Abstract
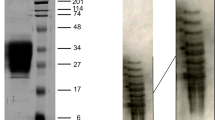
Recently, we established two mouse monoclonal antibodies (R-10G and R-17F). The R-17F antibody (IgG1 subtype) exhibited a strong cytotoxic effect on hiPS/ES cells. The R-17F antigen isolated from a total lipid extract of hiPS (Tic) cells was identified as LNFP I (Fucα1–2Galβ1–3GlcNAcβ1–3Galβ1–4Glc). In the present study, R-17F binding proteins were isolated from hiPS (Tic) cell lysates with an affinity column of R-17F. They gave one major R-17F positive band around 250 kDa, and several minor bands between 150 kDa and 25 kDa. The former band was identified as podocalyxin by LC/MS/MS after SDS-PAGE. Hapten inhibition studies on R-17F binding to R-17F column-purified proteins with various synthetic oligosaccharides revealed that the blood group H type 1 triaose structure (Fucα1–2Galβ1–3GlcNAc) was the predominant epitope on all the R-17F binding proteins. These bands disappeared completely on digestion with α1–2 fucosidase, but not with α1–3/4 fucosidase. Upon PNGase F digestion, the R-17F positive band around and above 250 kDa did not show any change, while the minor bands between 150 kDa and 25 kDa disappeared completely, suggesting that the epitope is expressed on N-glycans in the latter and probably on O-glycans in the former. These results, together with those obtained in our previous studies on R-10G (Kawabe et al. Glycobiology, 23, 322–336 (2013)), indicated that both R-10G and R-17F epitopes are carried on the same podocalyxin molecule. The R-17F epitopes on these glycoproteins expressed on hiPS cells could be associated with the molecular mechanism underlying the carbohydrate-mediated cytotoxic activity of R-17F.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- hES:
-
Human embryonic stem
- hiPS:
-
Human induced pluripotent stem
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- KS:
-
Keratan sulfate
- LC/MS/MS:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
All of the sugar residues have the D-configuration except fucose, which has the L-configuration
References
Cummings, R.D., Etzler, M.E.: Antibodies and Lectins in Glycan. In: Varki A, Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., et al. (eds). Antibodies and lectins in glycan analysis, Essentials of Glycobiology. 2nd ed. pp 633–647. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor (NY) (2009)
Okuda, S., Nakao, H., and Kawasaki, T.: GlycoEpitope: A Database for Carbohydrate Antigen and Antibody. In Glycoscience: Biology and Medicine, pp 1–7, Springer Japan. (2014)
Kawabe K., Tateyama D., Toyoda H., Kawasaki N., Hashii N., Nakao H., Matsumoto S., Nonaka M., Matsumura H., Hirose Y., Morita A., Katayama M., Sakuma M., Kawasaki N., Furue M.K., Kawasaki T.: A novel antibody for human induced pluripotent stem cells and embryonic stem cells recognizes a type of keratan sulfate lacking oversulfated structures. Glycobiology. 23, 322–336 (2013)
Matsumoto S., Nakao H., Kawabe K., Nonaka M., Toyoda H., Takishima Y., Kawabata K., Yamaguchi T., Furue M.K., Taki T., Okumura T., Yamazaki Y., Nakaya S., Kawasaki N., Kawasaki T.: A cytotoxic antibody recognizing lacto-N-fucopentaose I (LNFP I) on human induced pluripotent stem (hiPS) cells. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 20071–20085 (2015)
Thomson J.A., Itskovitz-Eldor J., Shapiro S.S., Waknitz M.A., Swiergiel J.J., Marshall V.S., Jones J.M.: Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 282, 1145–1147 (1998)
Inokuchi J., Radin N.S.: Preparation of the active isomer of 1-phenyl-2-decanoylamino-3-morpholino-1-propanol, inhibitor of murine glucocerebroside synthetase. J. Lipid Res. 28, 565–571 (1987)
Toyoda M., Yamazaki-Inoue M., Itakura Y., Kuno A., Ogawa T., Yamada M., Akutsu H., Takahashi Y., Kanzaki S., Narimatsu H., Hirabayashi J., Umezawa A.: Lectin microarray analysis of pluripotent and multipotent stem cells. Genes Cells. 16, 1–11 (2011)
Takahashi K., Tanabe K., Ohnuki M., Narita M., Ichisaka T., Tomoda K., Yamanaka S.: Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 131, 861–872 (2007)
Kerjaschki D., Sharkey D.J., Farquhar M.G.: Identification and characterization of podocalyxin--the major sialoprotein of the renal glomerular epithelial cell. J. Cell Biol. 98, 1591–1596 (1984)
Andrews, P.W., Banting, G,, Damjanov, I., Arnaud, D., Avner, P.: Three monoclonal antibodies defining distinct differentiation antigens associated with different high molecular weight polypeptides on the surface of human embryonal carcinoma cells. Hybridoma 3, 347–361 (1984)
Schopperle W.M., DeWolf W.C.: The TRA-1-60 and TRA-1-81 human pluripotent stem cell markers are expressed on podocalyxin in embryonal carcinoma. Stem Cells. 25, 723–730 (2007)
Tateno H., Matsushima A., Hiemori K., Onuma Y., Ito Y., Hasehira K., Nishimura K., Ohtaka M., Takayasu S., Nakanishi M., Ikehara Y., Nakanishi M., Ohnuma K., Chan T., Toyoda M., Akutsu H., Umezawa A., Asashima M., Hirabayashi J.: Podocalyxin is a glycoprotein ligand of the human pluripotent stem cell-specific probe rBC2LCN. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2, 265–273 (2013)
Tang C., Lee A.S., Volkmer J.P., Sahoo D., Nag D., Mosley A.R., Inlay M.A., Ardehali R., Chavez S.L., Pera R.R., Behr B., Wu J.C., Weissman I.L., Drukker M.: An antibody against SSEA-5 glycan on human pluripotent stem cells enables removal of teratoma-forming cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 829–834 (2011)
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Saori Kamo for the secretarial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, C- 24,570,171 (to T.K.), from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas 24,110,517 (to T.K.) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (MEXT), Adaptable and Seamless Technology Transfer Programs through Target-driven R&D (A-STEP), AS242Z01520P (to T.K.), and AS251Z01560P (to H.T.) from the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), the R-GIRO (Ritsumeikan Global Innovation Research Organization) Program (to H.T.), and the Mizutani Foundation Research Grant 160,204 (to T.K.).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakao, H., Matsumoto, S., Nagai, Y. et al. Characterization of glycoproteins expressing the blood group H type 1 epitope on human induced pluripotent stem (hiPS) cells. Glycoconj J 34, 779–787 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-016-9710-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-016-9710-2