Abstract
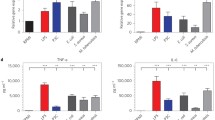
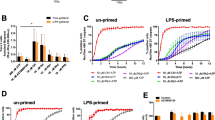
The structures of phosphoglycolipids PGL1 and PGL2 from the thermophilic bacteria Meiothermus taiwanensis, Meiothermus ruber, Thermus thermophilus, and Thermus oshimai are determined recently (Yang et al. in J Lipid Res. 47:1823–1932, 2006). These bacteria belong to Gram-negative bacteria that do not contain lipopolysaccharide, but high amounts of phosphoglycolipids and glycoglycerolipids. Here we show that PGL1/PGL2 mixture (PGL1: PGL2 = 10:1 ~ 10:2) from M. taiwanensis and T. oshimai, but not T. thermophilus and M. ruber, up-regulate interleukin-1β (IL-1β) production in human THP-1 monocytes and blood-isolated primary monocytes. PGL2 was purified after phospholipase A2 hydrolysis of PGL1 in the PGL1/PGL2 mixture followed by column chromatography. PGL2 did not induce proIL-1 production, even, partially (35–40%) inhibited PGL1-mediated proIL-1 production, showing that PGL1 is the main inducer of proIL-1 production in PGL1/PGL2 mixture. The production of proIL-1 stimulated by phosphoglycolipids was strongly inhibited by specific PKC-α, MEK1/2, and JNK inhibitors, but not by p38-specific inhibitor. The intracellular calcium influx was involved in phosphoglycolipids-mediated proIL-1 production. Using blocking antibody and Toll-like receptor (TLR)-linked NF-κB luciferase assays, we found that the cellular receptor(s) for phosphoglycolipids on proIL-1 production was TLR-independent. Further, phosphoglycolipids isolated from T. thermophilus and M. ruber did not induce proIL-1 production, even though T. thermophilus possess more PGL1 than PGL2 (6:4). Specially, the fatty acid composition of phosphoglycolipids from both T. thermophilus and M. ruber consists of a low percentage of C15 (<10%) and a high percentage of C17 (>75%). It suggests, the C15 percentage of PGL may play a critical role in PGL-mediated proIL-1 induction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ray, P.H., White, D.C., Brock, T.D.: Effect of growth temperature on the lipid composition of Thermus aquaticus. J. Bacteriol. 108, 227–235 (1971)
Williams, R.A.D., Da Costa, M.S.: The genus Thermus and related microorganisms. In: Balows, A., Truper, H.G., Dworkin, M., Harder, W., Schleifer, K.-H. (eds.) The Prokaryotes, 2nd edn., pp 3745–3753. Springer, New York (1992)
Ferreira, A.M., Wait, R., Nobre, M.F., Da Costa, M.S.: Characterization of glycolipids from Meiothermus spp. Microbiology 145, 1191–1199 (1999)
Silva, Z., Borges, N., Martins, L.O., Wait, R., Da Costa, M.S., Santos, H.: Combined effect of the growth temperature and salinity of the medium of the accumulation of compatible solutes by Rhodothermus marinus and Rhodothermus obamensis. Extremophiles 3, 163–172 (1999)
Forterre, P., Bouthier de la Tour, C., Philippe, H., Duguet, M.: Reverse gyrase from hyperthermophiles: probable transfer of a thermoadaptation trait from archaea to bacteria. Trends Genet. 16, 152–154 (2000)
Lesley, S.A., Kuhn, P., Godzik, A., Deacon, A.M., Mathews, I., Kreusch, A., Spraggon, G., Klock, H.E., McMullan, D., Shin, T., et al.: Structural genomics of the Thermotoga maritima proteome implemented in a high-throughput structure determination pipeline. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 11664–11669 (2002)
De Groot, A., Chapon, V., Servant, P., Chriten, R., Saux, M.F., Sommer, S., Heulin, T.: Deinococcus deserti sp. nov., a gamma-radiation-tolerant bacterium isolated from the Sahara desert. Inst. J. Sys. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 2441–2446 (2005)
