Abstract
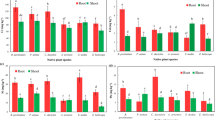
The aim of the present work was to monitor the Hg pollution in water and sediments of G.B. Pant Sagar located in Singrauli Industrial Region, India and to suggest the efficient aquatic plants for its phytoremediation. The study assessed the comparative potential of a free floating water fern Azolla pinnata and submerged aquatic macrophyte Vallisneria spiralis to purify waters polluted by Hg. Six days laboratory experiments have been conducted to mark the percentage removal of Hg at initial concentration of 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 and 3.0 mg L−1. The percentage removal of Hg was higher for A. pinnata (80–94%) than V. spiralis (70–84%). Likewise, the Hg accumulated in dry mass was much higher for A. pinnata and a high correlation (R 2 = 0.91 for A. pinnata and 0.99 for V. spiralis) was obtained between applied Hg doses and accumulated amounts in biomass. A concentration dependent decrease in chlorophyll a, protein, RNA, DNA and nutrients (NO3− and \({\text{PO}}_{\text{4}}^{{\text{3 - }}}\)) uptake was detected in A. pinnata and V. spiralis due to Hg toxicity. The decrease was more prominent in Azolla than Vallisneria. The results recommended the use of A. pinnata and V. spiralis to ameliorate the industrial effluents (thermal power, chlor-alkali and coal mine effluent) contaminated with Hg.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers, P. H., & Camardese, M. B. (1993). Effects of acidification on metal accumulation by aquatic plants and invertebrates. I. Constructed wetlands. Environmental and Toxicological Chemistry, 12, 959–967.
American Public Health Association (APHA) (2000). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (10th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Bennicelli, R., Stezpniewska, Z., Banach, A., Szajnocha, K., & Ostrowski, J. (2004). The ability of Azolla caroliniana to remove heavy metals (Hg(II), Cr(III), Cr(VI)) from municipal waste water. Chemosphere, 55, 141–146.
Bureau of Indian Standards (1983). General standards for discharge of environment pollutants effluents. http://hppcb.nic.in/standard.htm.
Bonaly, J., Bariand, A., Duret, S., & Mestre, J. C. (1980). Cadmium cytotoxicity and variation in nuclear content of DNA in Euglena gracilis. Physiologia Plantarum, 49, 286–290.
Cardwell, A. J., Hawker, D. W., & Greenway, M. (2002). Metal accumulation in aquatic macrophytes from south east Queensland, Australia. Chemosphere, 48, 653–663.
Denisova, A. I., Timchenko, V. M., & Nakhshyna, Y. P. (1989). Hydrology and hydrochemistry of the Dnieper and its reservoirs. Naukova Dumka Press: Kiev (in Russian).
EPA (1991). EPA method 245.6: Determination of mercury in tissues by cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry. Revision 2.3, April.
Finkelman, R. B., & Gross, P. M. K. (1999). The types of data needed for assessing the environmental and human health impacts of coal. International Journal of Coal Geology, 40, 91–101.
Gupta, M., & Chandra, P. (1996). Bioaccumulation and physiological changes in Hydrilla verticillata (l.f.) role in response to mercury. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 56, 319–326.
Herbert, D., Phipps, P. J., & Strange, R. F. (1971). Chemical analysis of microbial cells. In J. R. Norris, & D. M. Ribbons (Eds.) Methods in Microbiology (pp. 209–344). New York: Academic.
Holtt, D., & Webb, M. (1986). The toxicity and teratogenicity of mercuric mercury in the pregnant rat. Archives of Toxicology, 58(4), 243–248.
Imaoke, T., & Teranishi, S. (1988). Rate of uptake nutrient uptake and growth of the water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes (mart) Solms). Water Research, 22, 943–951.
Jana, S. (1988). Accumulation of Hg and Cr by three aquatic species and subsequent changes in several physiological and biochemical plant parameters. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 38, 105–109.
Jana, S., & Choudhuri, M. A. (1984). Synergistic effects of heavy metal pollutants on senescence in submerged aquatic plants. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 21, 351–357.
Jana, S., Dalal, T., & Barua, B. (1987). Effects and relative toxicity of heavy metals on Cuscuta reflexa. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 33, 23–27.
Kamal, M., Ghaly, A. E., Mohmud, N., & Cote, R. (2004). Phytoaccumulation of heavy metals by aquatic plants. Environmental International, 29, 1029–1039.
Kudo, A., & Miyahara, S. (1991). A case history – Minamata mercury pollution in Japan – From loss of human lives to decontamination. Water Science Technology, 23, 283.
Lenka, M., Panda, K. K., & Panda, B. B. (1990). Studies on the ability of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) to bioconcentrate and biomonitor aquatic mercury. Environmental Pollution, 66, 89–99.
Lenka, W., Panda, K. K., & Panda, B. B. (1992). Monitoring and assessment of mercury pollution in the vicinity of a chloralkali plant IV. Bioconcentration of mercury in in situ aquatic and terrestrial plant at Ganjam, India. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 22, 195–202.
Linnik, P. N., Zhuravleva, L. A., Samoilenko, V. N., & Nabivanets, Y. B. (1993). Influence of exploitation regime on quality of water in the Dnieper reservoirs and mouth zone of the Dnieper River. Gidrobiologicheskiy Zhurnal, 29(1), 86–99 (in Russian).
