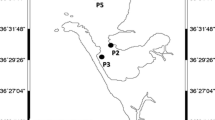
Abstract
An integrated ecotoxicological assessment of marine sediments affected by land-based marine fish farm effluents was developed using physicochemical and benthic community structure analyses and standardised laboratory bioassays with bacteria (Vibrio fischeri), amphipods (Ampelisca brevicornis) and sea urchin larvae (Paracentrotus lividus). Intertidal sediment samples were collected at five sites of the Rio San Pedro (RSP) creek, from the aquaculture effluent to a clean site. The effective concentration (EC50) from bacterial bioluminescence and A. brevicornis survival on whole sediments and P. lividus larval developmental success on sediment elutriates were assessed. Numbers of species, abundance and Shannon diversity were the biodiversity indicators measured in benthic fauna of sediment samples. In parallel, redox potential, pH, organic matter and metal levels (Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn) in the sediment and dissolved oxygen in the interstitial water were measured in situ. Water and sediment physicochemical analysis revealed the exhibition of a spatial gradient in the RSP, evidenced by hypoxia/anoxia, reduced and acidic conditions, high organic enrichment and metal concentrations at the most contaminated sites. Whereas, the benthic fauna biodiversity decreased the bioassays depicted decreases in EC50, A. brevicornis survival, P. lividus larval success at sampling sites closer to the studied fish farms. This study demonstrates that the sediments polluted by fish farm effluents may lead to alterations of the biodiversity of the exposed organisms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Guerra M, Viguri JR, Voulvoulis N (2009) A multicriteria-based methodology for site prioritisation in sediment management. Environ Int 35:920–930
Anderson MJ (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Aust J Ecol 26:32–46
Anderson MJ, Gorley RN, Clarke KR (2008) PERMANOVA + for PRIMER: guide to software and statistical methods. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
Antunes P, Gil O (2004) PCB and DDT contamination in cultivated and wild sea bass from Ria de Aveiro, Portugal. Chemosphere 54(10):1503–1507
Araújo CVM, Diz FR, Laiz I, Lubián LM, Blasco J, Moreno- Garrido I (2009) Sediment integrative assessment of the Bay of Cádiz (Spain): an ecotoxicological and chemical approach. Environ Int 35(6):831–841
Azur Environmental (1998) Microtox acute toxicity basic test procedures. Azur Environmental, Carlsbad, CA
Beiras R (2002) Comparison of methods to obtain a liquid phase in marine sediment toxicity bioassays with Paracentrotus lividus sea urchin embryos. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 42:23–28
Beiras R, Fernández N, Bellas J, Besada V, González-Quijano A, Nunes T (2003) Integrative assessment of marine pollution in Galician estuaries using sediment chemistry, mussel bioaccumulation, and embryo-larval toxicity bioassays. Chemosphere 52:1209–1224
Blasco J, Gomes T, García-Barrera T, Rodriguez-Romero A, González-Rey M, Morán-Roldán F, Trombini C, Miotk M, Gómez-Ariza JL, Bebianno M (2010) Trace metal concentrations in sediments from the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Sci Mar 74S1:99–106
Borja A, Franco J, Pérez V (2000) A marine biotic index to establish the ecological quality of soft-bottom benthos within European estuarine and coastal environments. Mar Poll Bull 40:1100–1114
Brooks KM, Mahnken C, Nash C (2002) Environmental effects associated with marine net pen waste with emphasis on salmon farming in the Pacific Northwest. In: Stickney RR, McVey JP (eds) Responsible marine aquaculture. World aquaculture society. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, p 391