Yang, Y.L., Yang, F.L., Jao, S.C., Chen, M.Y., Tsay, S.S., Zou, W., Wu, S.H.: Structural elucidation of phosphoglycolipids from strains of the bacterial thermophiles Thermus and Meiothermus. J. Lipid Res. 47, 1823–1832 (2006)
Dutronc, Y., Porcelli, S.A.: The CD1 family and T cell recognition of lipid antigens. Tissue Antigens 60, 337–353 (2002)
Parekh, V.V., Wilson, M.T., Van Kaer, L.: iNKT-cell responses to glycolipids. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 25, 183–213 (2005)
Krishnan, L., Dicaire, C., Patel, G.B., Sprott, G.D.: Archaeosome vaccine adjuvants induce strong humoral, cell-mediated and memory responses: comparison to conventional liposomes and alum. Infect. Immun. 68, 54–63 (2000)
Kinjo, Y., Wu, D., Kim, G., Xing, G.-W., Poles, M.A., Ho, D.D., Kawahara, K., Wong, C.-H., Kronenberg, M.: Recognition of bacterial glycosphingolipids by natural killer T cells. Nature 434, 520–525 (2005)
Kinjo, Y., Tupin, E., Wu, D., Fujio, M., Garcia-Navarro, R., Benhnia, M.R.-E.-I., Zajonc, D.M., Ben-Menachem, G., Ainge, G.D., Painter, G.F., Khurana, A., Hoebe, K., Behar, S.M., Beutler, B., Wilson, I.A., Tsuji, M., Sellati, T.J., Wong, C.-H., Kronenberg, M.: Natural killer T cells recognize diacylglycerol antigens from pathogenic bacteria. Nature Immun. 7, 978–986 (2006)
Stetson, D.B., Mohrs, M., Reinhardt, R.L., Baron, J.L., Wang, Z.E., Gapin, L., Kronenberg, M., Locksley, R.M.: Constitutive cytokine mRNAs mark natural killer (NK) and NK T cells poised for rapid effector function. J. Exp. Med. 198, 1069–1076 (2003)
Bruno, A., Rossi, C., Marcolongo, G., Di Lena, A., Venzo, A., Berrie, C.P., Corda, D.: Selective in vivo anti-inflammatory action of the galactolipid monogalactosyl-diacylglycerol. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 524, 159–168 (2005)
Phoebe, C.H., Jr., Combie, J., Albert, F.G., Van Tran, K., Cabrera, J., Correira, H.J., Guo, Y., Lindermuth, J., Rauert, N., Galbraith, W., Selitrennikoff, C.P.: Extremophilic organisms as an unexplored source of antifungal compounds. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 54, 56–65 (2001)
Anderson, R., Huang, Y.: Fatty acids are precursors of alkylamines in Deinococcus radiodurans. J. Bacteriol. 174, 7168–7173 (1992)
Cerretti, D.P., Kozlosky, C.J., Mosley, B., Nelson, N., Van Ness, K., Greenstreet, T.A., March, C.J., Kronheim, S.R., Druck, T., Cannizzaro, L.A., Huebner, K., Black, R.A.: Molecular cloning of the interleukin-1β converting enzyme. Science 256, 97–100 (1992)
Thornberry, N.A., Bull, H.G., Calaycay, J.R., Chapman, K.T., Howard, A.D., Kostura, M.J., Miller, D.K., Molineaux, S.M., Weidner, J.R., Aunins, J., et al.: A novel heterodimeric cysteine protease is required for interleukin-1β processing in monocytes. Nature 356, 768–774 (1992)
Dinarello, C.A.: Interleukin-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 8, 253–265 (1997)
Schumann, R.R., Belka, C., Reuter, D., Lamping, N., Kirschning, C.J., Weber, J.R., Pfeil, D.: Lipopolysaccharide activates caspase-1 (interleukin-1-converting) in cultured monocytic and endothelial cells. Blood 91, 577–584 (1998)
Loppnow, H., Werdan, K., Reuter, G., Flad, H.D.: The interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 converting enzyme families in cardiovascular system. Eur. Cytokine. Netw. 9, 675–680 (1998)
Li, X., Commane, M., Jiang, Z., Stark, G.R.: IL-1-induced NFκB and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation diverge at IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 4461–4465 (2001)
