Abstract
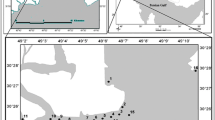
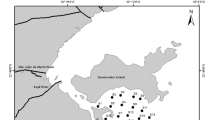
Τhe present research investigates the partitioning of six selected toxic metals (Ni, Cr, Pb, Zn, Cu, and As) in eight sediment samples; half of them were collected from Elefsis Gulf, and the other half were taken from Koumoundourou Lake, Athens, Greece. Each one of them was treated by applying Tessier’s five-step sequential extraction procedure. Regarding gulf sediments, the results indicated that Cu exhibits a strong affinity to the organic matter with percentages ranging from 65 to 78 %. Considerable amount of Zn (32–40 %) is bound to the Fe-Mn fraction and the non-residual fraction, while Cr and Ni are bound to the organic fraction, an observation that suits all toxic metals examined. Regarding lake sediments, Pb is the predominant metal bound to Fe-Mn (48–51 %). It is also noteworthy that the percentage of Zn bound to carbonated fraction (5–15 %), indicating biological availability. In conclusion, the application of several ecological risk indicators demonstrated that Elefsis Gulf sediments correspond to a moderate pollution level, with Pb and Ni being less bioavailable than in the lake’s samples, in contrast to Zn which is more bioavailable. Finally, Koumoundourou Lakes’ basin is characterized of “low risk.”



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahim, G., & Parker, R. (2002). Heavy metal contaminants in Tamaki Estuary: impact of city development and growth, Auckland, New Zealand. Environmental Geology, 42, 883–89.
Abrahim, G., & Parker, R. (2008). Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 136, 227–238.
Bacon, J. R., & Davidson, C. M. (2008). Is there a future for sequential chemical extraction? Analyst, 133, 25–46.
Christophoridis, C., Dedepsidis, D., & Fytianos, K. (2009). Occurrence and distribution of selected toxic metals in the surface sediments of Thermaikos Gulf, N. Greece. Assessment using pollution indicators. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 1082–1091.
Conides, A., Diapoulis, A., & Koussouris, T. (1996). Ecological study of an oil polluted coastal lake ecosystem. Fresenious Environmental Bulletin, 5, 324–332.
Davidson, C. M., Thomas, R. P., McVey, S. E., Perala, R., Littlejohn, D., & Ure, A. M. (1994). Evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure for the partitioning of toxic metals in sediments. Analytica Chimica Acta, 291, 277–286.
Davidson, C. M., Duncan, A. L., Littlejohn, D., & Ure, A. M. (1998). A critical evaluation of the three-stage BCR sequential extraction procedure to assess the potential mobility and toxicity of toxic metals in industrially-contaminated land. Analytica Chimica Acta, 363, 45–55.
Galán, E., Gómez Ariza, J. L., González, I., Fernández Caliani, J. C., Morales, E., & Giráldez, I. (1999). Utilidad de las tecnicas de extraccion secuencial en la mejora de la caracterización mineralogica por DRX de suelos y sedimentos con altos contenidos de oxidos de hierro. Libro de conferencias y Resumenes de la XV Reunion Cientifica de la Sociedad Española de Arcillas, 15, 68–69.
Gao, H., Bai, J., Xiao, R., Liu, P., Jiang, W., & Wang, J. (2013). Levels, sources and risk assessment of trace elements in wetland soils of a typical shallow freshwater lake, China. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 27, 275–284.
Giacalone, A., Gianguzza, A., Orecchio, S., Piazzese, D., Dongarrà, G., Sciarrino, S., & Varrica, D. (2005). Metal distribution in the organic and inorganic fractions of soil: a case-study on soils from Sicily. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability, 17, 83–94.
Gupta, S. K., & Chen, K. Y. (1975). Partitioning of trace metals in selective chemical fractions of near shore sediments. Environmental Letters, 10, 129–158.
Hahladakis, J., Smaragdaki, E., Vasilaki, G., & Gidarakos, E. (2013). Use of Sediment Quality Guidelines and pollution indicators for the assessment of heavy metal and PAH contamination in Greek surficial sea and lake sediments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 2843–2853.
