Abstract
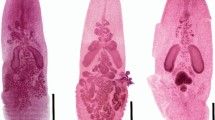
A new species in the genus Ditylenchus, D. stenurus n. sp. collected from western Iran, is described and illustrated herein based on morphological and molecular studies. The new species is characterised by a body length of 772 (663–863) μm, delicate stylet 6 (5–7) μm long, six lines in the lateral field. Median bulb of pharynx well-developed, muscular with crescentic valve. Post-vulval uterine sac well-developed, 35 (30–45) μm long, female tail elongate-conoid, becoming narrow suddenly with finely rounded terminus. The new species comes close in morphology and morphometrics to five known species of the genus, namely D. arachis, D. caudatus, D. clarus, D. myceliophagus, and D. nanus. DNA sequencing data was obtained on the partial 18S, D2/D3 expansion segments of the 28S rRNA gene and internal transcribed spacer (ITS). The phylogenetic relationships of this species with other Ditylenchus spp. using partial 18S–rDNA and D2/D3 indicated that D. stenurus n. sp. clustered together with several species belongs to the D. triformis-group i. e. D. africanus, D. destructor and D. halictus: all sharing a rounded tail terminus and six lines in lateral fields.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The species epithet refers to the morphology of the female tail (Greek words, στενός = narrow, and ουρά = tail)
References
Andrássy, I. (2007). In C. Csuzdi & S. Mahunka (Eds.), Free-living nematodes of Hungary (Nematoda errantia) II. Pedozoologica Hungarica No. 4. Budapest: Hungary, Hungarian Natural History Museum and Systematic Research Group of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
Arnold, T. W. (2010). Uninformative parameters and model selection using Akaike's information criterion. Journal of Wildlife Manage, 74, 1175–1178.
Brzeski, M. W. (1991). Review of the genus Ditylenchus Filipjev, 1936 (Nematoda: Anguinidae). Revue de Nématologie, 14, 9–59.
De Grisse, A. T. (1969). Redescription ou modifications de quelques techniques utilisées dans l'étude des nématodes phytoparasitaires. Mededelingen Faculteit Landbouwwetenschappen Rijksuniversiteit Gent, 34, 351–369.
De Ley, P., Félix, M. A., Frisse, L. M., Nadler, S. A., Sternberg, P. W., & Thomas, W. K. (1999). Molecular and morphological characterisation of two reproductively isolated species with mirror-image anatomy (Nematoda: Cephalobidae). Nematology, 2, 591–612.
Esmaeili, M., Heydari, R., Pourjam, E., & Atighi, M. R. (2014). Description of Ektaphelenchoides fuchsi n. sp. (Nematoda: Ektaphelenchinae) from western Iran. Zootaxa, 3846, 430–438.
Filipjev, I. N. (1936). On the classification of the Tylenchinae. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 3, 80–82.
Fortuner, R. (1982). On the genus Ditylenchus Filipjev, 1936 (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Revue Nématologie, 5, 17–38.
Giblin-Davis, R. M., Erteld, C., Kanzaki, N., Ye, W., Zeng, Y., & Center, B. J. (2010). Ditylenchus halictus n. sp. (Nematoda: Anguinidae), an associate of the sweat bee, Halictus sexcinctus (Halictidae), from Germany. Nematology, 12, 891–904.
Goodey, J. B. (1958). Ditylenchus myceliophagus n. sp. (Nematoda: Tylenchidae). Nematologica, 3, 91–96.
Goodey, T. (1933). Plant parasitic nematodes and the diseases they cause. E.P. Dutton and Co. Inc., London, 306 pp.
Greeff, R. (1872). Ueber Nematoden in Wurzelandschwellungen (Gallen) verschiedener Pflanzen. Sber Ges Beförd Ges Nature Marburg, 11, 169–174.
Holterman, M., van der Wurff, A., van den Elsen, S., van Megen, H., Holovachov, T. M. O., Bakker, J., & Helder, J. (2006). Phylum wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 1792–1800.
Huelsenbeck, J. P., & Ronquist, F. (2001). Mr Bayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics, 17, 1754–1755.
Hooper, D. J. (1973). Ditylenchus destructor. CIH Descriptions of plant-parasitic nematodes, Set 2, No. 21. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, Farnham Royal:UK.
Kühn, J. (1857). Über das Vorkommen von Anguillulen in erkrankten Bluhtenkopfen von Dipsacus fullonum L. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Zoologie, 9, 129–137.
Larget, B., & Simon, D. L. (1999). Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms for the Bayesian analysis of phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 750–759.
Mizukubo, T., & Minagawa, N. (1985). Taxonomic study of the genus Cephalenchus (Nematoda: Tylenchida) from Japan. Descriptions of three new species and records of C. planus Siddiqui and Khan with a key to species. Japanese Journal of Nematology, 15, 26–40.
Oliveira, R. D. L., Santin, A. M., Seni, D. J., Dietrich, A., Salazar, L. A., Subbotin, S. A., Mundo-Ocampo, M., Goldenberg, R., & Barreto, R. W. (2013). Ditylenchus gallaeformans sp. n. (Tylenchida: Anguinidae) – A neotropical nematode with biocontrol potential against weedy Melastomataceae. Nematology, 15, 179–196.
Paramonov, A. A. (1967). A critical review of the suborder Tylenchina (Filipjev, 1934) (Nematoda: Secernentea). Akademiya Nauk SSSR, Trudy Gel'mintologicheskoi Laboratorii, 18, 78–101 (In Russian).
Posada, D., & Criandall, K. A. (1998). Modeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14, 817–818.