Loppnow, H., Libby, P.: Proliferating or interleukin 1-activated human vascular smooth muscle cells secrete copious interleukin 6. J. Clin. Invest. 85, 731–738 (1990)
Beales, I.L.: Effect of Interlukin-1 on proliferation of gastric epithelial cells in culture. BMC Gastroenterology 2, 7 (2002)
Xaus, J., Comalada, M., Valledor, A.F., Lloberas, J., Lopez-Soriano, F., Argiles, J.M., Yang, J., Hooper, W.C., Phillips, D.J., Talkington, D.F.: Interleukin-1beta responses to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection are cell-type specific. Microb. Pathog. 34, 17–25 (2003)
Pearson, G., Robinson, F., Beers Gibson, T., Xu, B.E., Karandikar, M., Berman, K., Cobb, M.H.: Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr. Rev. 22, 153–183 (2001)
Raingeaud, J., Gupta, S., Rogers, J.S., Dickens, M., Han, J., Ulevitch, R.J., Davis, R.J.: Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7420–7426 (1995)
Scherle, P.A., Jones, E.A., Favata, M.F., Daulerio, A.J., Covington, M.B., Nurnberg, S.A., Magolda, R.L., Tracks, J.M.: Inhibition of MAP kinase kinase prevents cytokine and prostaglandin E2 production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated monocytes. J. Immunol. 161, 5681–5686 (1998)
Carter, A.B., Monick, M., Hunninghake, G.W.: Both Erk and p38 kinases are necessary for cytokine gene transcription. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 20, 751–758 (1999)
Binétruy, B., Smeal, T., Karin, M.: Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature 351, 122–127 (1991)
Devary, Y., Gottlieb, R.A., Lau, L.F., Karin, M.: Rapid and preferential activation of the c-jun gene during the mammalian UV response. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11, 2804–2811 (1991)
Pombo, C.M., Bonventre, J.V., Avruch, J., Woodgett, J.R., Kyriakis, J.M., Force, T.: The stress-activated protein kinases are major c-Jun amino-terminal kinases activated by ischemia and reperfusion. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 26546–26551 (1994)
Hambleton, J., Weinstein, S.L., Lem, L., DeFranco, A.L.: Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93, 2774–2778 (1996)
Derijard, B., Hibi, M., Wu, I.H., Barrett, T., Su, B., Deng, T., Karin, M., Davis, R.J.: JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Has that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell 76, 1025–1037 (1994)
Kallunki, T., Su, B., Tsigelny, I., Sluss, H.K., Derijard, B., Moore, G., Davis, R., Karin, M.: JNK2 contains a specificity-determining region responsible for efficient c-Jun binding and phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 8, 2996–3007 (1994)
Reimann, T., Buscher, D., Hipskind, R.A., Krautwald, S., Lohmann-Matthes, M.L., Baccarini, M.: Lipopolysaccharide induces activation of the Raf-1/MAP kinase pathway. A putative role for Raf-1 in the induction of the IL-1 beta and TNF-alpha genes. J. Immunol. 153, 5740–5749 (1994)
Bennett, B.L., Sasaki, D.T., Murray, B.W., O’Leary, E.C., Sakata, S.T., Xu, W., Leisten, J.C., Motiwala, A., Pierce, S., Satoh, Y., Bhagwat, S.S., Manning, A.M., Anderson, D.W.: SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 13681–13686 (2001)
Han, J., Lee, J.D., Bibbs, L., Ulevitch, R.J.: A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science 265, 808–811 (1994)
Lee, J.C., Laydon, J.T., McDonnell, P.C., Gallagher, T.F., Kumar, S., Green, D., McNulty, D., Blumenthal, M.J., Heys, J.R., Landvatter, S.W., Strickler, J.E., McLaughlin, M.M., Siemens, I.R., Fisher, S.M., Livi, G.P., White, J.R., Adams, J.L., Young, P.R.: A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature 372, 739–746 (1994)
