Abstract
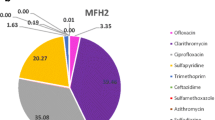
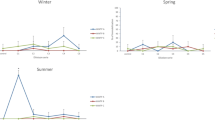
Pharmaceutical effluents have recently been recognized as an important contamination source to aquatic environments and the toxicity related to the presence of antibiotics in effluents has attracted great attention. Conventionally, these effluents have been treated using physico-chemical and aerobic biological processes, usually with low rates of pharmaceuticals removal. Due to the complexity of effluents, it is impossible to determine all pharmaceuticals and their degradation products using analytical methods. Ecotoxicity tests with different organisms may be used to determine the effect level of effluents and thus their environmental impacts. The objective of this work was to compare the sensitivities of five ecotoxicity tests using aquatic and terrestrial organisms to evaluate the toxicity of effluents from the production of veterinary medicines before and after treatment. Raw and chemically treated effluent samples were highly toxic to aquatic organisms, achieving 100,000 toxic units, but only few of those samples presented phytotoxicity. We observed a reduction in the toxicity in the biologically treated effluent samples, which were previously chemically pre-treated, however the toxicity was not eliminated. The rank of test organisms’ reactions levels was: Daphnia similis > Raphidocelis subcapitata > Aliivibrio fischeri > Allium cepa ~ Lactuca sativa. Effluent treatment employed by the evaluated company was only partially efficient at removing the effluent toxicity, suggesting potential risks to biota. The acute toxicity test with D. similis proved to be the most sensitive for both raw and treated effluents and is a suitable option for further characterization and monitoring of pharmaceutical effluents.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akintonwa A, Awodele O, Olofinnade AT, Anyakora C, Afolayan GO, Coker HAB (2009) Assessment of the mutagenicity of some pharmaceutical effluents. Am J Pharmacol Toxicol 4:144–150. doi:10.3844/ajptsp.2009.144.150
APHA—American Public Health Association (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th edn), Washington: American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Pollution Control Federation
Arslan-Alaton I, Caglayan AE (2006) Toxicity and biodegradability assessment of raw and ozonated procaine penicillin G formulation effluent. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:131–140. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.02.014
ABNT. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas (2009) ABNT NBR 12713: ecotoxicologia aquática—toxicidade aguda—Método de ensaio com Daphnia spp. (Cladocera, Crustacea). Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas, Rio de Janeiro p 21
ABNT. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas (2011) ABNT NBR 12648: Ecotoxicologia aquática—Toxicidade crônica—Método de ensaio com algas (Chlorophyceae). Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. São Paulo, p 24
Awad YM, Kim SC, El-Azeem SAMA, Kim KH, Kim KR, Kim K, Jeon C, Lee SS, Ok YS (2014) Veterinary antibiotics contamination in water, sediment, and soil near a swine manure composting facility. Environ Earth Sci 71:1433–1440. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2548-z
Bakare AA, Okunola AA, Adetunji OA, Jenmi HB (2009) Genotoxicity assessment of a pharmaceutical effluent using four bioassays. Genet Mol Biol 32:373–381. doi:10.1590/S1415-47572009000200026
Balcioğlu IA, Ötker M (2003) Treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater containing antibiotics by O3 and O3/H2O2 processes. Chemosphere 50:85–95. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00534-9
Blaise C, Gagné F, Eullaffroy P, Férard J-F (2006) Ecotoxicity of selected pharmaceuticals of urban origin discharged to the Saint-Lawrence River (Québec, Canada): a review. Braz J Aquat Sci Technol 10:29–51. doi:10.14210/bjast
Boxall ABA, Kolpin DW, Halling-Sørensen B, Tolls J (2003) Are veterinary medicines causing environmental risks? Environ Sci Technol 37:286–294. doi:10.1021/es032519b
Boxall ABA, Johnson P, Smith EJ, Sinclair CJ, Stutt E, Levy LS (2006) Uptake of veterinary medicines from soils into plants. J Agric Food Chem 54:2288–2297. doi:10.1021/jf053041t