Cabello FC (2006) Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: a growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ Microbiol 8(7):1137–1144
Carballeira C, De Orte MR, VianaI IG, Carballeira A (2011a) Implementation of a minimal biological test set for assessment of ecotoxic effect of effluents from land-based fish farms. Ecotox Environ Safe 78:148–161
Carballeira C, Martín-Díaz L, DelValls TA (2011b) Influence of salinity on fertilization and larval development toxicity tests with two species of sea urchin. Mar Environ Res 72:196–203
Carballeira C, Ramos-Gómez J, Martín-Díaz L, DelValls TA (2012) Identification of specific malformations of sea urchin larvae for toxicity assessment: application to marine pisciculture effluents. Mar Environ Res 77:12–22
Casado-Martínez MC, Campisi T, Díaz A, Lo Re R, Obispo R, Postma JF, Riba I, Sneekes AC, Buceta JL, DelValls TA (2006a) Interlaboratory assessment of marine bioassays to evaluate the environmental quality of coastal sediments in Spain. II. Bioluminescence inhibition test for rapid sediment toxicity assessment. Cienc Mar 32:129–138
Casado-Martínez MC, Beiras R, Belzunce MJ, González-Castromil MA, Marin-Guirao L, Postma JF, Riba I, DelValls TA (2006b) Interlaboratory assessment of marine bioassays to evaluate the environmental quality of coastal sediments in Spain. IV. Whole sediment toxicity test using crustacean amphipods. Cienc Mar 32:149–157
Casado-Martínez MC, Fernández N, Lloret J, Marín A, Martínez-Gómez C, Riba I, Beiras R, Saco-Álvarez L, DelValls TA (2006c) Interlaboratory assessment of marine bioassays to evaluate the environmental quality of coastal sediments in Spain. III. Bioassay using embryos of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Cienc Mar 32:139–147
Cesar A, Marín A, Marín-Guirao L, Vita R (2004) Amphipod and sea urchin tests to assess the toxicity of Mediterranean sediments: the case of Portman Bay. Sci Mar 68:205–213
Cesar A, Marín A, Marin-Guirao L, Vita R, Lloret J, DelValls TA (2009) Integrative ecotoxicological assessment of sediment in Portmán Bay (southeast Spain). Ecotox Environ Safe 72:1832–1841
Chapman PM (1996) Presentation and interpretation of sediment quality triad data. Ecotoxicology 5:327–339
Chapman PM (2007) Determining when contamination is pollution — weight of evidence determinations for sediments and effluents. Environ Int 33(4):492–501
Chapman PM, Hollert H (2006) Should the sediment quality triad become a tetrad, a pentad, or possibly even a hexad? J Soils Sediments 6(1):4–8
Chapman PM, McDonald BG, Lawrence GS (2002) Weight of evidence frameworks for sediment quality and other assessments. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 8:1489–1515
Choueri RB, Cesar A, Abessa DMS, Torres RJ, Morais RD, Riba I, Pereira CDS, Nascimento MRL, Mozeto A, DelValls TA (2009) Development of site-specific sediment quality guidelines for North and South Atlantic littoral zones: comparison against national and international sediment quality benchmarks. J Hazard Mat 170:320–331
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation, 2nd edn. PRIMER-E Ltd. Plymouth Marine Laboratory, Plymouth
Comreys AL (1973) A first course in factor analysis. Academic, New York
De la Paz M, Gómez-Parra A, Forja JM (2008a) Variability of the partial pressure of CO2 on a daily-to-seasonal time scale in a shallow coastal system affected by intensive aquaculture activities (Bay of Cadiz, SW Iberian Peninsula). Mar Chem 110:195–204
De la Paz M, Gómez-Parra A, Forja JM (2008b) Tidal-to-seasonal variability in the parameters of the carbonate system in a shallow tidal creek influenced by anthropogenic inputs, Río San Pedro (SW Iberian Peninsula). Cont Shelf Res 28:1394–1404