Hakanson, L. (1980). Ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control, a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
Hall, G. E. M., Gauthier, G., Pelchat, J. G., Pelchat, P., & Vaive, J. (1996). Application of a sequential extraction scheme to ten geological certified reference materials for the determination of 20 elements. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 11, 787–796.
Jain, C. K. (2004). Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of River Yamuna, India. Water Research, 38, 569–578.
Karageorgis, A. P., Katsanevakis, S., & Kaberi, H. (2009). Use of enrichment factors for the assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediments of Koumoundourou Lake, Greece. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 204, 243–258.
Kokovides, K., Loizidou, M., Haralambous, K. J., & Moropoulou, T. (1992). Environmental study of the marinas, Part I. A study on the pollution in the marinas area. Environmental Technology, 13, 239–244.
Kumar, K. S., Sajwan, K. S., Richardson, J. P., & Kannan, K. (2008). Contamination profiles of toxic metals, organochlorine pesticides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and alkylphenols in sediment and oyster collected from marsh/estuarine, Savannah GA, USA. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56, 136–149.
Laing, G. D., De Vos, R., Vandecasteele, B., Lesage, E., Tack, F. M. G., & Verloo, M. G. (2007). Effect of salinity on heavy metal mobility and availability in intertidal sediments of the Scheldt estuary. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 77, 589–602.
Liang, P. Y., Tan, Y. J., Chen, L. J., & Li, W. K. (2012). Influence of inorganic salts on concentration of different Cd forms in the soil. Advanced Materials Research, 356–360, 943–950.
Lim, H. S., Lee, J. S., Chon, H. T., & Sager, M. (2008). Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of the abandoned Songcheon Au–Ag mine in Korea. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 96, 223–230.
Maiz, I., Esnaola, V., & Millán, E. (1997). Evaluation of heavy metal availability in contaminated soils by a short sequential extraction procedure. Science of the Total Environment, 206, 107–115.
Maiz, I., Arambarri, Ι., Garcia, R., & Millán, E. (2000). Evaluation of heavy metal availability in polluted soils by two sequential extraction procedures using factor analysis. Environmental Pollution, 110, 3–9.
Mester, Z., Cremisini, C., Ghiara, E., & Morabito, R. (1998). Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures for metal fractionation in sediment samples. Analytica Chimica Acta, 359, 133–142.
Meyer, J. S. (2002). The utility of the terms “bioavailability” and “bioavailable fraction” for metals. Marine Environmental Research, 53, 417–423.
Oyeyiola, A. O., Olayinka, K. O., & Alo, B. I. (2011). Comparison of three sequential extraction protocols for the fractionation of potentially toxic metals in coastal sediments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 172, 319–327.
Patrick, W. H., Gambrell, R. P., & Khalid, R. A. (1977). Physiochemical factors regulating solubility and bioavailability of toxic metals in contaminated dredged sediment. Journal of Environmental Science and Health: Part A, 12, 475–492.
Perin, G., Craboledda, L., Lucchese, M., Cirillo, R., Dotta, L., Zanetta, M. L., & Oro, A. A. (1985). Heavy metal partitioning in the sediments of northern Adriatic Sea—a new approach for environmental toxicity determination. In T. D. Lakkas (Ed.), Toxic metals in the environment (pp. 454–456). Edinburgh: CEP Consultants.
Petrucci, E., Montanaro, D., & Merli, C. (2011). Sequential extraction analysis provides decision-making tools for the use of contaminated sediments. Chemistry and Ecology, 27, 107–118.
Ratuzny, T., Gong, Ζ., & Wilke, Β. Μ. (2009). Total concentrations and partitioning of toxic metals in soils of the Shenyang Zhangshi Irrigation Area, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 156, 171–180.
Rauret, G. (1998). Extraction procedures for the determination of toxic metals in contaminated soil and sediment. Talanta, 46, 449–455.
Roussakis, G. (2003). Bathymetry of Lake Koumoundourou. In A. Pavlidou (Ed.), Monitoring of the groundwaters, Lake Koumoundourou and the adjacent marine area in relation to the landfill of Western Attica. Technical report (pp. 17–22). Anavyssos: Hellenic Centre for Marine Research. In Greek.