BRASIL (2011) Conselho Nacional do Meio ambiente—CONAMA. Resolução CONAMA no 430 de 13 de maio de 2011. Dispões sobre as condições e padrões de lançamento de efluentes, complementa e altera a Resolução 357, de 17 de março de 2005, do Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente—CONAMA. D.O.U., 16 de maio de 2011
Burgess RM, Ho KT, Brack W, Lamoree M (2013) Effects-directed analysis (EDA) and toxicity identification evaluation (TIE): complementary but different approaches for diagnosing causes of environmental toxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:1935–1945. doi:10.1002/etc.2299
Carlsson C, Johansson AK, Alvan G, Bergman K, Kühler T (2006) Are pharmaceuticals potent environmental pollutants? Part I: environmental risk assessments of selected active pharmaceutical ingredients. Sci Total Environ 364:67–87. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.06.035
Carvalho PN, Pirra A, Basto MCP, Almeida CMR (2013) Activated sludge systems removal efficiency of veterinary pharmaceuticals from slaughterhouse wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8790–8800. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-1867-7
CETESB—Companhia Ambiental do Estado de São Paulo (2011) Guia nacional de coleta e preservações de amostras: água, sedimento, comunidades aquáticas e efluentes líquidos. CETESB, São Paulo
Chen Z, Wang H, Chen Z, Ren N, Wang A, Shi Y, Li X (2011) Performance and model of a full-scale up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) to treat the pharmaceutical wastewater containing 6-APA and amoxicillin. J Hazard Mater 185:905–913. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.106
Costa CR, Olivi P, Botta CMR, Espindola ELG (2008) A toxicidade em ambientes aquáticos: discussão e métodos de avaliação. Quim Nova 31:1820–1830. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422008000700038
D’abrosca B, Fiorentino A, Izzo A, Cefarelli G, Pascarella MT, Uzzo P, Monaco P (2008) Phytotoxicity evaluation of five pharmaceutical pollutants detected in surface water on germination and growth of cultivated and spontaneous plants. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 43:285–294. doi:10.1080/10934520701792803
Eguchi K, Nagase H, Ozawa M, Endoh YS, Goto K, Hirata K, Miyamoto K, Yoshimura H (2004) Evaluation of antimicrobial agents for veterinary use in the ecotoxicity test using microalgae. Chemosphere 57:1733–1738. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.07.017
Environment Canada (2007) Biological test method: growth inhibition test using a freshwater alga. Environ Prot Ser. Report EPS 1/RM/25. Environment Canada
Farré M, Barceló D (2003) Toxicity testing of wastewater and sewage sludge by biosensors, bioassays and chemical analysis. Trends Anal Chem 22:299–310. doi:10.1016/S0165-9936(03)00504-1
Ferreira DF (1999) Sistema de análise de variância (Sisvar). versão 4.6. Lavras; Universidade Federal de Lavras CD-ROM
Fick J, Söderström H, Lindberg RH, Phan C, Tysklind M, Larsson DGJ (2009) Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:2522–2527. doi:10.1897/09-073.1
Gellert G (2000) Relationship between summarizing chemical parameters like AOX, TOC, TN, and toxicity tests for effluent from the chemical production. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 65:508–513. doi:10.1007/s001280000153
Girotti S, Ferri EN, Fumo MG, Maiolini E (2008) Monitoring of environmental pollutants by bioluminescent bacteria. Anal Chim Acta 608:2–29. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2007.12.008
Halling-Sørensen B, Nielsen SN, Lanzky PF, Ingerslev F, Liitzhøfl HHC, Jørgensen SE (1998) Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—a review. Chemosphere 36:357–393. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00354-8
Hamilton MA, Russo RC, Thurfton RB (1977) Trimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentration in toxicity bioassays. Environ Sci Technol 11:714–719. doi:10.1021/es60130a004
Hernando MD, Fernández-Alba AR, Tauler R, Barceló D (2005) Toxicity assays applied to wastewater treatment. Talanta 65:358–366. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2004.07.012