DelValls TA, Forja JM, González-Mazo E, Gómez-Parra A (1998a) Determining contamination sources in marine sediments using multivariate analysis. Trends Anal Chem 17(4):181–192
DelValls TA, Conradi M, García-Adiego E, Forja JM, Gómez-Parra A (1998b) Analysis of macrobenthic community structure in relation to different environmental sources of contamination in two littoral ecosystems from the Gulf of Cádiz (SW Spain). Hydrobiologia 385:59–70
DelValls TA, Forja JM, Gómez-Parra A (1999) An integrative study of environmental quality of sediments from the Bay of Cadiz. Ecotoxicol Environ Res 2:26–33
DelValls TA, Andres A, Belzunce MJ, Buceta JL, Casado-Martinez MC, Castro R, Riba I, Viguri JR, Blasco J (2004) Chemical and ecotoxicological guidelines for managing disposal of dredged material. Trends Anal Chem 23:819–828
Environment Canada (1992a) Biological test method: acute test for sediment toxicity using marine or estuarine amphipods. Environmental Protection Service, Ottawa, ON, Report EPS 1/RM/26, p 111
Environment Canada (1992b) Biological test method: fertilization assay using echinoids (sea urchins and sand dollars). Environmental Protection Service, Ottawa, ON, Report EPS 1/RM/27, p 97
Environment Canada (2002) Biological test method: reference method for determining the toxicity of sediment using luminescent bacteria in a solid-phase test. Environmental Protection Service, Ottawa, ON, Report EPS 1/RM/42, p 83
Ferrón S, Ortega T, Forja JM (2009) Benthic fluxes in a tidal salt marsh creek affected by fish farm activities: Río San Pedro (Bay of Cadiz, SW Spain). Mar Chem 113:50–62
França S, Vinagre C, Pardal MA, Cabral HN (2009) Spatial and temporal patterns of benthic invertebrates in the Tagus estuary (Portugal): comparison between subtidal and intertidal mudflat. Sci Mar 73:307–318
Heilskov AC, Alperin M, Holmer M (2006) Benthic fauna bio-irrigation effects on nutrient regeneration in fish farm sediments. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 339:204–225
Hernando MD, De Vettori S, Martínez Bueno MJ, Fernández-Alba AR (2007) Toxicity evaluation with Vibrio fischeri test of organic chemicals used in aquaculture. Chemosphere 68:724–730
Holmer M (2010) Environmental issues of fish farming in offshore waters: perspectives, concerns and research needs. Aquac Environ Interact 1:57–70
Holmer M, Wildish D, Hargrave BT (2005) Organic enrichment from marine finfish aquaculture and effects on sediment biogeochemical processes. In: Hargrave BT (ed) Environmental effects of marine finfish aquaculture. Springer, Berlin, pp 181–206
Isidori M, Lavorgna M, Nardelli A, Pascarella L, Parrella A (2005) Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. Sci Total Environ 346:87–98
ISO11466 (1995) Soil quality—extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia. International Organization for Standardization, Switzerland
Kalantzi I, Karakassis I (2006) Benthic impacts of fish farming: meta-analysis of community and geochemical data. Mar Pollut Bull 52:479–483
Karakassis I, Tsapakis M, Smith CJ, Rumohr H (2002) Fish farming impacts in the Mediterranean studied through sediment profiling imagery. Mar Ecol Prog Series 227:125–133
Lalumera GM, Calamari D, Galli P, Castiglioni S, Crosa G, Fanelli R (2004) Preliminary investigation on the environmental occurrence and effects of antibiotics used in aquaculture in Italy. Chemosphere 54:661–668
Long ER, Morgan LG (1990) The potential for biological effects of sediment-sorbed contaminants tested in the National Status and Trends Program. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Technical Memorandum NOS OMA 52, USA, p 175
Macken A, Giltrap M, Foley B, McGovern E, McHugh B, Davoren M (2008) An integrated approach to the toxicity assessment of Irish marine sediments: validation of established marine bioassays for the monitoring of Irish marine sediments. Environ Int 34(7):1023–1032
