Abstract
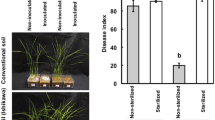
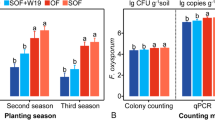
Organic management of soils is generally considered to reduce the incidence and severity of plant diseases caused by soil-borne pathogens. In this study, take-all severity on roots of barley and wheat, caused by Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici, was significantly lower in organically-managed than in conventionally-managed soils. This effect was more pronounced on roots of barley and wheat plants grown in a sandy soil compared to a loamy organically-managed soil. Fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. and in particular phlD+ pseudomonads, key factors in the take-all decline phenomenon, were represented at lower population densities in organically-managed soils compared to conventionally-managed soils. Furthermore, organic management adversely affected the initial establishment of introduced phlD+ P. fluorescens strain Pf32-gfp, but not its survival. In spite of its equal survival rate in organically- and conventionally-managed soils, the efficacy of biocontrol of take-all disease by introduced strain Pf32-gfp was significantly stronger in conventionally-managed soils than in organically-managed soils. Collectively, these results suggest that phlD+ Pseudomonas spp. do not play a critical role in the take-all suppressiveness of the soils included in this study. Consequently, the role of more general mechanisms involved in take-all suppressiveness in the organically-managed soils was investigated. The higher microbial activity found in the organically-managed sandy soil combined with the significantly lower take-all severity suggest that microbial activity plays, at least in part, a role in the take-all suppressiveness in the organically-managed sandy soil. The significantly different bacterial composition, determined by DGGE analysis, in organically-managed sandy soils compared to the conventionally-managed sandy soils, point to a possible additional role of specific bacterial genera that limit the growth or activity of the take-all pathogen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-DAPG:
-
2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol
- CFU:
-
colony forming units
- Ggt:
-
Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici
- Pf32-gfp:
-
Pseudomonas fluorescens strain (Pf32) gfp tagged
References
Ball DF (1964) Loss on ignition as an estimate of organic matter and organic carbon in non-calcareous soils. Journal of Soil Science. 15:84–92. In: Houba VJG, van der Lee JJ, Novozamsky I and Walinga I (1989) Soil and plant analysis. A serie of syllabi, part 5. Soil analysis procedures, Pages 4/1–4/2. Department of soil science and plant nutrition, Wageningen University
AHC Bruggen van (1995) ArticleTitlePlant-disease severity in high-input compared to reduced-input and organic farming systems Plant Disease 79 976–984
AHC Bruggen van AJ Termorshuizen (2003) ArticleTitleIntegrated approaches to root disease management in organic farming systems Australasian Plant Pathology 32 141–156
L Carpenter-Boggs AC Kennedy JP Reganold (2000) ArticleTitleOrganic and biodynamic management: effects on soil biology Soil Scientific Society of America Journal 64 1651–1659 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXntlGmu74%3D
RJ Cook (2003) ArticleTitleTake-all of wheat Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 62 73–86
JR Freitas ParticleDe JJ Germida (1992a) ArticleTitleGrowth promotion of winter wheat by fluorescent pseudomonads under growth chamber conditions Soil Biology and Biochemistry 24 1127–1135
JR Freitas Particle De JJ Germida (1992b) ArticleTitleGrowth promotion of winter wheat by fluorescent pseudomonads under field conditions Soil Biology and Biochemistry 24 1137–1146
LE Drinkwater K Letourneau F Workneh AHC Bruggen van C Shennan (1995) ArticleTitleFundamental differences between conventional and organic tomato agroecosystems in California Ecological Applications 5 1098–1112
BK Duffy DM Weller (1994) ArticleTitleA semiselective and diagnostic medium for Gaeumanomyces graminis var. tritici Phytopathology 84 1407–1415
BK Duffy G Défago (1999) ArticleTitleEnvironmental factors modulating antibiotic and siderophore biosynthesis by Pseudomonas fluorescens biocontrol strains Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65 2429–2438 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjs12gsLo%3D Occurrence Handle10347023
CA Eichner RW Erb KN Timmis I Wagner-Döbler (1999) ArticleTitleThermal gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of bioprotection from pollutant shocks in the activated sludge microbial community Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65 102–109 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjvVyhsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9872766
D Fravel (1999) ArticleTitleHurdles and bottlenecks on the road to biocontrol of plant pathogens Australasian Plant Pathology 28 53–56 Occurrence Handle10.1071/AP99007
M Gerlagh (1968) Introduction of Ophiobolus graminis Into New Polders and its Decline. Agricultural Reseach reports 713 Centre for Agricultural Publishing and Documentation Wageningen 97
JJ Germida SD Siciliano (2001) ArticleTitleTaxonomic diversity of bacteria associated with the roots of modern, recent and ancient wheat cultivars Biology and Fertility of Soils 33 410–415
BR Glick (1995) ArticleTitleThe enhancement of plant growth by free-living bacteria Canadian Journal of Microbiology 41 109–117 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXks1ygsrY%3D
