Abstract
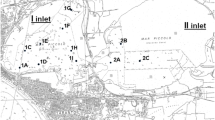
Sediments are an ecologically important component of the aquatic environment and may play a key role in mediating the exchange of contaminants between particulate, dissolved, and biological phases. For a comprehensive assessment of potential sediment toxicity, the use of a single species may not detect toxicant with a specific mode of action. Therefore it is advisable to carry out ecotoxicological tests on a base-set of taxa utilizing test species belonging to different trophic levels. This paper describes the ecotoxicological evaluation of marine sediments from seven sites of Mar Piccolo estuary (Southern, Italy), four of them were located in the first inlet and three in the second inlet of Mar Piccolo estuary. Sediment samples from a site in Taranto Gulf were used as control sediment. Dunaliella tertiolecta, Tigriopus fulvus, Mytilus galloprovincialis, and Corophium insidiosum, were employed to identify the quality of sediments. The integration of biological tests results showed that all sampling sites located in the first inlet of Mar Piccolo were identified as toxic, according to all tests, while the sites of second inlet were found not toxic. The results obtained in this study indicate that the use of a battery of biological tests have important implications for risk assessment in estuarine e coastal waters.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, W. J., Kimerle, R. A., & Barnett, J. W. (1992). Sediment quality and aquatic life assessment. Environmental Science and Technology, 26, 1865–1875.
American Public Health Association. (1995). Standard methods (19th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Annicchiarico, C., Biandolino, F., Cardellicchio, N., Di Leo, A., Giandomenico, S., & Prato, E. (2007). Predicting toxicity in marine sediments in Taranto Gulf (Ionian Sea, Southern Italy) using sediment quality guidelines and a battery of bioassay. Ecotoxicology, 16, 239–246.
APHA/AWWA/WEF (1999). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th edn.
ASTM (1993). Standard guide for conducting 10-d static sediment toxicity tests with marine and estuarine amphipods. In Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Water and Environmental Technology 11.04, E1367-92. ASTM, Philadelphia.
ASTM (2004). Standard guide for conducting static acute toxicity tests starting with embryos of four species of saltwater bivalve molluscs. PA: E 724–98. 21. ASTM, Philadelphia.
Beiras, R., & His, E. (1995). Effects of dissolved mercury on embryogenesis, survival and growth of Mytilus galloprovincialis mussel larvae. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 126, 185–189.
Bettinetti, R., Giarei, C., & Provini, A. (2003). Chemical analysis and sediment toxicity bioassays to assess the contamination of the River Lambro (Northern Italy). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 45, 72–78.
Burton, G. A., Jr., Baudo, R., Beltrami, M., & Rowland, C. (2001). Assessing sediment contamination using six toxicity assays. Journal of Limnology, 60(2), 263–267.
Cardellicchio, N., Buccolieri, A., Di Leo, A., & Spada, L. (2006). Heavy metals in marine sediments from the Mar Piccolo of Taranto (Ionian Sea, Southern Italy). Annali di Chimica, 96, 727–741.
Cardellicchio, N., Buccolieri, A., Giandomenico, S., Lopez, L., Pizzulli, F., & Spada, L. (2007). Organic pollutants (PAHs, PCBs) in sediments from the Mar Piccolo in Taranto (Ionian Sea, Southern Italy). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 55, 451–458.
Carli, A., & Fiori, M. A. (1977). Sviluppo larvale de1 Tigriopus fulvus Fischer. Atti IX Congr. S.I.B.M., Lacco Ameno d’Ischia, 19-22/5/77, pp. 181–190.
Castillo, G. C., Vila, I. C., & Neild, E. (2000). Ecotoxicity assessment of metals and waste water using multitrophic assays. Environmental Toxicology, 15, 370–375.
Chapman, P. M. (1990). The sediment quality triad approach to determining pollution-induced degradation. Science of the Total Environment, 97(98), 815–825.
Chapman, P. M., & Wang, F. Y. (2001). Assessing sediment contamination in estuaries. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 3–22.
Chapman, P. M., Swartz, R. C., Roddie, B., Phelps, H. L., van den Hurk, P., & Butler, R. (1992). An international comparison of sediment toxicity tests in the North Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 91, 253–264.
Christophoridis, C., & Fytianos, K. (2006). Conditions affecting the release of phosphorus from lake sediments. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 1181–1192.
Ciarelli, S. (1994). Guideline for conducting 10-day static sediment toxicity tests using marine or estuarine amphipods. Report from the Tidal Water Division, Middelburg, The Netherlands. Report RIKZ. 94.031.
Davoren, M., Illeabhain, N. S., Ohalloran, J., Hartl, M. G. J., Sheehan, D., Obrien, N. M., et al. (2005). A test battery approach for the ecotoxicological evaluation of estuarine sediments. Ecotoxicology, 14, 741–755.
Dutka, B. J., Tuominen, T., Churchland, L., & Kwan, K. K. (1989). Fraser river sediments and waters evaluated by the battery of the screening tests and techniques. Hydrobiologia, 188(189), 301–305.