Macleod CK, Crawford CM, Moltschaniwskyj NA (2004) Assessment of long term change in sediment condition after organic enrichment: defining recovery. Mar Pollut Bull 49:79–88
Mantzavrakos E, Kornaros M, Lyberatos G, Kaspiris P (2007) Impacts of a marine fish farm in Argolikos Gulf (Greece) on the water column and the sediment. Desalination 210:110–124
Marín A, Montoya S, Vita R, Marín-Guirao L, Lloret J, Aguado F (2007) Utility of sea urchin embryo-larval bioassays for assessing the environmental impact of marine fish cage farming. Aquaculture 271:286–297
Martín-Díaz ML, Blasco J, Sales D, DelValls A (2008) Field validation of a battery of biomarkers to assess sediment quality in Spanish ports. Environ Pollut 20:1–10
McPherson C, Chapman PM, deBruyn AMH, Cooper L (2008) The importance of benthos in weight of evidence sediment assessments—a case study. Sci Total Environ 394(2–3):252–264
Mendiguchía C, Moreno C, Mánuel-Vez MP, García-Vargas M (2006) Preliminary investigation on the enrichment of heavy metals in marine sediments originated from intensive aquaculture effluents. Aquaculture 254:317–325
Montero N, Belzunce-Segarra MJ, Del Campo A, Garmendia JM, Ferrer L, Larreta J (2011) Integrative environmental assessment of the impact of Pasaia harbour activities on the Oiartzun estuary (southeastern Bay of Biscay). J Mar Syst (in press). doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2011.06.002
Morales-Caselles C, Kalman J, Riba I, DelValls TA (2007) Comparing sediment quality in Spanish littoral areas affected by acute (Prestige, 2002) and chronic (Bay Of Algeciras) oil spills. Environ Pollut 146:233–240
Muxika I, Borja A, Bald J (2007) Using historical data, expert judgement and multivariate analysis in assessing reference conditions and benthic ecological status, according to the European Water Framework Directive. Mar Poll Bull 55:16–29
Ocaña-Martín A, Sanchez-Tocino LL, López-González S, Viciana JF (2000) Guía Submarina de invertebrados no artrópodos, 2nd edn. Granada, Comares, p 512
Papageorgiou N, Sigala K, Karakassis I (2009) Changes of macrofaunal functional composition at sedimentary habitats in the vicinity of fish farms. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 83:561–568
Pearson TH, Black KD (2001) The environmental impacts of marine fish cage culture. In: Black KD (ed) Environmental impacts of aquaculture. Academic, Sheffield, pp 1–27
Pearson TH, Rosemberg R (1978) Macrobenthic succession in relation to organic enrichment and pollution of the marine environment. Oceanogr Mar Biol 16:229–311
Pérez E, Blasco J, Solé M (2004) Biomarker responses to pollution in two invertebrate species: Scrobicularia plana and Nereis diversicolor from the Cadiz bay. Mar Environ Res 58:275–279
Peters C, Becker S, Noack U, Pfitzner S, Bülow W, Barz K, Ahlf W, Berghahn R (2002) A marine bioassay test set to assess marine water and sediment quality-its need, the approach and first results. Ecotoxicology 11:379–383
Pusceddu A, Fraschetti S, Mirto S, Holmer M, Danovaro R (2007) Effects of intensive mariculture on sediment biochemistry. Ecol Appl 17:1366–1378
Ramos-Gómez J, Martín-Díaz ML, DelValls TA (2009) Acute toxicity measured in the amphipod Ampelisca brevicornis after exposure to contaminated sediments from Spanish littoral. Ecotoxicology 18:1068–1076
Read P, Fernandes T (2003) Management of environmental impacts of marine aquaculture in Europe. Aquaculture 226:139–163
Riba I, DelValls TA, Forja JM, Gómez-Parra A (2003) Comparative toxicity of contaminated sediment from a mining spill using two amphipods species: Corophium volutator (Pallas, 1776) and Ampelisca brevicornis (A. Costa, 1853). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 71:1061–1068
