Abstract
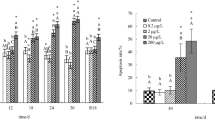
Tilapia were exposed to sublethal methomyl concentrations of 0, 0.2, 2, 20 or 200 μg/L for 30 days, and then transferred to methomyl-free water for 18 days. The sexual steroid hormones 17β-estradiol (E2), testosterone (T), and 11-ketotestosterone (11-KT) in tilapia testes were examined at 0, 6, 12, 18, 24 and 30 days after methomyl exposure, and at 18 days after fish were transferred to methomyl-free water. There were no significant changes in the hormone parameters in testes of tilapia exposed to low concentration 0.2 and 2 μg/L methomyl compared with the controls. However, high concentration 20 and 200 μg/L methomyl had the potential to disrupt the endocrine system of male tilapia, as shown by an increase in E2 and a decrease in T and 11-KT in the testes. Thus, it would appear that the 2 μg/L methomyl might be considered the no-observed-adverse-effect level. Recovery data showed that the effects produced by the lower concentration of 20 μg/L were reversible but the effects were not reversible at the higher concentration of 200 μg/L.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcand-Hoy LD, Benson WH (1998) Fish reproduction: an ecologically relevant indicator of endocrine disruption. Environ Toxicol Chem 17(1):49–57
Athauda S, Anderson T (2013) The effect of age/size on plasma sex steroids and aromatase activity of Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer) when transferred to ideal hatchery conditions. Eur Int J Sci Tech 2(9):29–40
Barannikova IA, Bayunova LV, Semenkova TB (2004) Serum levels of testosterone, 11-ketotestosterone and oestradiol-17β in three species of sturgeon during gonadal development and final maturation induced by hormonal treatment. J Fish Biol 64(5):1330–1338
Borg B (1994) Androgens in teleost fishes. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 109:219–245
Chen YJ, Lu YH, Chen YL, Ren JL (1996) Study on the Solid-Phase Extraction enrichment method for methomyl residual in water. J Jining Med Univ (Chinese) 19(4):12–14
Devlin RH, Nagahama Y (2002) Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: an overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 208:191–364
El-Saeid MH, Al-Turki AM, Al-Wable MI, Abdel-Nasser G (2011) Evaluation of pesticide residues in saudi arabia ground water. R J Environ Sci 5(2):171–178
Farré M, Fernandez J, Paez M, Granada L, Barba L, Gutierrez H, Barcelo D (2002) Analysis and toxicity of methomyl and ametryn after biodegradation. Anal Bioanal Chem 373(8):704–709
Fitzpatrick MS, Pereira CB, Schreck CB (1993) In vitro steroid secretion during early development of mono-sex rainbow trout: sex differences, onset of pituitary control, and effects of dietary steroid treatment. Gen Comp Endocrinol 91:199–215
Francis RC (1992) Sexual lability in teleosts: developmental factors. Q Rev Biol 67:1–18
Gaete H, Olivares Y, Escobar C (2013) Assessment of the effect of a commercial formulation of Methomyl on reproduction of Daphnia obtusa Kürz (1874). Lat Am J Aquat Res 41(5):979–984
Gillesby BE, Zacharewski TR (1998) Exoestrogens: mechanism of action and strategies for identification and assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 17(1):3–14
Goksøyr A (2006) Endocrine disruptors in the marine environment: mechanisms of toxicity and their influence on reproductive processes in fish. J Toxicol Environ Health A 69(1–2):175–184
Guo XB (2006) Environmental Health. Peking University Medical Press, Beijing
Hachfi L, Couvray S, Simide R (2012) Impact of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals [EDCs] on Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonad-Liver [HPGL] Axis in Fish. World J Fish Mar Sci 4(1):14–30
Harris CA, Santos EM, Janbakhsh A, Pottinger TG, Tyler CR, Sumpter JP (2001) Nonylphenol affects gonadotropin levels in the pituitary gland and plasma of female rainbow trout. Environ Sci Technol 35(14):2909–2916
Hecker M, Tyler CR, Hoffmann M, Maddix S, Karbe L (2002) Plasma biomarkers in fish provide evidence for endocrine modulation in the Elbe River, Germany. Environ Sci Technol 36:2311–2321
Jensen KM, Kahl MD, Makynen EA, Korte JJ, Leino RL, Butterworth BC, Ankley GT (2004) Characterization of responses to the antiandrogen flutamide in a short-term reproduction assay with the fathead minnow. Aquat Toxicol 70:99–110
Ji K, Hong S, Kho Y, Choi K (2013) Effects of bisphenol S exposure on endocrine functions and reproduction of zebrafish. Environ Sci Technol 47(15):8793–8800
Kime DE (1993) Classical and nonclassical reproductive steroids in fish. Rev Fish Biol Fish 3:160–180
Kime DE (1999) A strategy for assessing the effects of xenobiotics on fish reproduction. Sci Total Environ 225:3–11
Kolpin DW, Barbash JE, Gilliom RJ (2000) Pesticides in ground water of the United States, 1992–1996. Groundwater 38(6):858–863
Larsson DGJ, Adolfson-Erici M, Parkkonen J, Pettersson M, Berg AH, Olsson PE, Förlin L (1999) Ethinyloestradiol – an undesired fish contraceptive? Aquat Toxicol 45:91–97
Leaños-Castañeda O, Kraak GVD, Rodríguez-Canul R, Gold G (2007) Endocrine disruption mechanism of o,p′-DDT in mature male tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 221(2):158–167
Leandro Carbo, Souza Valéria, Dores Ribeiro EFGC, Maria L (2008) Determination of pesticides multiresidues in shallow groundwater in a cotton-growing region of mato grosso, brazil. J Brazil Chem Soc 19(6):1111–1117