Qiao, Y., Qing Yu, Q., Badiss, A., Zaidi, M. A., Ponomareva, E., Hu, Y., & Ye, W. (2016). Paraphyletic genus Ditylenchus Filipjev (Nematoda, Tylenchida), corresponding to the D. triformis-group and the D. dipsaci-group scheme. ZooKeys, 568, 1–12.
Siddiqi, M. R. (1963). Four new species in the subfamily Tylenchinae (Nematoda) from North India. Z. ParasitKde, 23, 397–404.
Siddiqi, M. R. (1980). Two new nematode genera, Safianema (Anguinidae) and Discotylenchus (Tylenchidae), with descriptions of three new species. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 47, 85–94.
Siddiqi, M. R. (2000). Tylenchida parasites of plants and insects (2nd ed.833 pp). Wallingford, UK: CABI Publishing.
Steinbuch, J. G. (1799). Das Grasalchen, Vibrio agrostis. Naturforscher, 28, 233–259.
Sturhan, D., & Brzeski, M. W. (1991). Stem and bulb nematodes, Ditylenchus spp. In W. R. Nickle (Ed.), Manual of agricultural nematology (pp. 423–465). New York, USA: Marcel Dekker, Inc..
Subbotin, S. A., & Moens, M. (2006). Molecular taxonomy and phylogeny. In R. N. Perry & M. Moens (Eds.), Plant nematology (pp. 33–58). Wallingford, UK: CABI.
Subbotin, S. A., Madani, M., Krall, E., Sturhan, D., & Moens, M. (2005). Molecular diagnostics, taxonomy and phylogeny of the stem nematode Ditylenchus dipsaci species complex based on the sequences of the ITS-rDNA. Phytopathology, 95, 1308–1315.
Subbotin, S. A., Sturhan, D., Chizhov, V., Vovlas, N., & Baldwin, J. (2006). Phylogenetic analysis of Tylenchida Thorne, 1949 as inferred from D2 and D3 expansion fragments of the 28S rRNA gene sequences. Nematology, 8, 455–474.
Tanha Maafi, Z., Subbotin, S. A., & Moens, M. (2003). Molecular identification of cyst-forming nematodes (Heteroderidae) from Iran and a phylogeny based on the ITS sequences of rDNA. Nematology, 5, 99–111.
Thorne, G. (1945). Ditylenchus destructor n. sp. the potato rot nematode, and Ditylenchus dipsaci (Kuhn, 1957) Filipjev, 1936, the teasel nematode (Nematoda: Tylenchidae). Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 12, 27–34.
Thorne, G. & Malek, R. B. (1968a). Nematodes of the Northem Great Plains. Part I. Tylenchida Nemata: Secementea. Brookings, S. Dakota, Agric. Exp. Statn, Bull. 31, 111 p.
Thorne, G. & Malek, R. B. (1968b). Nematodes of the Northern Great Plains. Part I. Tylenchida Nemata: Secernentea. Brookings, South Dakota, USA, Agricultural Experimental Station Bulletin 31.
Tzortzakakis, E. A., Archidona-Yuste, A., Liébanas, G., Birmpilis, I. G., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Navas-Cortés, J. A., Castillo, P., & Palomares-Rius, J. E. (2016). Rotylenchus cretensis n. sp. and R. cypriensis Antoniou 1980 (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae) recovered from the rhizosphere of olive at Crete (Greece) with a molecular phylogeny of the genus. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 144, 167–184.
Thorne, G. (1941). Some nematodes of the family Tylenchidae which do not possess a valvular median oesophageal bulb. The Great Basin Naturalist, 2, 37–85.
Vovlas, N., Subbotin, S. A., Troccoli, A., Liébanas, G., & Castillo, P. (2008). Molecular phylogeny of the genus Rotylenchus (Nematoda, Tylenchida) and description of a new species. Zoologica Scripta, 37, 521–537.
Vovlas, N., Troccoli, A., Palomares-Rius, J. E., De Luca, F., Lie’banas, G., Landa, B. B., Subbotin, S. A., & Castillo, P. (2011). Ditylenchus gigas n. sp. parasitizing broad bean: A new stem nematode singled out from the Ditylenchus dipsaci species complex using a polyphasic approach with molecular phylogeny. Plant Pathology, 60, 762–775.
Vovlas, N., Troccoli, A., Palomares-Rius, J. E., De Luca, F., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Liébanas, G., Landa, B. B., Subbotin, S. A., & Castillo, P. (2016). A new stem nematode, Ditylenchus oncogenes n. sp. (Nematoda: Tylenchida), parasitizing sowthistle from Adriatic coast dunes in southern Italy. Journal of Helminthology, 90, 152–165.
Wendt, K. R., Swart, A., Vrain, T. C., & Webster, J. M. (1995). Ditylenchus africanus sp. n. From South Africa; a morphological and molecular characterization. Fundamental Applied Nematology, 18, 241–250.
Whitehead, A. G., & Hemming, J. R. (1965). A comparison of some quantitative methods of extracting small vermiform nematodes from soil. Annals of Applied Biology, 55, 25–38.
Zhang, S. L., Liu, G. K., Janssen, T., Zhang, S. S., Xiao, S., Li, S. T., Couvreur, M., & Bert, W. (2014). A new stem nematode associated with peanut pod rot in China: Morphological and molecular characterization of Ditylenchus arachis n. sp. (Nematoda: Anguinidae). Plant Pathology, 63, 1193–1206.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the University of Tehran for financial support and Mr. Mahdi Esmaeili for his help during sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esmaeili, M., Heydari, R., Ziaie, M. et al. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Ditylenchus stenurus n. sp. (Nematoda: Anguinidae) from western Iran. Eur J Plant Pathol 149, 533–542 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1201-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1201-1