Abstract
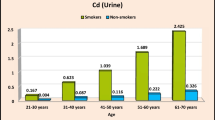
The combined exposure to aluminum (Al) and cadmium (Cd) causes more pronounced adverse health effects on humans. The kidneys are the main organs affected by internal exposure to Cd and Al via food and non-food items. The objective of present study was to measure the Al and Cd concentrations in cigarettes tobacco (branded and non-branded) and drinking water (domestic treated, ground and lake water) samples in southern part of Pakistan, to assess the risk due to ingestion of water and inhalation of cigarettes smoke containing high concentrations of both elements. The study population (kidney disorder and healthy) divided into two group based on consuming lake and ground water, while smoking non-branded cigarette as exposed, while drinking domestic treated water and smoking branded cigarette as non-exposed. Electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry was used to determined Cd and Al concentrations in tobacco, drinking water and blood samples. The resulted data indicated that the levels of Al and Cd in lake and underground water were higher than the permissible limit in drinking water recommended by the World Health Organization. The biochemical parameters of exposed and referent patients, especially urinary N-acetyl-h-glucosaminidase, were used as a biomarkers of kidney disorder. Exposed kidney disorder patients have higher levels of Cd and Al than the exposed referents subjects, while difference was significant when compared to resulted data of non-exposed patients and referents (p = 0.01–0.001). The pearson correlation showed positive correlation between both toxic element concentrations in water, cigarettes versus blood samples of exposed subjects (r = 0.20–0.67 and 0.71–0.82), while lower values were observed for non-exposed subjects (r = 0.123–0.423 and 0.331–0.425), respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afridi, H. I., Kazi, T. G., Kazi, N., Jamali, M. K., Arain, M. B., Jalbani, N., et al. (2008). Evaluation of status of toxic metals in biological samples of diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 80(2), 280–288.
Andrée, S., Jira, W., Schwind, K.-H., Wagner, H., & Schwägele, F. (2010). Chemical safety of meat and meat products. Meat Science, 86(1), 38–48.
Arain, M. B., Kazi, T. G., Jamali, M. K., Jalbani, N., Afridi, H. I., Kandhro, G. A., et al. (2008). Hazardous impact of toxic metals on tobacco leaves grown in contaminated soil by ultrasonic assisted pseudo-digestion: Multivariate study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 155(1), 216–224.
Azizullah, A., Khattak, M. N. K., Richter, P., & Häder, D.-P. (2011). Water pollution in Pakistan and its impact on public health—a review. Environment International, 37(2), 479–497.
Bagchi, S. S. D. B. M. (1997). Toxicity of trace elements in tobacco smoke. Inhalation Toxicology, 9(9), 867–890.
Becaria, A., Lahiri, D. K., Bondy, S. C., Chen, D., Hamadeh, A., Li, H., et al. (2006). Aluminum and copper in drinking water enhance inflammatory or oxidative events specifically in the brain. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 176(1), 16–23.
Bishop, N. J., Morley, R., Day, J. P., & Lucas, A. (1997). Aluminum neurotoxicity in preterm infants receiving intravenous-feeding solutions. New England Journal of Medicine, 336(22), 1557–1562.
Brahman, K. D., Kazi, T. G., Afridi, H. I., Naseem, S., Arain, S. S., & Ullah, N. (2013). Evaluation of high levels of fluoride, arsenic species and other physicochemical parameters in underground water of two sub districts of Tharparkar, Pakistan: A multivariate study. Water Research, 47(3), 1005–1020.
Buschmann, J., Berg, M., Stengel, C., Winkel, L., Sampson, M. L., Trang, P. T. K., & Viet, P. H. (2008). Contamination of drinking water resources in the Mekong delta floodplains: Arsenic and other trace metals pose serious health risks to population. Environment International, 34(6), 756–764.
Carpenter, D. O., Arcaro, K., & Spink, D. C. (2002). Understanding the human health effects of chemical mixtures. Environmental Health Perspectives, 110(Suppl 1), 25.
Coen, N., Mothersill, C., Kadhim, M., & Wright, E. (2001). Heavy metals of relevance to human health induce genomic instability. The Journal of Pathology, 195(3), 293–299.
Cui, Y., Zhu, Y.-G., Zhai, R., Huang, Y., Qiu, Y., & Liang, J. (2005). Exposure to metal mixtures and human health impacts in a contaminated area in Nanning, China. Environment International, 31(6), 784–790.
