Abstract
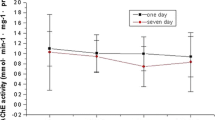
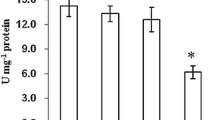
In order to observe the toxic effects of butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP) on zebrafish, the AChE and SOD activity of zebrafish exposed to different concentrations of BBP (0, 0.332, 0.665, 1.33 mg L−1) in a short-term (7d) test were determined. Semi-quantitative PCR was used to determine the mRNA transcript levels of the AChE and SOD gene in zebrafish brain and muscle. The results showed: AChE activity decreased with increased exposure concentration, and was significantly inhibited (p < 0.01) compared with the control group at 0.665 mg L−1 concentration. Low BBP concentrations stimulated and high concentrations inhibited SOD activity with a concentration of 0.332 mg L−1 resulting in a significant induction (p < 0.05) compared with the control, and 0.665 and 1.33 mg L−1 concentrations resulting in significant inhibition (p < 0.05, p < 0.01) relative to the control group. The RT-PCR data showed a decrease in brain and muscle mRNA transcription of AChE gene with an increase in exposure concentration. The mRNA transcription of SOD in the brain was not different between the exposed groups and control group; in muscle, the mRNA transcription inhibition decreased and then increased: all differences from the control were statistically significant.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams WJ, Biddinger GR, Robillard KA et al (1995) A summary of the acute toxicity of 14 phthalate esters to representative aquatic organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1569–1574
Archana Y, Anita G, Ravi SP (2009) Acetylcholinesterase: a potential biochemical indicator for biomonitoring of fertilizer industry effluent toxicity in freshwater teleost, Channa striatus. Ecotoxicol 18:325–333
David RM, Moore MR, Cifone MA, Finney DC (1999) Guest, Chronic peroxisome proliferation and hepatomegaly associated with the hepatocellular tumorigenesis of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phtha-late and the effects of recovery. Toxicol Sci 50:195–205
Duysen EG, Stribley JA, Fry DL (2002) Rescue of the acetylcholinesterase knockout mouse by feeding a liquid diet, phenotype of the adult acetylcholinesterase deficient mouse. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 137(1):43–54
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres VJ, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Härtl R, Gleinich A, Zimmermann M (2011) Dramatic increase in read through acetylcholinesterase in a cellular model of oxidative stress. J Neurochem 116:1088–1096
Moshe M, Vered Z, Nava N et al (2003) Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase plays important role in immune response. J Immunol 170(6):2993–3001
Orbea A, Ortiz-Zarragoitia M, Solé M, Porte C, Cajaraville MP (2002) Antioxidant enzymes and peroxisome proliferation in relation to contaminant body burdens of PAHs and PCBs in bivalve mollusks, crabs and fish from the Urdaibai and Plentzia estuaries (Bay of Biscay). Aquat Toxicol 58:75–98
Piersma AH, Verhoef A, Te Biesebeek J, Pieters MN, Slob W (2000) Developmental toxicity of butyl benzyl phthalate in the rat using a multiple dose study design. Reprod Toxicol 14:417–425
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Michael Newman (Virginia Institute of Marine Sciences, College of William and Mary, USA) for helpful discussions and editing of this manuscript. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.31071653) and Hubei Key Laboratory of Genetic Regulation and Integrative Biology (GRIB201303).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Yang, X., He, Z. et al. Influence of BBP exposure on nervous system and antioxidant system in zebrafish. Ecotoxicology 23, 1854–1857 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1351-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1351-2