Abstract
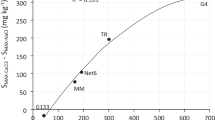
This study investigated the effects of surface functional groups, cation exchange capacity (CEC), surface charge, sesquioxides and specific surface area (SSA) of three soil clay fractions (SCFs) (kaolinite–illite, smectite and allophane) on the retention of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soils. Physico-chemical properties of the SCFs before and after removing native carbon and/or sesquioxides were characterised, and the DOC adsorption–desorption tests were conducted by a batch method. Native organic carbon (OC)/sesquioxide removal treatments led to a small change in the CEC values of kaolinite–illite, but significant changes in those of smectite and allophane. The net negative surface charge increased in all samples with an increase in pH indicating their variable charge characteristics. The removal of native OC resulted in a slight increase in the net positive charge on soil clay surfaces, while sesquioxide removal increased the negative charge. Changes in the functional groups on the SCF surfaces contributed to the changes in CEC and zeta potential values. There was a strong relationship (R 2 = 0.93, p < 0.05) between the Langmuir maximum DOC adsorption capacity (Q max) and SSA. The Q max value also showed a moderately strong relationship (R 2 = 0.55, p < 0.05) with zeta potential (at pH 7). Q max was only poorly correlated with CEC and native OC content. Therefore, along with SSA, the surface charge and functional groups of SCFs played the key role in determining the adsorption affinity and hence retention of DOC in soils.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 January 2018
Unfortunately, in the original publication of the article, Prof. Yong Sik Ok’s affiliation was incorrectly published. The author’s affiliation is as follows.
References
Angove, M. J., Fernandes, M. B., & Ikhsan, J. (2002). The sorption of anthracene onto goethite and kaolinite in the presence of some benzene carboxylic acids. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 247, 282–289.
Aryal, R., Nirola, R., Beecham, S., & Sarkar, B. (2016). Influence of heavy metals in root chemistry of Cyperus vaginatus R.Br: A study through optical spectroscopy. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.04.008.
Baham, J., & Sposito, G. (1994). Adsorption of dissolved organic carbon extracted from sewage sludge on montmorillonite and kaolinite in the presence of metal ions. Journal of Environmental Quality, 23, 147–153.
Blakemore, L.C., Searle, P.L., & Daly, B.K. (1987). Methods for chemical analysis of soils. New Zealand soil Bureau scientific report (vol. 80, p A1.1).
Bolan, N. S., Adriano, D. C., Kunhikrishnan, A., James, T., McDowell, R., & Senesi, N. (2011). Chapter One—Dissolved organic matter: Biogeochemistry, dynamics, and environmental significance in soils. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Advances in Agronomy (Vol. 110, pp. 1–75). Burlington: Academic Press.
Bolan, N. S., Naidu, R., Syers, J. K., & Tillman, R. W. (1999). Surface charge and solute interactions in soils. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Advances in Agronomy (Vol. 67, pp. 87–140). Burlington: Academic Press.
Calabi-Floody, M., Bendall, J. S., Jara, A. A., Welland, M. E., Theng, B. K. G., Rumpel, C., et al. (2011). Nanoclays from an Andisol: Extraction, properties and carbon stabilization. Geoderma, 161, 159–167.
Cavallaro, N., & McBride, M. B. (1984). Effect of selective dissolution on charge and surface properties of an acid soil clay. Clays and Clay Minerals, 32, 283–290.
Chao, T. T., & Zhou, L. (1983). Extraction techniques for selective dissolution of amorphous iron oxides from soils and sediments. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 47, 225–232.
Chen, W., Westerhoff, P., Leenheer, J. A., & Booksh, K. (2003). Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 5701–5710.
Chorom, M., & Rengasamy, P. (1995). Dispersion and zeta potential of pure clays as related to net particle charge under varying pH, electrolyte concentration and cation type. European Journal of Soil Science, 46, 657–665.
Churchman, G. J. (2010). Is the geological concept of clay minerals appropriate for soil science? A literature-based and philosophical analysis. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 35, 927–940.
Churchman, G. J., Foster, R. C., D’Acqui, L. P., Janik, L. J., Skjemstad, J. O., Merry, R. H., et al. (2010). Effect of land-use history on the potential for carbon sequestration in an Alfisol. Soil and Tillage Research, 109, 23–35.