Leistra M, Dekker A, van der Burg AMM (1984) Computed and measured leaching of the insecticide methomyl from greenhouse soils into water courses. Water Air Soil Poll 23(2):155–167
Li H, Jiang H, Gao X, Wang X, Qu W, Lin R, Chen J (2008) Acute toxicity of the pesticide methomyl on the topmouth gudgeon (Pseudorasbora parva): mortality and effects on four biomarkers. Fish Physiol Biochem 34:209–216
MacLatchy DL, Courtenay SC, Rice CD, Van der Kraak GJ (2003) Development of a short-term reproductive bioassay using steroid hormone and vitellogenin end points in the estuarine mummichog (Fundulus heteroclitus). Environ Toxicol Chem 22:996–1008
Mahgoub AA, El-Medany AH (2001) Evaluation of chronic exposure of the male rat reproductive system to the insecticide methomyl. Pharmacol Res 44:73–80
Makynen EA, Kahl MD, Jensen KM, Tietge JE, Wells KL, Van der Kraak G, Ankley GT (2000) Effects of the mammalian antiandrogen vinclozolin on development and reproduction of the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Aquat Toxicol 48:461–475
Mandich A, Bottero S, Benfenati E, Cevasco A, Erratico C, Maggioni S (2007) In vivo exposure of carp to graded concentrations of bisphenol A. Gen Comp Endrocrinol 153:15–24
Meucci V, Arukwe A (2006) Transcriptional modulation of brain and hepatic estrogen receptor and P450arom isotypes in juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) after waterborne exposure to the xenoestrogen, 4-nonylphenol. Aquat Toxicol 77(2):167–177
Nagahama Y (1994) Endocrine regulation of gametogenesis in fish. Int J Dev Biol 38:217–229
O'Donnell L, Robertson KM, Jones ME, Simpson ER (2001) Estrogen and spermatogenesis. Endocr Rev 22(3):289–318
Papaevangelou VA, Gikas GD, Tsihrintzis VA, Antonopoulou M, Konstantinou IK (2016) Removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals in hsf and vf pilot-scale constructed wetlands. Chem Eng J 294:146–156
Pereira JL, Gonçalves F (2007) Effects of food availability on the acute and chronic toxicity of the insecticide methomyl to Daphnia spp. Sci Total Environ 386:9–20
Rotchell JM, Ostrander GK (2003) Molecular markers of endocrine disruption in aquatic organisms. J Toxicol Environ Health B 6(5):453–495
Schultz JR, Petz LN, Nardulli AM (2003) Estrogen receptor α and Sp1 regulate progesterone receptor gene expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol 201:165–175
Scognamiglio V, Antonacci A, Patrolecco L, Lambreva MD, Litescu SC, Ghuge SA, Rea G (2016) Analytical tools monitoring endocrine disrupting chemicals. TrAC-Trend Anal Chem 80:555–567
Sellin MK, Kolok AS (2006) Cd exposures in fathead minnows: effects on adult spawning success and reproductive physiology. Arch Environ Con Tox 51(4):594–599
Shalaby MA, Zorba HYE, Ziada RM (2010) Reproductive toxicity of methomyl insecticide in male rats and protective effect of folic acid. Food Chem Toxicol 48:3221–3226
Solé M, Raldua D, Piferrer F, Barceló D, Porte C (2003) Feminization of wild carp, Cyprinus carpio, in a polluted environment: plasma steroid hormones, gonadal morphology and xenobiotic metabolizing system. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 136:145–156
Spanò L, Tyler CR, Aerle RV, Devos P, Mandiki SNM, Silvestre F (2004) Effects of atrazine on sex steroid dynamics, plasma vitellogenin concentration and gonad development in adult goldfish ( carassius auratus). Aquat Toxicol 66(4):369–379
State Environmental Protection Agency of China (2002) Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, 725–729
U.S. EPA (2012) 2012 Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories. EPA 822-S-12-001. Office of Water U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Van-Scoy AR, Yue M, Deng X, Tjeerdema RS (2013) Environmental Fate and Toxicology of Methomyl. Rev Environ Contam T 222:93–109
WHO (1996) Methomyl Environmental Health Criteria 178. WHO, Geneva, p 74
Wang J, Liu ZZ, Pan HF, Ye WH, Sun XH, Xu XY, Pang XL (2010) Analytical method, pollution pattern and health risk of carbamate for the city raw water of Zhejiang. Environ Chem (Chinese) 29(4):623–628
Xu EG, Ho PW, Tse Z, Ho SL, Leung KM (2016) Revealing ecological risks of priority endocrine disrupting chemicals in four marine protected areas in Hong Kong through an integrative approach. Environ Pollut 215:103–112
Yang L, Li L, Weng S, Feng Z, Luan T (2008) Sexually disrupting effects of nonylphenol and diethylstilbestrol on male silver carp (carassius auratus) in aquatic microcosms. Ecotox Environ Safe 71(2):400–411
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support from Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province for Youth (No.BK20150117), Special Scientific Research Funds for Central Non-profit Institutes, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences (No.2015C02XK01) and China Agriculture Research System (No.CARS-49) for the financial supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights and informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. All applicable international, national, and or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, S.L., Qiu, L.P., Hu, G.D. et al. Responses and recovery pattern of sex steroid hormones in testis of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to sublethal concentration of methomyl. Ecotoxicology 25, 1805–1811 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1726-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1726-7