Abstract
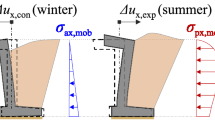
The studies of excavations in soft clayey soils are normally based on undrained total stress analyses. A better approach consists of taking into account the effects of consolidation during the excavation-bracing process and after the completion of the construction by means of coupled finite element analyses in effective stresses. In this paper, the geotechnical behaviour of a braced excavation in the soft soils of San Francisco (USA) is analysed, both during and after the construction period. Numerical analyses are performed with a finite element program, which incorporates the Biot consolidation theory (coupled formulation of the water flow and equilibrium equations) and soil constitutive relations simulated by the p-q-θ critical state model. Numerical results are compared with field results.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves Costa P (2005) Braced excavations in soft clay. Behavior analysis including the consolidation effects. MSc Thesis. Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Portugal, (in Portuguese)
Bjerrum L, Clausen C, Duncan J (1972) Stability of flexible structures. Proceedings of the 5th European conference on soil mechanism and foundation, Madrid, General Report
Bonaparte R, Mitchell JK (1979) The properties of San Francisco bay mud at Hamilton air force base, California. Geotechnology Research Report, University of California, Berkeley
Borges JL (1995) Geosynthetic reinforced embankments on soft soils—Analysis and design. PhD Thesis in civil engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Portugal, (in Portuguese)
Borges JL, Cardoso AS (1998) Numerical simulation of the p-q-θ critical state model in embankments on soft soils. R Geotecnia 84, 39–63 (in Portuguese)
Borges JL, Cardoso AS (2000) Numerical simulation of the consolidation processes in embankments on soft soils. R Geotecnia 89, 57–75 (in Portuguese)
Borja RI (1990) Analysis of incremental excavation based on critical state theory. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE 116(6):964–985
Borja RI (1992) Free boundary, fluid flow, and seepage forces in excavations. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE 118(1):125–146
Bose SK, Som NN (1998) Parametric study of a braced cut by finite element method. In: Computers and Geotechnics, vol 22, no. 2. Elsevier Science Publishers, England, pp 91–107
Britto AM, Gunn MJ (1987) Critical state soil mechanics via finite elements. Ellis Horwood Limited, England
Clough GW, Hansen LA (1981) Clay anisotropy and braced wall behaviour. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE GT7:893–913
Clough GW, Reed MW (1984) Measured behaviour of braced wall in very soft clay. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE 110(1):1–19
Dibiagio E, Roti JA (1972) Earth pressure measurements on a braced slurry-trench wall in soft clay. Proceedings of the 5th European conference on soil mechanics and foundation engineering, vol. 1. Madrid, pp 473–483
Finno RJ, Atmatzidis DK, Perkins SB (1989) Observed performance of a deep excavation in clay. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE 115:1045–1064
Finno RJ, Harahap IS, Sabatini PJ (1991) Analysis of braced excavations with coupled finite element formulations. In: Computers and Geotechnics vol 12, no 2. Elsevier Science Publishers, England, pp 91–114
Fourier AB (1994) Finite element analysis of braced excavations in soft clay. Proceedings of the 13th Internacional Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, vol 4. New Delhi, pp 1375–1380
Lade PV, Duncan JM (1973) Cubical triaxial tests on cohesionless soils. J Soil Mech Found Div ASCE, 99(10): 793–812
Lambe TW, Turner EK (1970) Braced excavations. Proceedings of the specality conference on lateral stresses in ground and design of earth retaining structures, ASCE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, pp 149–218
Lewis RW, Schrefler BA (1987) The finite element method in the deformation and consolidation of porous media. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
Liao SSC, Neff TL (1990) Estimating lateral earth pressures for design of excavation support. In: Lambe PC, Hansen LA (eds) Design and performance of earth retaining structures, Geotechnical Special Publication N. 25, ASCE, pp 489–509
Mana AI (1978) Finite-element analyses of deep excavation behaviour in Soft Clay. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University
Matos Fernandes M, Cardoso AS, Fortunato E (1997) A reappraisal of arching around braced excavations in soft ground. In: Azevedo et al. (eds) Proceedings of the Applications of Computational Mechanics in Geotechnical Engineering, Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 333–350
Mita KA, Dasari GR, Lo KW (2004) Performance of a three-dimensional Hvorslev-Modifided Cam Clay model for overconsolidated clay. Int J Geomech ASCE 4(4):296-309
Ng CWW (1998) Observed performance of multipropped excavation in stiff clay. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 124(9):889–905
Ng CWW (1999) Stress paths in relation to deep excavations. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 125(5):357–363
Ou CY, Lai CH (1994) Finite-element analysis of deep excavation in layered sandy and clayey soil Deposits. Can Geotech J, Otawa, Canada, 31:204–214
Ou CY, Liao JT, Lin HD (1998) Performance of diaphragm wall constructed using top-down Method. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE, 124(9):798–808
Potts DM, Zdravkovic L (1999) Finite element analysis in geotechnical engineering—theory. Thomas Telford, London
Terzaghi K (1943) Theoretical soil mechanics. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, P.A., Borges, J.L. & Fernandes, M.M. Analysis of A Braced Excavation In Soft Soils Considering The Consolidation Effect. Geotech Geol Eng 25, 617–629 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-007-9134-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-007-9134-7