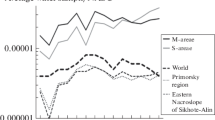
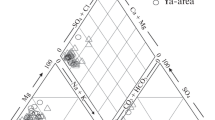
Abstract
Rocks eaten by wild animals on the Bolshoy Shanduyskiy kudur in the Sikhote-Alin region (Russian Federation) are zeolite–clay mineral complexes—products of weathering of zeolitized vitric tuffs of rhyolite composition, deposited in aqueous medium within the volcanic caldera of about 55 million years ago. By composition of rock-forming oxides, the tuffs refer to high-potassium calc-alkaline series. In trace elements of most favorite kudurites of the Bolshoy Shanduyskiy kudur, there are significantly increased contents of most of rare earth elements (2–5 times in comparison with surrounding rocks). The results of our analysis of geological and geochemical data on kudurs and kudurites in another part of the Sikhote-Alin, as well as on other regions of the world (particularly, in Africa and Indonesia), taking into account new data on the prevalence of rare earth elements in living matter and their medical and biological properties, enable us to consider the version of causal connection of the geophagy with rare earth elements.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brittain, H. G., Richardson, F. S., & Martin, R. B. (1976). Terbium (III) emission as a probe of calcium (II) binding sites in proteins. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 98, 8255–8260.
Chekryzhov, I Yu., Popov, V. K., Panichev, A. M., Seredin, V. V., & Smirnova, E. V. (2010). New data on the stratigraphy, volcanism, and zeolite mineralization of the Cenozoic Vanchinskaya Depression in Primorye. Russian Journal of Pacific Geology, 4(4), 314–330.
Ekosse, G. E., Ngole, V. M., & Longo-Mbenz, B. (2011). Mineralogical and geochemical aspects of geophagic clayey soils from the Democratic Republic of Congo. International Journal of the Physical Sciences, 6(31), 7302–7313.
Feng, L., Xiao, H., He, X., Li, Z., Li, F., Liu, N., et al. (2006). Neurotoxicological consequence of long-term exposure to lanthanum. Toxicology Letters, 165, 112–120.
Hancock, R. G. V., Aufreiter, S., Wrangham, R., & Pier, H. W. (1997). Analysis of geophagy soils in Kibale Forest, Uganda. Primates, 38(2), 159–176.
He, M. L., Ranz, D., & Rambeck, W. A. (2003). Effect of dietary rare earth elements on growth performance and blood parameters of rats. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 87, 1–7.
He, R., & Xia, Z. (1998). Effects of rare earth elements on growing and fattening of pigs. Guangxi Agricultural Sciences, 5, 243–245 (in Chinese).
Houston, D. C., Gilardi, J. D., & Hall, A. J. (2001). Soil consumption by elephants might help to minimize the toxic effects of plant secondary compounds in forest browse. Mammal Review, 31(3–4), 249–254.
Kharitonova, N. A. (2013). Acidulated waters of the North-East of Asia: origin and evolution. Ph.D. Thesis, Tomsk, Russia (in Russian).
Liu, J., Shen, Z., Yang, W., Che, J., Xie, L., & Lei, H. (2002). Effect of long-term intake of rare earth in drinking water on trace elements in brains of mice. Journal of Rare Earths, 20(5), 562–564.
Mahaney, W. C., & Hancock, R. G. V. (1990). Geochemical analysis of African buffalo geophagic sites and dung on Mount Kenya. East Africa. Mammalia, 54(1), 25–32.
Mahaney, W. C., Miller, M. W., Muliono, H., Hancock, R. G. V., & Aufreiter, S. (2000). Mineral and chemical analyses of soil eaten by humans in Indonesia. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 10, 93–109.
Mahaney, W. C., Watts, D., & Hancock, R. G. V. (1990). Geophagia by mountain gorillas (Gorilla gorilla beringei) in the Virunga Mountains. Rwanda. Primates, 31(1), 113–120.
Mahaney, W. C., Zippin, J., Hancock, R. G. V., Aufreiter, S., Campbell, S., Malloch, D., et al. (1999). Chemistry, mineralogy and microbiology of termite mound soils eaten by the chimpanzees of the Mahale mountains, Western Tanzania. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 15, 565–588.
Martin, R. B., & Richardson, F. (1979). Lanthanides as probes for calcium in biological systems. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics, 12, 181–209.
Mattson, D. J., Green, G. I., & Swalley, R. (1999). Geopfagy by Yellowstone grizzly bears. Ursus, 11, 109–116.
Mills, A., & Milewski, A. (2007). Geophagy and nutrient supplementation in the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Tanzania, with particular reference to selenium, cobalt and molybdenum. Journal of Zoology, 271, 110–118.