N Gunapala KM Scow (1998) ArticleTitleDynamics of soil microbial biomass and activity in conventional and organic farming systems Soil Biology and Biochemistry 30 805–816 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXjsFylsLs%3D
AO Hannukukulla E Tapio (1990) ArticleTitleConventional and organic cropping systems at Suitita. V. Cereal diseases Journal of Agricultural Science Finland 62 339–347
O Heinemeyer H Insam EA Kaiser G Walenzik (1989) ArticleTitleSoil microbial biomass and respiration measurements: an automated technique based on infra-red gas analysis Plant and Soil 116 191–195 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02214547
H Heuer K Smalla (1997) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis for studying soil microbial communities JD Van Elsas ParticleVan JT Trevors EMH Wellington (Eds) Modern Soil Microbiology Marcel Dekker Inc New York 353–373
TW Hollins PR Scott RS Gregory (1986) ArticleTitleThe relative resistance of wheat, rye and triticale to take-all caused by Gaeumannomyces graminis Plant Pathology 35 93–100
Houba VJG and Novozamsky I (1998) Influence of storage time and temperature of dry soils on pH and extractable nutrients using 0.01 M CaCl2. Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry 360: 362–365. In: Houba VJG, van der Lee JJ, Novozamsky I and Walinga I (1989) Soil and plant analysis. A serie of syllabi, part 5. Soil analysis procedures, Pages 15/5–15/21. Department of soil science and plant nutrition, Wageningen University
JW Kloepper R Lifshitz Zablotowicz (1989) ArticleTitleFree-living bacterial inocula for enhancing crop productivity Trends in Biotechnology 7 39–44 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0167-7799(89)90057-7
IMB Knudsen K Debosz J Hockenhull DF Jensen S Elmholt (1999) ArticleTitleSuppressiveness of organically managed soils towards brown foot rot of barley Applied Soil Ecology 12 61–72 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0929-1393(98)00156-5
B Koch J Worm LE Jensen O Hojberg O Nybroe (2001) ArticleTitleCarbon limitation induces ss-dependent gene expression in Pseudomonas fluorescens in soil Applied and Environmental Microbiology 67 3363–3370 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.67.8.3363-3370.2001 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlvFSltLg%3D Occurrence Handle11472905
G Koch (1991) ArticleTitleFungal pathogens on winter wheat in comparison of 2 conventional farms and one biodynamic farm in Hess (FRG) 1986/87 Zeitschrift für Pflanzenkrankheiten Pflanzenschütz 98 125–136
BB Landa JA Navas-Cortés RM Jiménez-Díaz (2004) ArticleTitleInfluence of temperature on plant-rhizobacteria interactions related to biocontrol potential for suppression of Fusarium wilt of chickpea Plant Pathology 53 341–352 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.0032-0862.2004.01008.x
RP Larkin DR Fravel (2002) ArticleTitleEffects of varying environmental conditions on biological control of Fusarium wilt of tomato by nonpathogenic Fusarium spp Phytopathology 92 1160–1166
DW Lotter J Granett AD Omer (1999) ArticleTitleDifferences in grape phylloxera related grapevine root damage in organically and conventionally-managed vineyards in California HortScience 34 1108–1111
P Lucas MH Jeuffroy A Schoeny A Sarniquet (1997) ArticleTitleBasis for nitrogen fertilisation management of winter wheat crops infected with take-all Aspects of Applied Biology 50 255–262
P Mäder A Fliessbach D Dubois L Gunst P Fried U Niggli (2002) ArticleTitleSoil fertility and biodiversity in organic farming Science 296 1694–1697 Occurrence Handle12040197
M Mazzola DL Funnell JM Raaijmakers (2004) ArticleTitleWheat cultivar-specific selection of 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol-producing fluorescent Pseudomonas species from resident soil populations Microbial Ecology 48 338–348 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00248-003-1067-y Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXos1emtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle15692854
WGL Miller SE Lindow (1997) ArticleTitleAn improved GFP cloning cassette designed for prokaryotic transcriptional fusions Gene 191 149–153 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00051-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXksVSrs70%3D Occurrence Handle9218713
M Nei WH Li (1979) ArticleTitleMathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 76 5269–5273 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXitVWn Occurrence Handle291943
Nieuwenhuizen J, Maas YEM and Middelburg JJ (1994) Rapid analysis of organic carbon and nitrogen in particulate materials. Marine Chemistry 45: 217–224. In: Houba VJG, van der Lee JJ, Novozamsky I and Walinga I (1989) Soil and plant analysis. A serie of syllabi, part 5. Soil analysis procedures, Pages 15/5–15/21. Department of soil science and plant nutrition, Wageningen University
BH Ownley BK Duffy DM Weller (2003) ArticleTitleIdentification and manipulation of soil properties to improve the biological control performance of phenazine-producing Pseudomonas fluorescens Applied and Environmental Microbiology 69 3333–3343 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.69.6.3333-3343.2003 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXks1GltLs%3D Occurrence Handle12788734
CL Patten BR Glick (2002) ArticleTitleRole of Pseudomonas putida indoleacetic acid in development of the host plant root system Applied and Environmental Microbiology 68 3795–3801 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.68.8.3795-3801.2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmtVaqur0%3D Occurrence Handle12147474
