Abstract
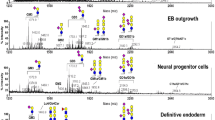
Glycosphingolipids (GSLs) are composed of complex glycans linked to sphingosines and various fatty acid chains. Antibodies against several GSLs designated as stage-specific embryonic antigens (SSEAs), have been widely used to characterize differentiation of embryonic stem (ES) cells. In view of the cross-reactivities of these antibodies with multiple glycans, a few laboratories have employed advanced mass spectrometry (MS) technologies to define the dynamic changes of surface GSLs upon ES differentiation. However, the amphiphilic nature and heterogeneity of GSLs make them difficult to decipher. In our studies, systematic survey of GSL expression profiles in human ES cells and differentiated derivatives was conducted, primarily with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization MS (MALDI-MS) and MS/MS analyses. In addition to the well-known ES-specific markers, SSEA-3 and SSEA-4, several previously undisclosed globo- and lacto-series GSLs, including Gb4Cer, Lc4Cer, fucosyl Lc4Cer, Globo H, and disialyl Gb5Cer were identified in the undifferentiated human ES and induced pluripotent stem cells. Furthermore, during differentiation to embryoid body outgrowth, the core structures of GSLs switched from globo- and lacto- to ganglio-series. Lineage-specific differentiation was also marked by alterations of specific GSLs. During differentiation into neural progenitors, core structures shifted to primarily ganglio-series dominated by GD3. GSL patterns shifted to prominent expression of Gb4Cer with little SSEA-3 and- 4 or GD3 during endodermal differentiation. Several issues relevant to MS analysis and novel GSLs in ES cells were discussed. Finally, unique GSL signatures in ES and cancer cells are exploited in glycan-targeted anti-cancer immunotherapy and their mechanistic investigations were discussed using anti-GD2 mAb and Globo H as examples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang Y.J., Kuo H.H., Lin C.H., Chen Y.Y., Yang B.C., Cheng Y.Y., Yu A.L., Khoo K.H., Yu J.: Switching of the core structures of glycosphingolipids from globo- and lacto- to ganglio-series upon human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107(52), 22564–22569 (2010). doi:10.1073/pnas.1007290108
Liang Y.J., Yang B.C., Chen J.M., Lin Y.H., Huang C.L., Cheng Y.Y., Hsu C.Y., Khoo K.H., Shen C.N., Yu J.: Changes in glycosphingolipid composition during differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to ectodermal or endodermal lineages. Stem Cells. 29(12), 1995–2004 (2011). doi:10.1002/stem.750
Barone A., Benktander J., Angstrom J., Aspegren A., Bjorquist P., Teneberg S., Breimer M.E.: Structural complexity of non-acid glycosphingolipids in human embryonic stem cells grown under feeder-free conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 288(14), 10035–10050 (2013). doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.436162
Barone A., Saljo K., Benktander J., Blomqvist M., Mansson J.E., Johansson B.R., Molne J., Aspegren A., Bjorquist P., Breimer M.E., Teneberg S.: Sialyl-lactotetra, a novel cell surface marker of undifferentiated human pluripotent stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 289(27), 18846–18859 (2014). doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.568832
Pera, M.F., Reubinoff, B., Trounson, A.: Human embryonic stem cells. J. Cell Sci. 113 ( Pt 1), 5–10 (2000).