Mollel, G. F. (2007). Petrocchemistry and geochronology of Ngorongoro volcanic highland complex and its relationship to Laetoli and Olduvai Gorge. Tanzania. Ph.D. Dissertation, New Brunswick, NJ.
Panichev, A. M. (2011). Geophagy: Geological, ecological and biomedical aspects. Moscow: Nauka (in Russian).
Panichev, A. M., Golokhvast, K. S., Gulkov, A. N., & Chekryzhov, I Yu. (2013). Geophagy and geology of mineral licks (kudurs): A review of Russian publications. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35(1), 133–152.
Panichev, A. M., Popov, V. K., & Chekryzhov, I Yu. (2009). Geological nature of kudyurs in the volcanic mountains on example of Vanchinskaya depression in the Sikhote-Alin. Achievements in the Life Sciences, 1, 52–70 (in Russian).
Panichev, A. M., Popov, V. K., Chekryzhov, I Yu., Golokhvast, K. S., & Seryodkin, I. V. (2012). Kudurs of paleovolcano Solontsoviy in the Tayojnaya river basin, East Sikhote-Alin. Achievements in the Life sciences, 5, 5–29 (in Russian).
Panichev, A. M., Trepet, S. A., Chekryzhov, I. Y., Loktionova, O. A., & Krupskaya, V. V. (2014). Causes of geophagy by ungulate animals in the Caucasus Mountains. Achievements in the Life Sciences, 8(1), 35–42.
Pushcharovskiy, D. Y. (2000). X-ray diffraction of minerals. Moscow: Geoinformmark (in Russian).
Sako, A., Mills, A. J., & Roychoudhury, A. N. (2009). Rare earth and trace element geochemistry of termite mounds in central and northeastern Namibia: Mechanisms for micro-nutrient accumulation. Geoderma, 153(1–2), 217–230.
Schramberg, C. K. (2004). Untersuchungen zum einfluss seltener erd-citrate auf leistungsparameter beim schwein und die ruminale fermentation im künstlichen pansen (RUSITEC). In Inaugural-Dissertation zur Erlangung der tiermedizinischen Doktorwürde der tierärztlichen Fakultät der Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, München.
Seredin, V. V. (1991). About new type of rare earth emplacement of cainozoic cola bearing depressions. Doklady Academy of Sciences SSSR, 320(6), 1446–1450 (in Russian).
Shivakumar, K., Renuka, N. R., & Valiathan, M. S. (1992). Paradoxical effect of cerium on collagen synthesis in cardiac fibroblasts. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 24(7), 775–780.
Sliwa, K., Damasceno, A., & Mayosi, B. M. (2005). Epidemiology and etiology of cardiomyopathy in Africa. Circulation, 112(23), 3577–3583.
Smitha, B., Chenerya, S. R. N., Cooka, J. M., Stylesa, M. T., Tiberindwab, J. V., Hamptonb, C., et al. (1998). Geochemical and environmental factors controlling exposure to cerium and magnesium in Uganda. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 65(1), 1–15.
Sun, S. S., & McDonough, W. F. (1989). Chemical and isotopic systematics of ocean basalts implications for mantle composition and processes. In A. D. Saunders & M. J. Norry (Eds.), Magmatism in ocean basin (pp. 313–345). London: Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1981). The composition and evolution of the continental crust: Rare Earth element evidence from sedimentary rocks. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A, 301, 381–399.
Vakh, E. A. (2012). Rare earth elements in natural and industrial waters of the Far East of Russia. Ph.D. Thesis, Tomsk, Russia (in Russian).
Vetrennikov, V. V. (1976). Geological framework of the Sikhote-Alin State Nature Reserve and the Central Sikhote-Alin. Vladivostok: Far Eastern Book Publishers (in Russian).
Young, S. L., Sherman, P. W., Lucks, J. B., & Pelto, G. H. (2011). Why on Earth?: Evaluating hypotheses about the physiological functions of human geophagy. The Quarterly Review of Biology, 86(2), 97–120.
Zhao, H., Hao, W.-D., Xu, H.-E., Shang, L.-Q., & Lu, Y.-Y. (2004). Gene expression profiles of hepatocytes treated with La(NO3)3 of rare earth in rats. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 10(11), 1625–1629.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panichev, A.M., Popov, V.K., Chekryzhov, I.Y. et al. Rare earth elements upon assessment of reasons of the geophagy in Sikhote-Alin region (Russian Federation), Africa and other world regions. Environ Geochem Health 38, 1255–1270 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9788-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9788-7