V., and Kim, B.K., Preparation of Iron Nanoparticles by Chemical Vapor Condensation, Mater. Lett., 2002, vol. 56, pp. 289–294.
Mathur, M.C.A., Hudson, G.F., Martin, R.J., et al., Kinetic Studies of Iron Metal Particle Degradation at Various Temperature and Humidity Conditions, IEEE Trans. Magn., 1991, vol. 27, pp. 4675–4677.
Kishimoto, M., Kitahata, S., and Amemiya, M., Morphology and Magnetic Properties of the Iron Oxide Layer Formed on Iron Acicular Particles, IEEE Trans. Magn., 1986, vol. 22, pp. 732–734.
Zhao, X.Q., Liu, B.X., Liang, Y., and Hu, Z.Q., Oxidation Behavior and Magnetic Properties of Metallic Ultrafine Particles, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1996, vol. 164, pp. 401–410.
Tyson, W.R. and Miller, W.A., Surface Free Energies of Solid Metals: Estimation from Liquid Surface Tension Measurements, Surf. Sci., 1977, vol. 62, pp. 267–276.
Kodama, R.H., Magnetic Nanoparticles, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 1999, vol. 200, pp. 359–372.
Gong, W., Zhao, H., Li, Z., and Chen, J., Ultrafine Particles of Fe, Co, and Ni Ferromagnetic Metals, J. Appl. Phys., 1991, vol. 69, pp. 5119–5121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original English Text Copyright © 2005 by Fizika i Khimiya Stekla, Lee, Jang, D. Kim, Tolochko, B. Kim.
This article was submitted by the authors in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.W., Jang, T.S., Kim, D. et al. Nanocrystalline Iron Particles Synthesized without Chilling by Chemical Vapor Condensation. Glass Phys Chem 31, 545–548 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10720-005-0096-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10720-005-0096-7