Hanna J., Cheng A.W., Saha K., Kim J., Lengner C.J., Soldner F., Cassady J.P., Muffat J., Carey B.W., Jaenisch R.: Human embryonic stem cells with biological and epigenetic characteristics similar to those of mouse ESCs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107(20), 9222–9227 (2010). doi:10.1073/pnas.1004584107
Tesar P.J., Chenoweth J.G., Brook F.A., Davies T.J., Evans E.P., Mack D.L., Gardner R.L., McKay R.D.: New cell lines from mouse epiblast share defining features with human embryonic stem cells. Nature. 448(7150), 196–199 (2007). doi:10.1038/nature05972
Hakomori S., Ishizuka I.: Glycolipids: Animal. Encycl. Life Sci. (2006). doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0000706.pub2
Hakomori S.: Structure and function of glycosphingolipids and sphingolipids: recollections and future trends. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1780(3), 325–346 (2008)
Hakomori S.: Glycosynaptic microdomains controlling tumor cell phenotype through alteration of cell growth, adhesion, and motility. FEBS Lett. 584(9), 1901–1906 (2010)
Yu R.K., Macala L.J., Taki T., Weinfield H.M., Yu F.S.: Developmental changes in ganglioside composition and synthesis in embryonic rat brain. J. Neurochem. 50(6), 1825–1829 (1988)
Yu R.K.: Development regulation of ganglioside metabolism. Prog. Brain Res. 101, 31–44 (1994)
Prinetti A., Loberto N., Chigorno V., Sonnino S.: Glycosphingolipid behaviour in complex membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1788(1), 184–193 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.09.001
Sonnino S., Prinetti A.: Sphingolipids and membrane environments for caveolin. FEBS Lett. 583(4), 597–606 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2009.01.007
Guan F., Handa K., Hakomori S.I.: Specific glycosphingolipids mediate epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human and mouse epithelial cell lines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106(18), 7461–7466 (2009). doi:10.1073/pnas.0902368106
Guan, F., Schaffer, L., Handa, K., Hakomori, S.I.: Functional role of gangliotetraosylceramide in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition process induced by hypoxia and by TGF-{beta}. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 24(12), 4889–4903 (2010). doi:10.1096/fj.10-162107
Kannagi R., Cochran N.A., Ishigami F., Hakomori S., Andrews P.W., Knowles B.B., Solter D.: Stage-specific embryonic antigens (SSEA-3 and −4) are epitopes of a unique globo-series ganglioside isolated from human teratocarcinoma cells. EMBO J. 2(12), 2355–2361 (1983)
Kannagi R., Levery S.B., Ishigami F., Hakomori S., Shevinsky L.H., Knowles B.B., Solter D.: New globoseries glycosphingolipids in human teratocarcinoma reactive with the monoclonal antibody directed to a developmentally regulated antigen, stage-specific embryonic antigen 3. J. Biol. Chem. 258(14), 8934–8942 (1983)
Solter D., Knowles B.B.: Monoclonal antibody defining a stage-specific mouse embryonic antigen (SSEA-1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 75(11), 5565–5569 (1978)
Shevinsky L.H., Knowles B.B., Damjanov I., Solter D.: Monoclonal antibody to murine embryos defines a stage-specific embryonic antigen expressed on mouse embryos and human teratocarcinoma cells. Cell. 30(3), 697–705 (1982)