Riba I, Casado-Martínez C, Forja JM, DelValls TA (2004) Sediment quality in the Atlantic coast of Spain. Environ Toxicol Chem 23(2):271–282
Riedl R (1986) Fauna y flora del mar Mediterráneo. Omega, Barcelona, p 858
Rodrigues AM, Meireles S, Pereira T, Gama A, Quintino V (2006) Spatial patterns of benthic macroinvertebrates in intertidal areas of a Southern European estuary: the Tagus, Portugal. Hydrobiologia 555:99–113
Sapkota A, Sapkota AR, Kucharski M, Burke J, McKenzie S, Walker P, Lawrence R (2008) Aquaculture practices and potential human health risks: current knowledge and future priorities. Environ Int 34:1215–1226
SEPA (2005) Scottish Environment Protection Agency. Regulation and monitoring of marine cage fish farming in Scotland. A manual of Procedures. Standard Monitoring Survey. Version 1.6. http://www.sepa.org.uk/guidance/fishfarmmanual/manual.asp
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. The University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Solan M, Cardinale BJ, Dowing AL, Engelhardt KAM, Ruesink JL, Srivastava DS (2004) Extinction and ecosystem function in the marine benthos. Science 306:1177–1180
Solé M, Kopecka-Pilarczyk J, Blasco J (2009) Pollution biomarkers in two estuarine invertebrates, Nereis diversicolor and Scrobicularia plana, from a Marsh ecosystem in SW Spain. Environ Int 35:523–531
Tello A, Corner RA, Telfer TC (2010) How do land-based salmonid farms affect stream ecology? Environ Pollut 158:1147–1158
Thorson G (1957) Bottom communities (sublittoral or shallow shelf). In: de Hedgpeth JH (ed) Treatise on marine ecology and paleoecology, vol 1. Ecology Mem Geol Soc Am 67:461–534
Tomassetti P, Porrello S (2005) Polychaetes as indicators of marine fish farm organic enrichment. Aquac Int 13:109–128
Tomassetti P, Persia E, Mercatali I, Vani D, Marussso V, Porrello S (2009) Effects of mariculture on macrobenthic assemblages in a western mediterranean site. Mar Pollut Bull 58:533–541
Tovar A, Moreno C, Mánuel-vez MP, García-Vargas M (2000a) Environmental impacts of intensive aquaculture in marine waters. Water Res 34:334–342
Tovar A, Moreno C, Mánuel-vez MP, García-Vargas M (2000b) Environmental implications of intensive marine aquaculture in earthen ponds. Mar Pollut Bull 40:981–988
US, EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1994) Methods for assessing the toxicity of sediment-associated contaminants with estuarine and marine amphipods (EPA/600/R-94/025). Office of Water, Washington
Usero J, Morillo J, El Bakouri H (2008) A general integrated ecotoxicological method for marine sediment quality assessment: application to sediments from littoral ecosystems on Southern Spain’s Atlantic coast. Mar Pollut Bull 56:2027–2036
Vezzulli L, Moreno M, Marin V, Pezzati E, Bartoli M, Fabiano M (2008) Organic waste impact of captured-based Atlantic bluefin tuna aquaculture at an exposed site in the Mediterranean Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 78:369–384
Acknowledgments
C. Silva is grateful to the Sistema Bicentenario BECAS CHILE from the Chilean Government and the international grant from Bank Santander/UNESCO Chair UNITWIN/WiCop for funding this work. The work described was also supported partially by grants from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (CTM2011-28437-C02-02). The authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, C., Yáñez, E., Martín-Díaz, M.L. et al. Integrated ecotoxicological assessment of marine sediments affected by land-based marine fish farm effluents: physicochemical, acute toxicity and benthic community analyses. Ecotoxicology 22, 996–1011 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1085-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1085-6