EPA (2000). Methods for Measuring the Toxicity and Bioaccumulation of Sediment-associated Contaminants with Freshwater Invertebrates, second ed. EPA 600/R-99/064, Washington DC, USA.
Faraponova, O., De Pascale, D., Onorati, F., & Finora, M. G. (2005). Tigriopus fulvus (Copepoda, Harparticoida) as a target species in biological assays. Meiofauna Marina, 14, 91–95.
García-Lorenzo, M. L., Martinez-Sánchez, M. J., Perez-Sirvent, C., & Molina, J. (2009). Ecotoxicological evaluation for the screening of areas polluted by mining activities. Ecotoxicology, 18, 1077–1086.
Hamilton, M. A., Russo, R. C., & Thurston, R. V. (1977). Trimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays. Environmental Science and Technology, 11, 714–719.
His, E., Seaman, R. N. L., & Beiras, R. (1997). A simplified bivalve larval bioassay method for seawater quality assessment. Water Research, 31, 351–355.
His, E., Beiras, R., & Seaman, M. (1999). The assessment of aquatic contamination: bioassays with bivalve larvae. Advances in Marine Biology, 37, 1–178.
Ingersoll, C. G., MacDonald, D. D., Brumbaugh, W. G., Johnson, B. T., Kemble, N. E., Kunz, J. L., et al. (2002). Toxicity assessment of sediments from the Grand Calumet river and Indiana Harbor canal in Northwestern Indiana, USA. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 43, 156–167.
International Organization for Standardization (1999). Water quality—Determination of acute lethal toxicity to marine copepods (Copepoda, Crustacea), ISO/DIS 14669:1999:
International Organization for Standardization 2004. Water quality—marine algal growth inhibition test with Skeletonema Costatum and Phaeodactylum tricornutum, revision of first edition (ISO/DIS 10253:1995).
ISO (2005). Water quality—Determination of acute toxicity of marine or estuarine sediment to amphipods, 16712.
Joubert, G. (1980). A bioassay application for quantitative toxicity management using the green algae, Selenastrum capricornutum. Water Research, 14, 1759–1763.
Leitgib, L., Kálmán, J., & Gruiz, K. (2007). Comparison of bioassays by testing whole soil and their water extract from contaminated sites. Chemosphere, 66, 428–434.
Levin, S. A., & Kimball, S. F. (1985). New perspectives in ecotoxicology. Environmental Management, 8, 375–442.
Lors, C., Ponge, J. F., Martínez Aldaya, M., & Damidot, D. (2010). Comparison of solid-phase bioassays and ecoscores to evaluate the toxicity of contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 158, 2640–2647.
Losso, C., Arizzi Novelli, A., Picone, M., Ghetti, P. F., & Volpi Ghirardini, A. (2009). Porewater as a matrix in toxicity bioassays with sea urchins and bivalves: Evaluation of applicability to the Venice lagoon (Italy). Environment International, 35, 118–126.
Macken, A., Giltrap, M., Foley, B., McGovern, E., McHugh, B., & Davoren, M. (2008). An integrated approach to the toxicity assessment of Irish marine sediments: Validation of established marine bioassays for the monitoring of Irish marine sediments. Environment International, 34, 1023–1032.
Magalhaes, C., Coasta, J., Teixeira, C., & Bordalo, A. A. (2007). Impact of trace metals on denitrification in estuarine sediments of the Douro River estuary, Portugal. Marine Chemistry, 107, 332–341.
Mariani, L., De Pascale, D., Faraponova, O., Tornambè, A., Sarni, A., Giuliani, S., et al. (2006). The use of a battery test in marine ecotoxicology: The acute toxicity of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Environmental Toxicology, 21, 373–379.
Mecozzi, M., Onorati, F., Oteri, F., & Sarni, A. (2008). Characterisation of a bioassay using the marine alga Dunaliella tertiolecta associated with spectroscopic (visible and infrared) detection. International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 32(1), 104–120.
Miller, W. E., Greene, J. C., & Shirocyama, T. C. (1978). The Selenstrum capricornum, Prinz. Algal assay bottle test. Experimental design, application and data interpretration protocol. US EPA 600/9-78-018: 1–126.
Narracci, M., Cavallo, R. A., Acquaviva, M. I., Prato, E., & Biandolino, F. (2009). A test battery approach for ecotoxicological characterization of Mar Piccolo sediments in Taranto (Ionian Sea, Sothern Italy). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 148, 307–314.
Nendza, M. (2002). Inventory of marine biotest methods for the evaluation of dredged material and sediments. Chemosphere, 48, 865–883.
OECD (2001). OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Proposal for a new guideline 218. Sediment-water chironomid toxicity test using spiked sediment.
Onorati, F., Bigongiari, N., Pellegrini, D., & Giuliani, S. (1999). The suitability of Corophium orientale (Crustacea, Amphipoda) in harbour sediment toxicity bioassessment. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management, 2, 465–473.