Levy M., Futerman A.H.: Mammalian ceramide synthases. IUBMB Life. 62(5), 347–356 (2010). doi:10.1002/iub.319
D'Angelo, G., Uemura, T., Chuang, C.C., Polishchuk, E., Santoro, M., Ohvo-Rekila, H., Sato, T., Di Tullio, G., Varriale, A., D'Auria, S., Daniele, T., Capuani, F., Johannes, L., Mattjus, P., Monti, M., Pucci, P., Williams, R.L., Burke, J.E., Platt, F.M., Harada, A., De Matteis, M.A.: Vesicular and non-vesicular transport feed distinct glycosylation pathways in the Golgi. Nature 501(7465), 116–120 (2013). doi:10.1038/nature12423
Hakomori S.I.: Cell adhesion/recognition and signal transduction through glycosphingolipid microdomain. Glycoconj. J. 17(3–4), 143–151 (2000)
Ngamukote S., Yanagisawa M., Ariga T., Ando S., Yu R.K.: Developmental changes of glycosphingolipids and expression of glycogenes in mouse brains. J. Neurochem. 103(6), 2327–2341 (2007)
Kwak D.H., Yu K., Kim S.M., Lee D.H., Kim S.M., Jung J.U., Seo J.W., Kim N., Lee S., Jung K.Y., You H.K., Kim H.A., Choo Y.K.: Dynamic changes of gangliosides expression during the differentiation of embryonic and mesenchymal stem cells into neural cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 38(6), 668–676 (2006)
Lee D.H., Koo D.B., Ko K., Ko K., Kim S.M., Jung J.U., Ryu J.S., Jin J.W., Yang H.J., Do S.I., Jung K.Y., Choo Y.K.: Effects of daunorubicin on ganglioside expression and neuronal differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 362(2), 313–318 (2007)
Cho H.C., Liao C.H., Yu A.L., Yu J.: Surface markers in stem cells and cancer from the perspective of glycomic analysis. Int. J. Biol. Markers. 27(4), e344–e352 (2012). doi:10.5301/JBM.2012.10361
Breimer M.E.: Gal/non-gal antigens in pig tissues and human non-gal antibodies in the GalT-KO era. Xenotransplantation. 18(4), 215–228 (2011). doi:10.1111/j.1399-3089.2011.00644.x
Tang C., Lee A.S., Volkmer J.P., Sahoo D., Nag D., Mosley A.R., Inlay M.A., Ardehali R., Chavez S.L., Pera R.R., Behr B., Wu J.C., Weissman I.L., Drukker M.: An antibody against SSEA-5 glycan on human pluripotent stem cells enables removal of teratoma-forming cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 29(9), 829–834 (2011). doi:10.1038/nbt.1947
Matsumoto S., Nakao H., Kawabe K., Nonaka M., Toyoda H., Takishima Y., Kawabata K., Yamaguchi T., Furue M.K., Taki T., Okumura T., Yamazaki Y., Nakaya S., Kawasaki N., Kawasaki T.: A Cytotoxic Antibody Recognizing Lacto-N-fucopentaose I (LNFP I) on Human Induced Pluripotent Stem (hiPS) Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 290(33), 20071–20085 (2015). doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.657692
Stanley, P., Cummings, R.D.: Structures Common to Different Glycans. In: Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Freeze, H.H., Stanley, P., Bertozzi, C.R., Hart, G.W., Etzler, M.E. (eds.) Essentials of Glycobiology. Cold Spring Harbor (NY) (2009)
Zhou, D., Henion, T.R., Jungalwala, F.B., Berger, E.G., Hennet, T.: The beta 1,3-galactosyltransferase beta 3GalT-V is a stage-specific embryonic antigen-3 (SSEA-3) synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 275(30), 22631–22634 (2000). doi:10.1074/jbc.C000263200