Ryan, P. C., Hillier, S., & Wall, A. J. (2008). Stepwise effects of the BCR sequential chemical extraction procedure on dissolution and metal release from common ferromagnesian clay minerals: A combined solution chemistry and X-ray powder diffraction study. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 603–614.
Sakellariadou, F., Ladakis, M., & Haralambides, L. (2009). Cu, Zn and Sn vertical distribution in sediment cores from the Elefsis Gulf (Attiki-Greece), Second International Conference on Environmental and Computer Science, ICECS (pp. 445–448).
Singh, K. P., Mohan, D., Singh, V. K., & Malik, A. (2005). Studies on distribution and fractionation of toxic metals in Gomati river sediments—a tributary of the Ganges, India. Journal of Hydrology, 312, 14–27.
Smith, B. J., Mcalister, J. J., Roe, H. M., & Royle, S. A. (2011). Metal and oxalate contamination in a suburban watershed in the greater Toronto area: the benefits of combining acid leach and selective extraction procedures. Journal of Environmental Management, 92, 848–858.
Tack, F. M. G., & Verloo, M. G. (1995). Chemical partitioning and fractionation in soil and sediment heavy metal analysis: a review. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 59, 225–238.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the partitioning of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51, 844–851.
Tsai, L. J., Yu, K. C., Chen, S. F., Kung, P. Y., Chang, C. Y., & Lin, C. H. (2003). Partitioning variation of toxic metals in contaminated river sediment via bioleaching: effect of sulfur added to total solids ratio. Water Research, 37, 4623–4630.
Ure, A. M., Quevauviller, P., Muntau, H., & Griepink, B. (1993). Partitioning of toxic metals in solids and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 51, 135–151.
US Environmental Protection Agency. (2001). Method 823-B-01-002, methods for collection, storage and manipulation of sediments for chemical and toxicological analyses: technical manual. Chapter 3. Paragraph, 3(1), 3–4.
Usero, J., Gamero, M., Morillo, J., & Gracia, I. (1998). Comparative study of three sequential extraction procedures for metals in marine sediments. Environment International, 24, 487–496.
Wang, Y., Yang, Z., Shen, Z., Tang, Z., Niu, J., & Gao, F. (2011). Assessment of heavy metals in sediments from a typical catchment of the Yangtze River, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 172, 407–417.
Weng, H. X., Zhu, Y. M., Qin, Y. C., Chen, J. Y., & Chen, X. H. (2008). Accumulation discrepancy of heavy metal and organic pollutants in three near-shore depositional environments, south eastern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 31, 522–532.
Xiao, R., Bai, J., Huang, L., Zhang, H., Cui, B., & Liu, H. (2013). Distribution and pollution, toxicity and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from urban and rural rivers of the Pearl River delta in southern China. Ecotoxicology, 22, 1564–1575.
Xiao, R., Bai, J., Lu, Q., Zhao, Q., Gao, Z., Wen, X., & Liu, X. (2015). Fractionation, transfer, and ecological risks of heavy metals in riparian and ditch wetlands across a 100-year chronosequence of reclamation in an estuary of China. Science of the Total Environment, 517, 66–75.
Yang, Y., Chun, Y., Sheng, G., & Huang, M. (2004). PH-dependence of pesticide adsorption by wheat-residue-derived black carbon. Langmuir, 20, 6736–6741.
Yang, Z., Wang, Y., Shen, Z., Niu, J., & Tang, Z. (2009). Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 1186–1194.
Yu, K. C., Tsai, L. J., Chen, S. H., & Ho, S. T. (2001). Chemical binding of toxic metals in anoxic river sediments. Water Research, 35, 4086–4094.
Zhong, A. P., Guo, S. H., Li, F. M., Li, G., & Jiang, K. X. (2006). Impact of anions on the toxic metals release from marine sediments. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 18, 1216–1220.
Zimmerman, AJ, & Weindorf, DC (2010). Heavy metal and trace metal analysis in soil by sequential extraction: a review of procedures. International Journal of Analytical Chemistry, Article ID 387803, 7 pages.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hahladakis, J.Ν., Vasilaki, G., Smaragdaki, E. et al. Application of ecological risk indicators for the assessment of Greek surficial sediments contaminated by toxic metals. Environ Monit Assess 188, 271 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5275-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5275-6