Churchman, G. J., & Lowe, D. J. (2012). Alteration, formation, and occurrence of minerals in soils. In P. Huang, Y. Li, & M. E. Sumner (Eds.), Hand book of soil sciences: Properties and processes (2nd ed.). USA: CRC Press.
Churchman, G., & Tate, K. (1986). Aggregation of clay in six New Zealand soil types as measured by disaggregation procedures. Geoderma, 37, 207–220.
Currie, W., Aber, J., McDowell, W., Boone, R., & Magill, A. (1996). Vertical transport of dissolved organic C and N under long-term N amendments in pine and hardwood forests. Biogeochemistry, 35, 471–505.
Dai, M. (1994). The effect of zeta potential of activated carbon on the adsorption of dyes from aqueous solution. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 164, 223–228.
Elliott, H. A., Liberati, M. R., & Huang, C. P. (1986). Effect of iron oxide removal on heavy metal sorption by acid subsoils. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 27, 379–389.
Escudey, M., & Galindo, G. (1983). Effect of iron oxide coatings on electrophoretic mobility and dispersion of allophane. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 93, 78–83.
Feng, X., Simpson, A., & Simpson, M. J. (2005). Chemical and mineralogical controls on humic acid sorption to clay mineral surfaces. Organic Geochemistry, 36, 1553–1566.
Ferris, A. P., & Jepson, W. B. (1975). The exchange capacities of kaolinite and the preparation of homoionic clays. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 51, 245–259.
Golchin, A., Oades, J., Skjemstad, J., & Clarke, P. (1994). Study of free and occluded particulate organic matter in soils by solid state 13C CP/MAS NMR spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Soil Research, 32, 285–309.
Golchin, A., Oades, J. M., Skjemstad, J., & Clarke, P. (1995). Structural and dynamic properties of soil organic-matter as reflected by 13C natural-abundance, pyrolysis mass-spectrometry and solid-state 13C NMR-spectroscopy in density fractions of an oxisol under forest and pasture. Soil Research, 33, 59–76.
Gu, B., Schmitt, J., Chen, Z., Liang, L., & McCarthy, J. F. (1994). Adsorption and desorption of natural organic matter on iron oxide: mechanisms and models. Environmental Science and Technology, 28, 38–46.
Guggenberger, G., & Kaiser, K. (2003). Dissolved organic matter in soil: challenging the paradigm of sorptive preservation. Geoderma, 113, 293–310.
Hussain, S. A., Demirci, Ş., & Özbayoğlu, G. (1996). Zeta potential measurements on three clays from Turkey and effects of clays on coal flotation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 184, 535–541.
Kahle, M., Kleber, M., & Jahn, R. (2002). Predicting carbon content in illitic clay fractions from surface area, cation exchange capacity and dithionite-extractable iron. European Journal of Soil Science, 53, 639–644.
Kahle, M., Kleber, M., & Jahn, R. (2003). Retention of dissolved organic matter by illitic soils and clay fractions: Influence of mineral phase properties. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 166, 737–741.
Kahle, M., Kleber, M., & Jahn, R. (2004). Retention of dissolved organic matter by phyllosilicate and soil clay fractions in relation to mineral properties. Organic Geochemistry, 35, 269–276.
Kaiser, K., & Guggenberger, G. (2003). Mineral surfaces and soil organic matter. European Journal of Soil Science, 54, 219–236.
Kaiser, K., & Guggenberger, G. (2007). Sorptive stabilization of organic matter by microporous goethite: sorption into small pores vs. surface complexation. European Journal of Soil Science, 58, 45–59.
Kindler, R., Siemens, J., Kaiser, K., Walmsley, D. C., Bernhofer, C., Buchmann, N., et al. (2011). Dissolved carbon leaching from soil is a crucial component of the net ecosystem carbon balance. Global Change Biology, 17, 1167–1185.
Kögel-Knabner, I., Ekschmitt, K., Flessa, H., Guggenberger, G., Matzner, E., Marschner, B., et al. (2008). An integrative approach of organic matter stabilization in temperate soils: Linking chemistry, physics, and biology. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 171, 5–13.
Lowe, D. J., & Palmer, D. J. (2005). Andisols of New Zealand and Australia. Journal of Integrated Field Science, 2, 39–65.
