Abstract
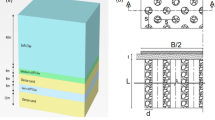
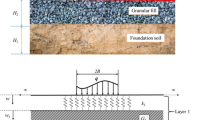
The paper presents a mechanical model to predict the behavior of geosynthetic-reinforced granular fill resting over soft soil improved with group of stone columns subjected to circular or axi-symmetric loading. The saturated soft soil has been idealized by spring-dashpot system. Pasternak shear layer and rough elastic membrane represent the granular fill and geosynthetic reinforcement layer, respectively. The stone columns are idealized by stiffer springs. The nonlinear behavior of granular fill and soft soil is considered. Consolidation of the soft soil due to inclusion of stone columns has also been included in the model. The results obtained by using the present model when compared with the reported results obtained from laboratory model tests shows very good agreement. The effectiveness of geosynthetic reinforcement to reduce the maximum and differential settlement and transfer the stress from soft soil to stone columns is highlighted. It is observed that the reduction of settlement and stress transfer process are greatly influenced by stiffness and spacing of the stone columns. It has been further observed that for both geosynthetic-reinforced and unreinforced cases, the maximum settlement does not change if the ratio between spacing and diameter of stone columns is greater than 4.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Radius of circular loading
- b :
-
Radius of geosynthetic-reinforced zone
- d c :
-
Diameter of the stone column
- E c :
-
Elastic modulus of the stone column material
- E s :
-
Elastic modulus of the soft soil
- G b0 :
-
Initial shear modulus of the bottom granular fill layer
- \( G_{b0}^{*} \) :
-
Normalized G b0
- G t0 :
-
Initial shear modulus of the top granular fill layer
- \( G_{t0}^{*} \) :
-
Normalized G 0t
- H b :
-
Thickness of the bottom granular fill layer
- H t :
-
Thickness of the top granular fill layer
- H s :
-
Thickness of the soft soil
- K 0 :
-
Coefficient of lateral stress
- k c0 :
-
Modulus of subgrade reaction for stone columns
- k s0 :
-
Initial modulus of subgrade reaction for soft foundation soil
- n s :
-
Stress concentration ratio
- q :
-
Uniform footing pressure on the top granular layer
- q * :
-
Normalized q
- q c :
-
Vertical reaction pressure of the stone columns
- q * c :
-
Normalized q c
- q s :
-
Vertical reaction pressure of the soft foundation soil
- \( q_{s}^{*} \) :
-
Normalized q s
- q u :
-
Ultimate bearing capacity of the soft soil
- \( q_{u}^{*} \) :
-
Normalized q u
- r :
-
Radial distance from centre of loading
- R :
-
Normalized r
- s :
-
Spacing between stone columns
- T :
-
Mobilized tension in the geosynthetic layer
- T * :
-
Normalized T
- t :
-
Time
- t c :
-
Thickness of the equivalent ring
- U :
-
Degree of consolidation
- w :
-
Vertical displacement
- w :
-
Normalized w
- α :
-
Spring constant ratio
- μ t , μ b :
-
Interface friction at the top and bottom of the geosynthetic layer
- ν c :
-
Poisson ratio of the stone column material
- ν s :
-
Poisson ratio of the soft soil
- ϕ:
-
Angle of shearing resistance
- τ b :
-
Shear stresses in the bottom granular layer
- \( \tau_{b}^{*} \) :
-
Normalized τ b
- τ t :
-
Shear stresses in the top granular layer
- \( \tau_{t}^{*} \) :
-
Normalized τ t
- \( \tau_{u} \) :
-
Ultimate shear resistance of the granular layer
- \( \tau_{u}^{*} \) :
-
Normalized \( \tau_{u} \)
- \( \tau_{ub} \) :
-
Ultimate shear resistance of the bottom granular layer
- \( \tau_{ub}^{*} \) :
-
Normalized \( \tau_{ub} \)
- \( \tau_{ut} \) :
-
Ultimate shear resistance of the top granular layer
- \( \tau_{ut}^{*} \) :
-
Normalized \( \tau_{ut} \)
- θ:
-
Slope of the membrane
References
Alamgir M, Miura N, Poorooshasb HB, Madhav MR (1996) Deformation analysis of soft ground reinforced by columnar inclusions. Comput Geotech 18(4):267–290
Alpan I (1967) The empirical evaluation of the coefficient K 0 and K 0r . Soils Found 7(1):31–40
Ambily AP, Gandhi SR (2007) Behavior of stone column based on experimental and FEM analysis. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 133(4):405–415
Balaam NP, Booker JR (1981) Analysis of rigid raft supported by granular piles. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 5:379–403
Brooker EW, Ireland HO (1965) Earth pressure at rest related to stress history. Can Geotech J 2(1–2):1–15
Deb K (2008) Modeling of granular bed-stone column-improved soft soil. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 32(10):1267–1288
Deb K, Basudhar PK, Chandra S (2007) Generalized model for geosynthetic-reinforced granular fill-soft soil with stone columns. Int J Geomech ASCE 7(4):266–276
Deb K, Chandra S, Basudhar PK (2008) Response of multi layer geosynthetic-reinforced bed resting on soft soil with stone columns. Comput Geotech 35(3):323–330
Elshazly HA, Hafez DH, Mossaad ME (2008) Reliability of conventional settlement evaluation for circular foundation on stone column. Geotech Geol Eng 26:323–334
Ghosh C, Madhav MR (1994) Settlement response of a reinforced shallow earth bed. Geotext Geomembr 13(9):643–656
Han J, Gabr MA (2002) Numerical analysis of geosynthetic-reinforced and pile-supported earth platform over soft soil. J Geotech Environ Eng ASCE 128(1):44–53
Han J, Ye SL (2001) Simplified method for consolidation rate of stone column reinforced foundations. J Geotech Environ Eng ASCE 127(7):597–603
Hausmann MR (1990) Engineering principles of ground modification. MaGraw-Hill, New York
Indraratna B, Aljorany A, Rujikiatkamjorn C (2008) Analytical and numerical modeling of consolidation by vertical drain beneath a circular embankment. Int J Geomech 8(3):199–206
Lee JS, Pande GN (1998) Analysis of stone-column reinforced foundations. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 12(12):1001–1020
Mitchell JK, Huber TR (1985) Performance of a stone column foundation. J Geotech Eng ASCE 111(2):205–223
Poorooshasb HB, Meyerhof GG (1997) Analysis of behavior of stone columns and lime columns. Comput Geotech 20(1):47–70
Selvadurai APS (1979) Elastic analysis of soil-foundation interaction. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Shahu JT, Madhav MR, Hayashi S (2000) Analysis of soft ground-granular pile-granular mat system. Comput Geotech 27(1):45–62
Shukla SK (1994) Foundation model for reinforced granular fill-soft soil system and its settlement response. PhD thesis. IIT Kanpur
Shukla SK, Chandra S (1994a) A generalized mechanical model for geosynthetic- reinforced foundation soil. Geotext Geomembr 13:813–825
Shukla SK, Chandra S (1994b) The effect of prestressing on the settlement characteristics of geosynthetic-reinforced soil. Geotext Geomembr 13(8):531–543
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deb, K., Basudhar, P.K. & Chandra, S. Axi-symmetric Analysis of Geosynthetic-reinforced Granular Fill-soft Soil System with Group of Stone Columns. Geotech Geol Eng 28, 177–186 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-009-9291-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-009-9291-y