Geng, Y., Valbracht, J., Lotz, M.: Selective activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase subgroups c-Jun NH2 terminal kinase and p38 by IL-1 and TNF in human articular chondrocytes. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 2425–2430 (1996)
Chen, M.Y., Lin, G.H., Lin, Y.T., Tsay, S.S.: Meiothermus taiwanensis sp. nov., a novel filamentous, thermophilic species isolated in Taiwan. Int. J. Sys. Evol. Microbiol. 52, 1647–1654 (2002)
Lu, T.L., Chen, C.S., Yang, F.L., Fung, J.M., Chen, M.Y., Tsay, S.S., Li, J., Zou, W., Wu, S.H.: Structure of a major glycolipid from Thermus oshimai NTU-063. Carbohydr. Research. 339, 2593–2598 (2004)
Hsu, H.Y., Wen, M.H.: Lipopolysaccharide-mediated reactive oxygen species and signal transduction in the regulation of interleukin-1 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22131–22139 (2002)
Chuang, T.S., Lee, J., Kline, L., Mathison, J.C., Ulevitch, R.J.: Toll-like receptor 9 mediates CpG-DNA signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 71, 538–544 (2002)
Kuo, C.C., Lin, W.T., Liang, C.M., Liang, S.M.: Class I and III phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase play distinct roles in TLR signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 176, 5943–5949 (2006)
Muzio, M., Natoli, G., Saccani, S., Levrero, M., Mantovani, A.: The human toll signaling pathway: divergence of nuclear factor kappaB and JNK/SAPK activation upstream of tumor necrosis factor receptor-association factor 6 (TRAF6). J. Exp. Med. 187, 2097–2101 (1998)
Pask-Hughes, R.A., Shaw, N.: Glycolipids from some extreme thermophilic bacteria belonging to the genus Thermus. J. Bacteriol. 149, 54–58 (1982)
Silipo, A., Molinaro, A., de Castro, C., Ferrara, R., Romano, I., Nicolaus, B., Lanzetta, R., Parrilli, M.: Structural analysis of a novel polysaccharide of the lipopolysaccharide-deficient extremophile gram-negative bacterium Thermus thermophilus HB8. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 24, 5047–5054 (2004)
Dobson, P.R., Skjodt, H., Plested, C.P., Short, A.D., Virdee, K., Russell, R.G., Brown, B.L.: Interleukin-1 stimulates diglyceride accumulation in the absence of protein kinase C activation. Regul. Pept. 29, 109–116 (1990)
Brooks, J.W., Mizel, S.B.: Interleukin-1 and signal transduction. Eur. Cytokine. Netw. 5, 547–561 (1994)
Beales, I., Calam, J.: Stimulation of IL-8 production in human gastric epithelial cells by Helicobacter pylori, IL-1b and TNF-a requires tyrosine kinase activity, but not protein kinase C. Cytokine 9, 514–520 (1997)
Beales, I., Calam, J.: lnterleukin-1b and tumor nexcrosis factor-a inhibit acid secretion in cultured rabbit parietal cells by multiple pathways. Gut 42, 227–234 (1998)
Beales, I.L., Calam, J.: Inhibition of carbachol stimulated acid secretion by interleukin 1beta in rabbit parietal cells requires protein kinase C. Gut 48, 782–789 (2001)
Chiodoni, C., Stoppacciaro, A., Sangaletti, S., Gri, G., Cappetti, B., Koezuka, Y., Colombo, M.P.: Different requirements for α-galactosylceramide and recombinant IL-12 antitumor activity in the treatment of C-26 colon carcinoma hepatic metastases. Eur. J. Immunol. 31, 3101–3110 (2001)
Antonopoulou, S., Nomikos, T., Oilonomou, A., Kyriacou, A., Andriotis, M., Fragopoulou, E., Pantazidou, A.: Characterization of bioactive glycolipids from Scytonema julianum (cyanobacteria). Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part B. 140, 219–231 (2005)