Ebisike, K., Ayejuyo, O., Sonibare, J., Ogunkunle, O., & Ojumu, T. (2004). Pollution impacts of cigarette consumption on indoor air quality in Nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences, 4, 623–629.
El-Rahman, S. S. A. (2003). Neuropathology of aluminum toxicity in rats (glutamate and GABA impairment). Pharmacological Research, 47(3), 189–194.
Flaten, T. P. (2001). Aluminium as a risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease, with emphasis on drinking water. Brain Research Bulletin, 55(2), 187–196.
Flora, S., Mittal, M., & Mehta, A. (2008). Heavy metal induced oxidative stress and its possible reversal by chelation therapy. Indian Journal of Medical Research, 128(4), 501.
Fowles, J., & Dybing, E. (2003). Application of toxicological risk assessment principles to the chemical constituents of cigarette smoke. Tobacco Control, 12(4), 424–430.
Hussain, A., Murtaza, G., Ghafoor, A., Basra, S. M. A., Qadir, M., & Sabir, M. (2010). Cadmium contamination of soils and crops by long term use of raw effluent, ground and canal waters in agricultural lands. Int J Agric Biol, 12, 851–856.
Järup, L., & Åkesson, A. (2009). Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 238(3), 201–208.
Jeffery, E., Abreo, K., Burgess, E., Cannata, J., & Greger, J. (1996). Systemic aluminum toxicity: Effects on bone, hematopoietic tissue, and kidney. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Part A, 48(6), 649–666.
Jin, Y. H., Clark, A. B., Slebos, R. J., Al-Refai, H., Taylor, J. A., Kunkel, T. A., et al. (2003). Cadmium is a mutagen that acts by inhibiting mismatch repair. Nature Genetics, 34(3), 326–329.
Johnston, H., Thomas, S., & Atterwill, C. (1993). Aluminium and iron induced metabolic changes in neuroblastoma cell lines and rat primary neural cultures. Toxicology in Vitro, 7(3), 229–233.
Kazi, T. G., Arain, M. B., Baig, J. A., Jamali, M. K., Afridi, H. I., Jalbani, N., et al. (2009a). The correlation of arsenic levels in drinking water with the biological samples of skin disorders. Science of the Total Environment, 407(3), 1019–1026.
Kazi, T. G., Jalbani, N., Arain, M. B., Jamali, M. K., Afridi, H. I., Sarfraz, R. A., & Shah, A. Q. (2009b). Toxic metals distribution in different components of Pakistani and imported cigarettes by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometer. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163(1), 302–307. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.088.
Kazi, T., Jalbani, N., Arain, M., Jamali, M., Afridi, H., Sarfraz, R., & Shah, A. (2009c). Toxic metals distribution in different components of Pakistani and imported cigarettes by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometer. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163(1), 302–307.
Khan, S., Kazi, T. G., Baig, J. A., Afridi, H. I., & Kolachi, N. F. (2011). Separation/preconcentration methods for the determination of aluminum in dialysate solution and scalp hair samples of kidney failure patients. Biological Trace Element Research, 144(1–3), 205–216.
Klaassen, C. D. (2001). Casarett and Doull’s Toxicology: The basic science of poisons (Vol. 1236). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Layten Davis, D., & Nielsen, M. T. (1999). Tobacco: Production, chemistry and technology. Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd.
Liangos, O., Perianayagam, M. C., Vaidya, V. S., Han, W. K., Wald, R., Tighiouart, H., et al. (2007). Urinary N-acetyl-β-(d)-glucosaminidase activity and kidney injury molecule-1 level are associated with adverse outcomes in acute renal failure. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 18(3), 904–912.
Locatelli, C. (2004). Heavy metals in matrices of food interest: Sequential voltammetric determination at trace and ultratrace level of copper, lead, cadmium, zinc, arsenic, selenium, manganese and iron in meals. Electroanalysis, 16(18), 1478–1486.
Muhammad, S., Shah, M. T., & Khan, S. (2011). Health risk assessment of heavy metals and their source apportionment in drinking water of Kohistan region, northern Pakistan. Microchemical Journal, 98(2), 334–343.
Neiva, T., Benedetti, A., Tanaka, S., Santos, J., & D’amico, E. (2002). Determination of serum aluminum, platelet aggregation and lipid peroxidation in hemodialyzed patients. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 35(3), 345–350.