Y Peer van de R Wachter Particle de (1994) ArticleTitleTREECON for Windows: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment Computer Applications in the Biosciences 10 569–570
EA Pierson DM Weller (1994) ArticleTitleUse of mixtures of fluorescent pseudomonads to suppress take-all and improve growth of wheat Phytopathology 84 940–947
JM Raaijmakers DM Weller LS Thomashow (1997) ArticleTitleFrequency of antibiotic-producing Pseudomonas spp. in natural environments Applied and Environmental Microbiology 63 881–887 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhsV2jtbk%3D
JM Raaijmakers DM Weller (1998) ArticleTitleNatural plant protection by 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol producing Pseudomonas spp. in take-all decline soils Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 11 144–152 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmsFWhsA%3D%3D
JP Reganold AS Palmer JC Lockhart AN Macgregor (1993) ArticleTitleSoil quality and financial performance of biodynamic and conventional farms in New Zealand Science 260 344–349 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXitlaqtrw%3D
AS Rosado GR Duarte L Seldin JD Elsas Particle van (1998) ArticleTitleGenetic diversity of nifH gene sequences in Paenibacillus azotofixans strains and soil samples analyzed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of PCR-amplified gene fragments Applied and Environmental Microbiology 64 2770–2779 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlsVKiu7Y%3D Occurrence Handle9687429
C Ryu MA Farag C Hu MS Reddy H Wei PW Pare JW Kloepper (2003) ArticleTitleBacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 100 4927–4932 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjt12nt7k%3D Occurrence Handle12684534
O Schabenberger FJ Pierce (2002) Contemporary Statisical Models for the Plant And Soil Sciences NumberInSeries7 CRC Press LLC Boca Raton, USA 405–520
P Schjønning S Elmholt LJ Munkholm K Debosz (2002) ArticleTitleSoil quality aspects of humid sandy loams as influenced by organic and conventional long-term management Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 88 195–214
DA Shah LV Madden (2004) ArticleTitleNonparametric analysis of ordinal data in designed factorial experiments Phytopathology 94 33–43
A Simon EH Ridge (1974) ArticleTitleThe use of ampicillin in a simplified selective medium for the isolation of fluorescent pseudomonads Journal of Applied Bacteriology 37 459–460 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXlsVSltg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle4425253
RW Smiley RJ Cook (1973) ArticleTitleRelationship between take-all of wheat and rhizosphere pH in soils fertilized with ammonium- vs. nitrate-nitrogen Phytopathology 63 882–890 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3sXltVCitrw%3D
RW Smiley (1978a) ArticleTitleColonization of wheat roots by Gaeumannomyces graminis inhibited by specific soils, microorganisms and ammonium-nitrogen Soil Biology and Biochemistry 10 175–179 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXls1Sjtr8%3D
RW Smiley (1978b) ArticleTitleAntagonists of Gaeumannomyces graminis from the rhizoplane of wheat in soils fertilized with ammonium- or nitrate-nitrogen Soil Biology and Biochemistry 10 169–174 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXlsVejur8%3D
KP Smith J Handelsman RM Goodman (1999) ArticleTitleGenetic basis in plants for interactions with disease suppressive bacteria Proceedings of the Nactional Academy of Sciences of the USA 96 4786–4790 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjtVKmsr8%3D
JT de Souza JM Raaijmakers (2003) ArticleTitlePolymorphisms within the prnD and pltC genes from pyrrolnitrin and pyoluteorin-producing Pseudomonas and Burkholderia spp FEMS Microbiology Ecology 43 21–34 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1574-6941.2003.tb01042.x
LS Thomashow DM Weller (1988) ArticleTitleRole of a phenazine antibiotic from Pseudomonas fluorescens in biological control of Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici Journal of Bacteriology 170 3499–3508 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXlsVKit7g%3D Occurrence Handle2841289
DM Weller (1988) ArticleTitleBiological control of soil-borne pathogens in the rhizosphere with bacteria Annual Review of Phytopathology 26 379–407 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.py.26.090188.002115
DM Weller JM Raaijmakers BB McSpadden Gardener LS Thomashow (2002) ArticleTitleMicrobial populations responsible for specific soil suppressiveness to plant pathogens Annual Review of Phytopathology 40 309–348 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.phyto.40.030402.110010 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xos1Cltbs%3D Occurrence Handle12147763
JM Whipps (1997) ArticleTitleDevelopments in the biological control of␣soil-borne plant pathogens Advances in Botanical Research 26 1–134
F Workneh AHC Bruggen Particle van (1994) ArticleTitleMicrobial density, composition, and diversity in organically and conventionally-managed rhizosphere soil in relation to suppression of corky root of tomatoes Applied Soil Ecology. 1 219–230 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0929-1393(94)90013-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiddink, G.A., van Bruggen, A.H.C., Termorshuizen, A.J. et al. Effect of Organic Management of Soils on Suppressiveness to Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici and its Antagonist, Pseudomonas fluorescens. Eur J Plant Pathol 113, 417–435 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-005-5402-7
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-005-5402-7