Isshiki S., Togayachi A., Kudo T., Nishihara S., Watanabe M., Kubota T., Kitajima M., Shiraishi N., Sasaki K., Andoh T., Narimatsu H.: Cloning, expression, and characterization of a novel UDP-galactose:beta-N-acetylglucosamine beta1,3-galactosyltransferase (beta3Gal-T5) responsible for synthesis of type 1 chain in colorectal and pancreatic epithelia and tumor cells derived therefrom. J. Biol. Chem. 274(18), 12499–12507 (1999)
Zhou D., Berger E.G., Hennet T.: Molecular cloning of a human UDP-galactose:GlcNAcbeta1,3GalNAc beta1, 3 galactosyltransferase gene encoding an O-linked core3-elongation enzyme. Eur. J. Biochem. 263(2), 571–576 (1999)
Badcock G., Pigott C., Goepel J., Andrews P.W.: The human embryonal carcinoma marker antigen TRA-1–60 is a sialylated keratan sulfate proteoglycan. Cancer Res. 59(18), 4715–4719 (1999)
Schopperle W.M., DeWolf W.C.: The TRA-1–60 and TRA-1–81 human pluripotent stem cell markers are expressed on podocalyxin in embryonal carcinoma. Stem Cells. 25(3), 723–730 (2007). doi:10.1634/stemcells.2005-0597
Somasiri A., Nielsen J.S., Makretsov N., McCoy M.L., Prentice L., Gilks C.B., Chia S.K., Gelmon K.A., Kershaw D.B., Huntsman D.G., McNagny K.M., Roskelley C.D.: Overexpression of the anti-adhesin podocalyxin is an independent predictor of breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 64(15), 5068–5073 (2004). doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0240
Kelley T.W., Huntsman D., McNagny K.M., Roskelley C.D., Hsi E.D.: Podocalyxin: a marker of blasts in acute leukemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 124(1), 134–142 (2005). doi:10.1309/7BHLAHHU0N4MHT7Q
Natunen S., Satomaa T., Pitkanen V., Salo H., Mikkola M., Natunen J., Otonkoski T., Valmu L.: The binding specificity of the marker antibodies Tra-1–60 and Tra-1–81 reveals a novel pluripotency-associated type 1 lactosamine epitope. Glycobiology. 21(9), 1125–1130 (2011). doi:10.1093/glycob/cwq209
Ariga T., Bhat S., Kanda T., Yamawaki M., Tai T., Kushi Y., Kasama T., Handa S., Yu R.K.: Expression and localization of Lewis(x) glycolipids and GD1a ganglioside in human glioma cells. Glycoconj. J. 13(2), 135–145 (1996)
Bosslet K., Mennel H.D., Rodden F., Bauer B.L., Wagner F., Altmannsberger A., Sedlacek H.H., Wiegandt H.: Monoclonal antibodies against epitopes on ganglioside GD2 and its lactones. Markers for gliomas and neuroblastomas. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 29(3), 171–178 (1989)
Schnitzer J., Schachner M.: Cell type specificity of a neural cell surface antigen recognized by the monoclonal antibody A2B5. Cell Tissue Res. 224(3), 625–636 (1982)
Dubois C., Manuguerra J.C., Hauttecoeur B., Maze J.: Monoclonal antibody A2B5, which detects cell surface antigens, binds to ganglioside GT3 (II3 (NeuAc)3LacCer) and to its 9-O-acetylated derivative. J. Biol. Chem. 265(5), 2797–2803 (1990)
Zhang S., Zhang H.S., Cordon-Cardo C., Reuter V.E., Singhal A.K., Lloyd K.O., Livingston P.O.: Selection of tumor antigens as targets for immune attack using immunohistochemistry: II. Blood group-related antigens. Int. J. Cancer. 73(1), 50–56 (1997)
Zhang, S., Zhang, H.S., Reuter, V.E., Slovin, S.F., Scher, H.I., Livingston, P.O.: Expression of potential target antigens for immunotherapy on primary and metastatic prostate cancers. Clin. Cancer Res.: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 4(2), 295–302 (1998).