Panhwar, A. H., Kazi, T. G., Afridi, H. I., Abbasi, A. R., Arain, M. B., Arain, S. A., et al. (2014). Ultrasonic-assisted ionic liquid-based microextraction for preconcentration and determination of aluminum in drinking water, blood and urine samples of kidney failure patients: a multivariate study. Analytical Methods, 6(20), 8277–8283.
Panhwar, A. H., Kazi, T. G., Afridi, H. I., Arain, S. A., Brahman, K. D., & Arain, M. S. (2015a). A new solid phase microextraction method using organic ligand in micropipette tip syringe system packed with modified carbon cloth for preconcentration of cadmium in drinking water and blood samples of kidney failure patients. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 138, 296–302.
Panhwar, A. H., Kazi, T. G., Afridi, H. I., Arain, S. A., Arain, M. S., Brahman, K. D., et al. (2015b). Comparative evaluation of essential and toxic elements in the blood of kidney failure patients and healthy referents. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(2), 1–11.
Reddy, D., & Gunasekar, A. (2013). Chronic kidney disease in two coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh, India: Role of drinking water. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35(4), 439–454.
Sargazi, M., Shenkin, A., & Roberts, N. B. (2006). Aluminium-induced injury to kidney proximal tubular cells: Effects on markers of oxidative damage. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 19(4), 267–273.
Satarug, S., Garrett, S. H., Sens, M. A., & Sens, D. A. (2011). Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva, 16(5), 2587–2602.
Satarug, S., Nishijo, M., Ujjin, P., Vanavanitkun, Y., & Moore, M. R. (2005). Cadmium-induced nephropathy in the development of high blood pressure. Toxicology Letters, 157(1), 57–68.
Savory, J., Exley, C., Forbes, W. F., Huang, Y., Joshi, J. G., Kruck, T., et al. (1996). Can the controversy of the role of aluminum in Alzheimer’s disease be resolved? What are the suggested approaches to this controversy and methodological issues to be considered? Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Part A, 48(6), 615–636.
Shaikh, A., Negi, B., & Sadasivan, S. (2002). Characterization of Indian cigarette tobacco and its smoke aerosol by nuclear and allied techniques. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 253(2), 231–234.
Shrivas, K., & Patel, D. K. (2010). Separation and preconcentration of trace level of lead in one drop of blood sample by using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 176(1), 414–417.
Sińczuk-Walczak, H., Matczak, W., Raźniewska, G., & Szymczak, M. (2004). Neurologic and neurophysiologic examinations of workers occupationally exposed to aluminium. Medycyna Pracy, 56(1), 9–17.
Sommar, J. N., Svensson, M. K., Björ, B. M., Elmståhl, S. I., Hallmans, G., Lundh, T., et al. (2013). End-stage renal disease and low level exposure to lead, cadmium and mercury: A population-based, prospective nested case-referent study in Sweden. Environmental health, 12(1), 9.
Torrence, K., McDaniel, R., Self, D., & Chang, M. (2002). Slurry sampling for the determination of arsenic, cadmium, and lead in mainstream cigarette smoke condensate by graphite furnace–atomic absorption spectrometry and inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 372(5–6), 723–731.
Venturini-Soriano, M., & Berthon, G. (1998). Aluminum speciation studies in biological fluids. Part 4. A new investigation of aluminum–succinate complex formation under physiological conditions, and possible implications for aluminum metabolism and toxicity. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 71(3), 135–145.
Wang, J. P., Wang, S. L., Lin, Q., Zhang, L., Huang, D., & Ng, J. C. (2009). Association of arsenic and kidney dysfunction in people with diabetes and validation of its effects in rats. Environment International, 35(3), 507–511.
Wang, F. Y., Wang, H., & Ma, J. W. (2010). Adsorption of cadmium (II) ions from aqueous solution by a new low-cost adsorbent—Bamboo charcoal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177(1), 300–306.
World Health Organization. (2004). Guidelines for drinking-water quality: Recommendations (Vol. 1). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Wu, D., Landsberger, S., & Larson, S. M. (1995). Evaluation of elemental cadmium as a marker for environmental tobacco smoke. Environmental Science and Technology, 29(9), 2311–2316.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the National Center of Excellence in Analytical Chemistry university of Sindh Pakistan for sponsoring this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panhwar, A.H., Kazi, T.G., Afridi, H.I. et al. Correlation of cadmium and aluminum in blood samples of kidney disorder patients with drinking water and tobacco smoking: related health risk. Environ Geochem Health 38, 265–274 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9715-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9715-y