Lützow, M., Kögel-Knabner, I., Ekschmitt, K., Matzner, E., Guggenberger, G., Marschner, B., et al. (2006). Stabilization of organic matter in temperate soils: Mechanisms and their relevance under different soil conditions—A review. European Journal of Soil Science, 57, 426–445.
Ma, W., Li, Z., Ding, K., Huang, B., Nie, X., Lu, Y., et al. (2016). Stability of soil organic carbon and potential carbon sequestration at eroding and deposition sites. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16, 1705–1717.
Madejova, J., & Komadel, P. (2001). Baseline studies of the clay minerals society source clays: infrared methods. Clays and Clay Minerals, 49, 410–432.
Marchuk, A., Rengasamy, P., & McNeill, A. (2013). Influence of organic matter, clay mineralogy, and pH on the effects of CROSS on soil structure is related to the zeta potential of the dispersed clay. Soil Research, 51, 34–40.
Mavi, M. S., Sanderman, J., Chittleborough, D. J., Cox, J. W., & Marschner, P. (2012). Sorption of dissolved organic matter in salt-affected soils: Effect of salinity, sodicity and texture. Science of the Total Environment, 435–436, 337–344.
Mayes, M. A., Heal, K. R., Brandt, C. C., Phillips, J. R., & Jardine, P. M. (2012). Relation between soil order and sorption of dissolved organic carbon in temperate subsoils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 76, 1027–1037.
Mehra, O. P., & Jackson, M. L. (1958). Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by a dithionite-citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate. In A. Swineford (Ed.), Proceedings of the 7th national conference on clays and clays minerals (pp. 317–327). Washigton DC: Pergamon Press.
Meier, M., Namjesnik-Dejanovic, K., Maurice, P. A., Chin, Y.-P., & Aiken, G. R. (1999). Fractionation of aquatic natural organic matter upon sorption to goethite and kaolinite. Chemical Geology, 157, 275–284.
Mikutta, R., Kleber, M., & Jahn, R. (2005). Poorly crystalline minerals protect organic carbon in clay subfractions from acid subsoil horizons. Geoderma, 128, 106–115.
Mikutta, R., Mikutta, C., Kalbitz, K., Scheel, T., Kaiser, K., & Jahn, R. (2007). Biodegradation of forest floor organic matter bound to minerals via different binding mechanisms. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71, 2569–2590.
Moche, M., Gutknecht, J., Schulz, E., Langer, U., & Rinklebe, J. (2015). Monthly dynamics of microbial community structure and their controlling factors in three floodplain soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 90, 169–178.
Naidu, R., Bolan, N. S., Kookana, R. S., & Tiller, K. G. (1994). Ionic-strength and pH effects on the sorption of cadmium and the surface charge of soils. European Journal of Soil Science, 45, 419–429.
Oades, J. M. (1988). The retention of organic matter in soils. Biogeochemistry, 5, 35–70.
Perelomov, L., Sarkar, B., Rahman, M. M., Goryacheva, A., & Naidu, R. (2016). Uptake of lead by Na-exchanged and Al-pillared bentonite in the presence of organic acids with different functional groups. Applied Clay Science, 119, 417–423.
Rayment, G. E. (2011). Soil chemical methods: Australasia. In G. E. Rayment & D. J. Lyons (Eds.), Australian soil and land survey handbooks. Collingwood: CSIRO Publishing.
Repacholi, M. (2012). Clay mineralogy: Spectroscopic and chemical determinative methods. London: Chapman & Hall.
Rinklebe, J., Shaheen, S. M., & Yu, K. (2016). Release of As, Ba, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Sr under pre-definite redox conditions in different rice paddy soils originating from the U.S.A. and Asia. Geoderma, 270, 21–32.
Rusmin, R., Sarkar, B., Liu, Y., McClure, S., & Naidu, R. (2015). Structural evolution of chitosan–palygorskite composites and removal of aqueous lead by composite beads. Applied Surface Science, 353, 363–375.
Saidy, A., Smernik, R., Baldock, J., Kaiser, K., & Sanderman, J. (2013). The sorption of organic carbon onto differing clay minerals in the presence and absence of hydrous iron oxide. Geoderma, 209, 15–21.