Chang W.W., Lee C.H., Lee P., Lin J., Hsu C.W., Hung J.T., Lin J.J., Yu J.C., Shao L.E., Yu J., Wong C.H., Yu A.L.: Expression of Globo H and SSEA3 in breast cancer stem cells and the involvement of fucosyl transferases 1 and 2 in Globo H synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105(33), 11667–11672 (2008). doi:10.1073/pnas.0804979105
Cheung S.K., Chuang P.K., Huang H.W., Hwang-Verslues W.W., Cho C.H., Yang W.B., Shen C.N., Hsiao M., Hsu T.L., Chang C.F., Wong C.H.: Stage-specific embryonic antigen-3 (SSEA-3) and beta3GalT5 are cancer specific and significant markers for breast cancer stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 113(4), 960–965 (2016). doi:10.1073/pnas.1522602113
Battula V.L., Shi Y., Evans K.W., Wang R.Y., Spaeth E.L., Jacamo R.O., Guerra R., Sahin A.A., Marini F.C., Hortobagyi G., Mani S.A., Andreeff M.: Ganglioside GD2 identifies breast cancer stem cells and promotes tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 122(6), 2066–2078 (2012). doi:10.1172/JCI59735
Lin J.J., Huang C.S., Yu J., Liao G.S., Lien H.C., Hung J.T., Lin R.J., Chou F.P., Yeh K.T., Yu A.L.: Malignant phyllodes tumors display mesenchymal stem cell features and aldehyde dehydrogenase/disialoganglioside identify their tumor stem cells. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 16(2), R29 (2014). doi:10.1186/bcr3631
Yu, A.L., Uttenreuther-Fischer, M.M., Huang, C.S., Tsui, C.C., Gillies, S.D., Reisfeld, R.A., Kung, F.H.: Phase I trial of a human-mouse chimeric anti-disialoganglioside monoclonal antibody ch14.18 in patients with refractory neuroblastoma and osteosarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol.: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 16(6), 2169–2180 (1998).
Yu, A.L., Gilman, A.L., Ozkaynak, M.F., London, W.B., Kreissman, S.G., Chen, H.X., Smith, M., Anderson, B., Villablanca, J.G., Matthay, K.K., Shimada, H., Grupp, S.A., Seeger, R., Reynolds, C.P., Buxton, A., Reisfeld, R.A., Gillies, S.D., Cohn, S.L., Maris, J.M., Sondel, P.M., Children's Oncology, G.: Anti-GD2 antibody with GM-CSF, interleukin-2, and isotretinoin for neuroblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 363(14), 1324–1334 (2010). doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0911123
Cheresh D.A., Harper J.R., Schulz G., Reisfeld R.A.: Localization of the gangliosides GD2 and GD3 in adhesion plaques and on the surface of human melanoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 81(18), 5767–5771 (1984)
Mahata B., Banerjee A., Kundu M., Bandyopadhyay U., Biswas K.: TALEN mediated targeted editing of GM2/GD2-synthase gene modulates anchorage independent growth by reducing anoikis resistance in mouse tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 5, 9048 (2015). doi:10.1038/srep09048
Cazet A., Bobowski M., Rombouts Y., Lefebvre J., Steenackers A., Popa I., Guerardel Y., Le Bourhis X., Tulasne D., Delannoy P.: The ganglioside G(D2) induces the constitutive activation of c-met in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells expressing the G(D3) synthase. Glycobiology. 22(6), 806–816 (2012). doi:10.1093/glycob/cws049
Tsai Y.C., Huang J.R., Cheng J.Y., Lin J.J., Hung J.T., Wu Y.Y., Yeh K.T., Yu A.L.: A Prevalent Cancer Associated Glycan, Globo H Ceramide, Induces Immunosuppression by Reducing Notch1 Signaling. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 5, 264–270 (2013)
Cheng J.Y., Wang S.H., Lin J., Tsai Y.C., Yu J., Wu J.C., Hung J.T., Lin J.J., Wu Y.Y., Yeh K.T., Yu A.L.: Globo-H ceramide shed from cancer cells triggers translin-associated factor X-dependent angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 74(23), 6856–6866 (2014). doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1651
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants of the Chang Gung Medical Foundation and the Ministry of Science and Technology for Ming-Yi Ho (CMRPG3D1592 and MOST104-2321-B-001-030) Alice L. Yu (OMRPG3C0013, MOST104-2321-B-182 A-002 and MOST104-2321-B-182 A-003) and John Yu (OMRPG3C0043, MOST104-2321-B-182 A-001 and MOST104-2321-B-182 A-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors..
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, MY., Yu, A.L. & Yu, J. Glycosphingolipid dynamics in human embryonic stem cell and cancer: their characterization and biomedical implications. Glycoconj J 34, 765–777 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-016-9715-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-016-9715-x