Hiromatsu, K., Dascher, C.C., Sugita, M., Gingrich-Baker, C., Behar, S.M., LeClair, K.P., et al.: Characterization of guinea-pig group 1 CD1 proteins. Immunol. 106, 159–172 (2002)
Buwitt-Beckmann, U., Heine, H., Wiesmüller, K.H., Jung, G., Brock, R., Ulmer, A.J.: Lipopeptide structure determines TLR2 dependent cell activation level. FEBS J. 272, 6354–6364 (2005)
Buwitt-Beckmann, U., Heine, H., Wiesmüller, K.H., Jung, G., Brock, R., Akira, S., Ulmer, A.J.: TLR1- and TLR6-independent recognition of bacterial lipopeptides. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 9049–9057 (2006)
Morr, M., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S., Simon, M.M., Mühlradt, P.F.:Differential recognition of structural details of bacterial lipopeptides by toll-like receptors. Eur. J. Immunol. 32, 3337–3347 (2002)
Kawahara, K., Moll, H., Knirel, Y.L., Seydel, U., Zahringer, U.: Structural analysis of two glycosphingolipids from the lipopolysaccharide-lacking bacterium Sphingomonas capsulata. Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 1837–1846 (2000)
Gray, J.G., Chandra, G., Clay, W.C., Stinnett, S.W., Haneline, S.A., Lorenz, J.J., Patel, I.R., Wisely, G.B., Furdon, P.J., Taylor, J.D., et al.: A CRE/ATF-like site in the upstream regulatory sequence of the human interleukin 1 beta gene is necessary for the induction in U937 and THP-1 monocytic cell lines. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 6678–6689 (1993)
Geppert, T.D., Whitehurst, C.E., Thompson, P., Beutler, B.: Lipopolysaccharide signals activation of tumor necrosis factor biosynthesis through the ras/raf-1/MEK/ MAPK pathway. Mol. Med. 1, 93–103 (1994)
Rousset, M., Cens, T., Van Mau, N., Charnet, P.: Ca2+-dependent interaction of BAPTA with phospholipids. FEBS Letters 576, 41–45 (2004)
Darveau, R.P.: Lipid A diversity and the innate host response to bacterial infection. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1, 36–42 (1998)
Dubois, M.J., Vincent, J.L.: Clinically-oriented therapies in sepsis: a review. J. Endotoxin. Res. 6, 463–469 (2000)
Proctor, R.A., Will, J.A., Burhop, K.E., Raetz, C.R.H.: Protection of mice against lethal endotoxemia by a lipid A precursor. Infect. Immun. 52, 905–907 (1986)
Christ, W.J., Asano, O., Robidoux, A.L., Perez, M., Wang, Y., Dubuc, G.R., Gavin, W.E., Hawkins, L.D., McGuinness, P.D., Mullarkey, M.A., et al.: E5531, a pure endotoxin antagonist of high potency. Science 268, 80–83 (1995)
Arend, W.P., Malyak, M., Guthridge, C.J., Gabay, C.: Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist; role in biology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16, 27–55 (1998)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Science Council, Taiwan, (NSC 92-2321-B-001-019 and 94-2311-B-001-045 to S-H Wu; NSC 93-2314-B-010-003 and 94-2120-M-010-002 to H-Y Hsu); National Health Research Institutes, Taiwan (NHRI-EX93-9211SI and support for the cost of reprints to H-Y Hsu); the Ministry of Education, Taiwan, on Program for Promoting Academic Excellence of Universities (A-91-B-FA09-2-4 to H-Y Hsu); a grant from Ministry of Education, Aim for the Top University Plan (95A-C-D01-PPG-10 to H-Y Hsu); Academia Sinica (Thematic project to H-Y Hsu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Feng-Ling Yang and Kuo-Feng Hua equally contributed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, FL., Hua, KF., Yang, YL. et al. TLR-independent induction of human monocyte IL-1 by phosphoglycolipids from thermophilic bacteria. Glycoconj J 25, 427–439 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-007-9088-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-007-9088-2