Hernando MD, Mezcua M, Fernández-Alba AR, Barceló D (2006) Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 69:334–342. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2005.09.037
Hillis DG, Fletcher J, Solomon KR, Sibley PK (2011) Effects of ten antibiotics on seed germination and root elongation in three plant species. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:220–232. doi:10.1007/s00244-010-9624-0
Hutchings M, Johnson I, Hayes E, Girling AE, Thain J, Thomas K, Benstead R, Whale G, Wordon J, Maddox R, Chown P (2004) Toxicity reduction evaluation, toxicity identification evaluation and toxicity tracking in direct toxicity assessment. Ecotoxicology 13:475–484. doi:10.1023/B:ECTX.0000035297.90620.73
Jelic A, Gros M, Ginebreda A, Cespedes-Sánchez R, Ventura F, Petrovic M, Barceló D (2011) Occurrence, partition and removal of pharmaceuticals in sewage water and sludge during wastewater treatment. Water Res 45:1165–1176. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.11.010
Jones OAH, Voulvoulis N, Lester JN (2002) Aquatic environmental assessment of the top 25 English prescription pharmaceuticals. Water Res 36:5013–5022. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00227-0
Jones OAH, Voulvoulis N, Lester JN (2004) Potential ecological and human health risks associated with the presence of pharmaceutically active compounds in the aquatic environment. Crit Rev Toxicol 34:335–350. doi:10.1080/10408440490464697
Kemper N (2008) Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol Indic 8:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2007.06.002
Kim S, Aga DS (2007) Potential ecological and human health impacts of antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant bacteria from wastewater treatment plants. J Toxicol Environ Health 10:559–573. doi:10.1080/15287390600975137
Krienitz L, Bock C, Nozaki H, Wolf M (2011) SSU rRNA gene phylogeny of morphospecies affiliated to the bioassay alga ‘‘Selenastrum capricornutum’’ recovered the polyphyletic origin of crescent-shaped chlorophyta. J Phycol 47:880–893. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2011.01010.x
Larsson DGJ, Fick J (2009) Transparency throughout the production chain - a way to reduce pollution from the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals? Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 53:161–163. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2009.01.008
Larsson DGJ, Pedro C, Paxeus N (2007) Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. J Hazard Mater 148:751–755. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.008
Martinez JL (2009) Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants. Environ Pollut 157:2893–2902. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.05.051
Mascolo G, Balest L, Cassano D, Laera G, Lopez A, Pollice A, Salerno C (2010) Biodegradability of pharmaceutical industrial wastewater and formation of recalcitrant organic compounds during aerobic biological treatment. Bioresour Technol 101:2585–2591. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.057
Maselli BS, Luna LAV, Palmeira JO, Barbosa S, Beijo LA, Umbuzeiro GA, Kummrow F (2013) Ecotoxicidade de efluentes brutos e tratados gerados por uma fábrica de medicamentos veterinários. Rev Ambient Água 8:168–179. doi:10.4136/1980-993X
Melo SAS, Trovó AG, Bautitz IR, Nogueira RFP (2009) Degradação de fármacos residuais por processos oxidativos avançados. Quim Nova 32:188–197. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422009000100034
Microtox Omni Software (1999) Azur environmental, Newark, Delaware, USA. http://www.sdimicrotox.com/pdf/MicrotoxOmni-Software-forWindows.pdf
Mitchell EJAK, Burgess JE, Stuetz RM (2002) Developments in ecotoxicity testing. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 1:169–198. doi:10.1023/A:1020842718996
Norbert-King TJ (1993) A linear interpolation method for sublethal toxicity: the inhibition concentration (ICp) approach (version 2.0). Dulunth: USEPA. Technical Report 03-93
OECD (2004) Daphnia sp. acute immobilization test. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development—Guideline for testing of chemicals (202)
OECD (2006) Freshwater alga and Cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development—Guideline for testing of chemicals (201)