Linnik, P. M., & Zubenko, I. B. (2000). Role of bottom sediments in the secondary pollution of aquatic environments by heavy-metal compounds. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research and Management, 5, 11–21.
Lowry, O. H., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the folin–phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
MacKinney, G. (1941). Absorption of light by chlorophyll solution. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 140, 315–322.
Nasu, Y., Kugimoto, M., Tanaka, O., & Takimoto, A. (1984). Lemna as an indicator of water pollution and the absorption of heavy metals by Lemna. In D. Pascoe, & R. W. Edwards (Eds.) Fresh Water Biological Monitoring Conference Proceedings (pp. 113–120). Oxford: Pergamon.
Nicholas, D. J. D., & Nason, A. (1957). Determination of nitrate and nitrite. In S. P. Colowick, & N. O. Kaplan (Eds.) Methods in enzymology (vol. III). New York: Academic.
Nor, Y. M. (1990). The absorption of metal ions by Eichhornia crassipes. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability, 2, 85–91.
Nriagu, J. O. (1996). History of global metal pollution. Science, 272, 223–224.
Prasad, D. D. K., & Prasad, A. R. K. (1987a). Effect of lead and mercury on chlorophyll synthesis in mung bean seedlings. Phytochemistry, 26(4), 881–883.
Prasad, D. D. K., & Prasad, A. R. K. (1987b). Altered d aminolaevulinic acid metabolism by lead and mercury in germinating seedlings of bajra (Pennisetum typhoideum). Journal of Plant Physiology, 127, 241–249.
Rai, P. K. (2007a). Heavy-metal pollution in aquatic ecosystems and its phytoremediation using wetland plants: An eco-sustainable approach. International Journal of Phytoremediation (in press).
Rai, P. K. (2007b). Phytoremediation of Pb and Ni from industrial effluents using Lemna minor: an eco-sustainable approach. Bulletin of Biosciences, 5(1), 67–73.
Rai, P. K. (2007c). Wastewater management through biomass of Azolla pinnata: An ecosustainable approach. Ambio: A Journal on Human Environment, 36(5), 426–428.
Rai, P. K., Sharma, A. P., & Tripathi, B. D. (2007). Urban environment status in Singrauli Industrial region and its eco-sustainable management: A case study on heavy metal pollution. In L. Vyas (Ed.) Urban planning and environment, strategies and challenges (pp. 213–217). New York: McMillan.
Rai, U. N., Sinha, S., Tripathi, R. D., & Chandra, P. (1995). Wastewater treatability potenital of some aquatic macrophytes in wetlands. Ecological Engineering, 5, 5–12.
Rai, P. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2006). Impact of thermal power effluent on aquatic environment. National Journal of Radiation Research, 3(4), 190–192.
Rai, P. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2007a). Heavy metals adsorption characteristics of free floating aquatic macrophyte Spirodela poyrhhiza. Journal of Environmental Research and Development (in press).
Rai, P. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2007b). Heavy metals removal using nuisance blue green alga Microcystis in continuous culture experiment. Environmental Sciences, 4(1), 53–59.
Rai, P. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2007c). Heavy metals in industrial wastewater, soil and vegetables in Lohta village, India, Toxicological Environmental Chemistry, published online 7 September, 2007 (in press). DOI 10.1080/02772240701458584.
Sela, M., Garty, J., & Tel-Or, E. (1989). The accumulation and the effect of heavy metals on the water fern Azolla filiculioides. New Phytologist, 112, 7–12.
Sharma, D. C. (2003). Concern over mercury pollution in India. The Lancet, 362, 1030.
Sinha, S., & Chandra, P. (1990). Removal of Cu and Cd from water by Bacopa monnieri L. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 40, 271–276.
Sinha, S., Gupta, M., & Chandra, P. (1996). Bioaccumulation and biochemical effects of mercury in the plant of Bacopa monnieri L. Environmental Toxicology and Water Quality, 11, 105–112.
Sinha, S., Rai, U. N., Tripathi, R. D., & Chandra, P. (1993). Chromium and manganese uptake by Hydrilla verticillata (l.f.) Royle: Amelioration of chromium toxicity by manganese. Journal of Environmental Sciience and Health A, 28, 1545–1552.
Stratton, G. W., & Corke, C. T. (1979). The effect of Ni on growth, photosynthesis and nitrogenase activity of Anabena inequalis. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 25, 1094–1099.
Thapa, D., Srivastava, H. S., & Ormord, D. P. (1988). Physiological and biochemical effects of lead in higher plants. Vegetos, 1(2), 107–119.
Toxic Link Factsheet no. 17 (2003). Mercury – Tiny drops that kill.
Van, A., & Clijsters, H. (1990). Effect of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell and Environment, 13, 195–206.
Wang, Q., Kim, D., Dionysiou, D. D., Sorial, G. A., & Timberlake, D. (2004). Sources and remediation for mercury contamination in aquatic systems – a literature review. Environmental Pollution, 131, 323–336.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, P.K., Tripathi, B.D. Comparative assessment of Azolla pinnata and Vallisneria spiralis in Hg removal from G.B. Pant Sagar of Singrauli Industrial region, India. Environ Monit Assess 148, 75–84 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0140-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0140-2