Onorati, F., Pellegrini, D., & Ausili, A. (1999). Valutazione della tossicità naturale nel saggio Microtox® in fase solida: La normalizzazione pelitica. Acqua & Aria, 6, 83–91.
Oslo and Paris Commission (1998). OSPAR Guidelines for the management of dredged material, pp. 32.
Pane, L., Giacco, E., & Mariottini, G. L. (2007). Uso di Tigriopus fulvus (Copepoda: Harpacticoida) nella valutazione del rischio ecotossicologico in ambiente marino. Biologia Marina Mediterranea, 14, 186–188.
Peeters, E. T. H. M., Dewitte, A., Koelmans, A. A., Van der Velden, J. A., & Besten, P. J. (2001). Evalutation of bioassays versus contaminant concentrations in explaining the macroinvertebrate community structure in the Rhine-Meuse delta, the Netherlands. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 2883–2891.
Phillips, B.M., Hunt, J.W., Anderson, B.S., Puckett, H.M., Fairey, R., Wilson, C.J., & Tjeerdema, R. (2001). Statistical significance of sediment toxicity test results: threshold values derived by the detectable significance approach. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 20, 371–373.
Prato, E., & Biandolino, F. (2006). Monocorophium insidiosum (Crustacea, Amphipoda) as a candidate species in sediment toxicity testing. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 77(1), 1–9.
Prato, E., Di Leo, A., Biandolino, F., & Cardellicchio, N. (2006). Sediment toxicity tests using two species ofmarine amphipods: Gammarus aequicauda and Corophium insidiosum. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 76, 629–636.
Prato, E., Scardicchio, C., & Biandolino, F. (2008). Effects of temperature on the acute toxicity of cadmium to Corophium insidiosum. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 136, 161–166.
Prato, E., Bigongiari, N., Barchigiani, C., & Biandolino, F. (2010). Comparison of amphipods Corophium insidiosum and C. orientale (Crustacea: Amphipoda) in sediment toxicity testing. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A, 45, 1461–1467.
Robert, R., & His, E. (1985). Combined e.ects of salinity and cadmium chloride upon embryos and larvae of the Japanese oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Marine Environmental Research, 15, 303–312.
SETAC- Europe (1993). Guidance document on sediment toxicity assessment for freshwater and marine environments. In I. R. Hill, P. Matthiessen, & F. Heinbach (Eds.), Workshop on Sediment Toxicity Assessment, Renesse, The Netherlands, 8–10 November 1993, SETAC-Europe.
Shin, P. K. S., & Lam, W. K. C. (2001). Development of a marine sediment pollution index. Environmental Pollution, 113, 281–291.
Sibley, P. K., Benoit, D. A., & Ankley, G. T. (1997). The significance of growth in Chironomus tentans sediment toxicity tests: relationship to reproduction and demographic endpoints. Environmental Toxicolology and Chemistry, 16(2), 336–345.
Silva, S., Ré, A., Pestana, P., Rodrigues, A., & Quintino, V. (2004). Sediment disturbance off the Tagus Estuary, Western Portugal: chronic contamination, sewage outfall operation and runoff events. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 154–162.
Singh, M., Ansari, A. A., Muller, G., & Singh, I. B. (1997). Heavy metals in freshly deposited sediments of Gomti river (a tributary of the Ganga river): Effects of human activities. Environmental Geology, 29(3/4), 246–252.
US Environmental Protection Agency. (1974). Quality criteria for water, office of water and hazardous materials. Washington DC: US EPA.
US Environmental Protection Agency (1995). Short-term methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to west coast marine and estuarine organisms. EPA/600/R-95/136, Cincinnati, Ohio, USA.
Viganò, L. (2000). Assessment of the toxicity of River Po sediments with Ceriodaphnia dubia. Aquatic Toxicology, 47, 191–202.
Volpi Ghirardini, A., Losso, C., Arizzi Novelli, A., Baugrave, A., His, E., & Ghetti, P. F. (2005). Mytilus galloprovincialis as bioindicator in embryotoxicity testing to evaluate sediment quality in the lagoon of Venice (Italy). Chemistry and Ecology, 21(6), 455–463.
Wang, F., Goulet, R. R., & Chapman, P. M. (2004). Testing sediment biological effects with the freshwater amphipod Hyalella azteca: The gap between laboratory and nature. Chemosphere, 57, 1713–1724.
Wangberg, S. A., Bergstrom, B., Blanck, H., & Svanberg, O. (1995). The relative sensitivity and sensitivity of short-term toxicity tests applied to industrial wastewaters. Environmental Toxicology and Water Quality, 10, 81–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prato, E., Parlapiano, I. & Biandolino, F. Evaluation of a bioassays battery for ecotoxicological screening of marine sediments from Ionian Sea (Mediterranea Sea, Southern Italy). Environ Monit Assess 184, 5225–5238 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2335-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2335-9