Oller I, Malato S, Sánchez-Pérez JA (2011) Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination—A review. Sci Total Environ 409:4141–4166. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.08.061
Pessala P, Schultz E, Nakari T, Joutti A, Herve S (2004) Evaluation of wastewater effluents by small-scale biotests and a fractionation procedure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 59:263–272. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2003.10.002
Phillips PJ, Smith SG, Kolpin DW, Zaugg SD, Buxton HT, Furlong ET, Esposito K, Stinson B (2010) Pharmaceutical formulation facilities as sources of opioids and other pharmaceuticals to waste water treatment plant effluents. Environ Sci Technol 44:4910–4916. doi:10.1021/es100356f
Power EA, Boumphrey RS (2004) International trends in bioassay use for effluent management. Ecotoxicology 13:377–398. doi:10.1023/B:ECTX.0000035290.89590.03
Ribeiro LO, Barbosa S, Balieiro FP, Beijo LA, Santos BR, Gouvea CMCP, Paiva LV (2012) Fitotoxicidade de extratos foliares de barbatimão [Stryphnodendron adstringens (Mart.) Coville] em bioensaio com alface. R bras Bioci 10:220–225
Rodrigues LCA, Barbosa S, Pazin M, Maselli BS, Beijo LA, Kummrow F (2013) Fitotoxicidade e citogenotoxicidade da água e sedimento de córrego urbano em bioensaio com Lactuca sativa. Agriambi 17:1099–1108. doi:10.1590/S1415-43662013001000012
Sanderson H, Brain RA, Johnson DJ, Wilson CJ, Solomon RK (2004) Toxicity classification and evaluation of four pharmaceuticals classes: antibiotics, antineoplastics, cardiovascular, and sex hormones. Toxicology 203:27–40. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2004.05.015
Santos LHMLM, Araujo AN, Fachini A, Pena A, Deleruematos C, Montenegro MCBSM (2010) Ecotoxicological aspects related to the presence of pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 175:45–95. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.100
Simões MS, Madail RH, Barbosa S, Nogueira ML (2013) Padronização de bioensaios para detecção de compostos alelopáticos e toxicantes ambientais utilizando alface. Biotemas 26:29–36. doi:10.5007/2175-7925
Sreekanth D, Sivaramakrishna D, Himabindu V, Anjaneyulu Y (2009) Thermophilic treatment of bulk drug pharmaceutical industrial wastewaters by using hybrid up flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Bioresour Technol 100:2534–2539. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.11.028
Tambosi JL, Yamanaka LY, José HJ, Moreira RFPM (2010) Recent research data on the removal of pharmaceuticals from sewage treatment plants (STP). Quim Nova 33:411–420. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422010000200032
Urbanczyk H, Ast JC, Higgins MJ, Carson J, Dunlap PV (2007) Reclassification of Vibrio fischeri, Vibrio logei, Vibrio salmonicida and Vibrio wodanis as Aliivibrio fischeri gen. nov., comb. nov., Aliivibrio logei comb. nov., Aliivibrio salmonicida comb. nov. and Aliivibrio wodanis comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2823–2829. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65081-0
Zhao D, Zhu C, Sun S, Yu H, Zhang L, Pan W, Zhang X, Yu H, Gu J, Cheng S (2007) Toxicity of pharmaceutical wastewater on male reproductive system of Mus musculus. Toxicol Ind Health 23:47–54. doi:10.1177/0748233707077446
Zounková R, Klimešvá Z, Nepejchalová L, Hilscherová K, Bláha L (2011) Complex evaluation of ecotoxicity and genotoxicity of antimicrobials oxytetracycline and flumequine used in aquaculture. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:1184–1189. doi:10.1002/etc.486
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq—Project no 475243/2011-0). Maselli BS thanks Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) for the scholarship granted. We also thank to Dr. Eldridge ML for helpful comments on this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maselli, B.d.S., Luna, L.A.V., Palmeira, J.d.O. et al. Ecotoxicity of raw and treated effluents generated by a veterinary pharmaceutical company: a comparison of the sensitivities of different standardized tests. Ecotoxicology 24, 795–804 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1425-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1425-9