Saidy, A. R., Smernik, R. J., Baldock, J. A., Kaiser, K., & Sanderman, J. (2015). Microbial degradation of organic carbon sorbed to phyllosilicate clays with and without hydrous iron oxide coating. European Journal of Soil Science, 66, 83–94.
Saidy, A., Smernik, R., Baldock, J., Kaiser, K., Sanderman, J., & Macdonald, L. (2012). Effects of clay mineralogy and hydrous iron oxides on labile organic carbon stabilisation. Geoderma, 173, 104–110.
Sarkar, B., Megharaj, M., Shanmuganathan, D., & Naidu, R. (2013). Toxicity of organoclays to microbial processes and earthworm survival in soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 261, 793–800.
Sarkar, B., Megharaj, M., Xi, Y., & Naidu, R. (2011). Structural characterisation of Arquad® 2HT-75 organobentonites: Surface charge characteristics and environmental application. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 195, 155–161.
Schneider, M. P. W., Scheel, T., Mikutta, R., van Hees, P., Kaiser, K., & Kalbitz, K. (2010). Sorptive stabilization of organic matter by amorphous Al hydroxide. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74, 1606–1619.
Sequi, P., & Aringhieri, R. (1977). Destruction of organic matter by hydrogen peroxide in the presence of pyrophosphate and its effect on soil specific surface area. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 41, 340–342.
Setia, R., Rengasamy, P., & Marschner, P. (2014). Effect of mono- and divalent cations on sorption of water-extractable organic carbon and microbial activity. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 50, 727–734.
Shaheen, S. M., Rinklebe, J., Rupp, H., & Meissner, R. (2014). Temporal dynamics of pore water concentrations of Cd Co, Cu, Ni, and Zn and their controlling factors in a contaminated floodplain soil assessed by undisturbed groundwater lysimeters. Environmental Pollution, 191, 223–231.
Singh, M., Sarkar, B., Biswas, B., Bolan, N. S., & Churchman, G. J. (2017). Relationship between soil clay mineralogy and carbon protection capacity as influenced by temperature and moisture. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 109, 95–106.
Singh, M., Sarkar, B., Biswas, B., Churchman, G. J., & Bolan, N. S. (2016). Adsorption–desorption behaviour of dissolved organic carbon by soil clay fractions of varying mineralogy. Geoderma, 280, 47–56.
SSS. (2014). Keys to soil taxonomy, soil survey staff (12th ed.). Washington, DC: USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service.
Stace, H.C.T., Hubble, G.D., Brewer, R., Northcote, K.H., Sleeman, J.R., Mulcahy, M.J. et al. (1968). A Handbook of Australian Soils. Rellim technical publications for the CSIRO and the International Society of Soil Science, Glenside, South Australia.
Tahir, S., & Marschner, P. (2016). Clay amendment to sandy soil—Effect of clay concentration and ped size on nutrient dynamics after residue addition. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16, 2072. doi:10.1007/s11368-016-1406-5.
Wada, K. (1985). Distinctive properties of Andosols. In B. S. Stewart (Ed.), Advances in soil science (pp. 173–229). NewYork: Springer.
Wilson, M. (1999). The origin and formation of clay minerals in soils: past, present and future perspectives. Clay Minerals, 34, 7–25.
Wright, A. F., & Bailey, J. S. (2001). Organic carbon, total carbon, and total nitrogen determinations in soils of variable calcium carbonate contents using a Leco CN-2000 dry combustion analyzer. Communication in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 32, 3243–3258.
Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, G., Wu, Y., & Jiang, T. (2015). A further study on adsorption interaction of humic acid on natural magnetite, hematite and quartz in iron ore pelletizing process: Effect of the solution pH value. Powder Technology, 271, 155–166.
Zhuang, J., & Yu, G.-R. (2002). Effects of surface coatings on electrochemical properties and contaminant sorption of clay minerals. Chemosphere, 49, 619–628.
Acknowledgements
Mandeep Singh is thankful to the University of South Australia and Department of Education and Training, Government of Australia, for awarding him a US-APA PhD Scholarship. This research was partly supported by an Australian Research Council Discovery-Project (DP140100323).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0045-0.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M., Sarkar, B., Hussain, S. et al. Influence of physico-chemical properties of soil clay fractions on the retention of dissolved organic carbon. Environ Geochem Health 39, 1335–1350 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-9939-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-9939-0